40 in the hr diagram 90 percent of all stars are
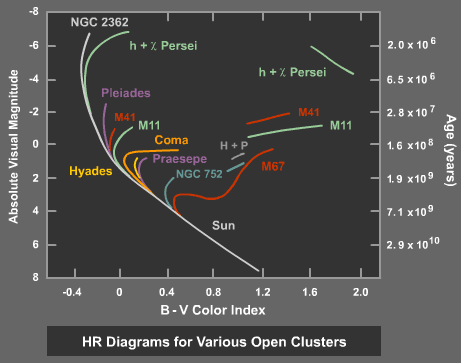
Describe: More than 90 percent of all stars in the universe, including the Sun, are main sequence stars. As main sequence stars age, they move up and to the right on the H-R diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer parts expand outwards. In a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where are the stars with the smallest radius found? Answer. in the upper left corner. in the upper right corner. ... Question 9. Question. In a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where are 90 percent of all the stars found? Answer. in the giant region. in the supergiant region. on the dwarf sequence. on the main ...
A Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram shows the relationship between ____. Q. About 90 percent of stars on the H-R diagram are ____ stars. Q. Use the diagram to answer the question.Using the figure, which is a main-sequence star? Q. As you move along the x-axis of the H-R diagram, temperature __________. Q.

In the hr diagram 90 percent of all stars are
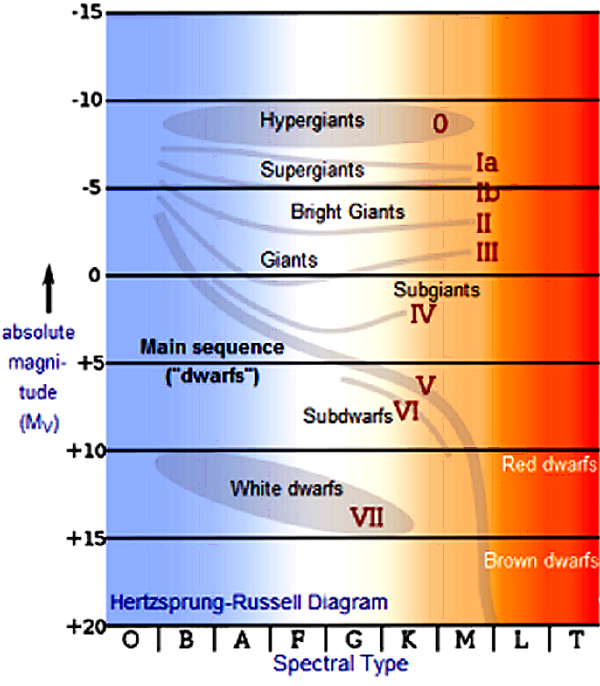
Describe: More than 90 percent of all stars in the universe, including the Sun, are main sequence stars. As main sequence stars age, they move up and to the right on the H-R diagram and become giants or supergiants What are the characteristics of giants? _____ What are the characteristics of Supergiants? Figure is a schematic H-R diagram for a large sample of stars, drawn to make the different types more apparent. Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) Schematic H-R Diagram for Many Stars. Ninety percent of all stars on such a diagram fall along a narrow band called the main sequence. Depending on the type of H-R diagram, any and all stars should fit somewhere on the graph. When plotting an H-R diagram any star in the galaxy could be measured for its brightness and temperature ...
In the hr diagram 90 percent of all stars are. We will say more about these puzzling objects in a moment. Figure 4 is a schematic H-R diagram for a large sample of stars, drawn to make the different types more apparent. Schematic H-R Diagram for Many Stars. Figure 4. Ninety percent of all stars on such a diagram fall along a narrow band called the main sequence. In an H-R Diagram, stars with the smallest radius are found in the _____ of the diagram. lower left corner. In the H-R diagram, 90 percent of all stars are. on the main sequence. We know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the sun because. they are more luminous but have about the same temperature. a diagonal area on an H-R diagram that includes more than 90 percent of all stars. Neutron Star. A star that has collapsed under its own gravity...not represented on the HR diagram b/c they do not emit visible light. Red (Star) coolest stars. Supergiant. an extremely bright star of very large diameter and low density. In a hertzsprung Russell diagram where are 90 percent of all stars found. ... Circini is located near the upper left hand corner in the HR diagram. Circini is hotter and more luminous than the sun. ... All stars spend approximately the same amount of time on the main sequence.
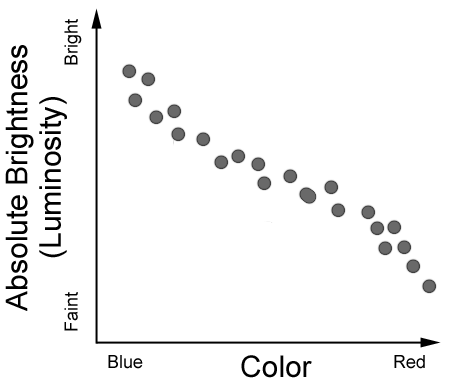
We can do something similar for stars. We find that, on average, 90% of all stars are located on the main sequence of the H–R diagram. If we can identify some activity or life stage with the main sequence, then it follows that stars must spend 90% of their lives in that activity or life stage. Understanding the Main Sequence Main sequence definition, a narrow band in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram in which 90 percent of all observed stars are plotted. See more. H-R Diagram for Stars. A Most Important Diagram Classifying stars according to their spectrum is a very powerful way to begin to understand how they work. As we said last time, the spectral sequence O, B, A, F, G, K, M is a temperature sequence, with the hottest stars being of type O (surface temperatures 30,000-40,000 K), and the coolest stars ... We observed that 90% of all stars seem to follow the relationship; these are the 90% of all stars that lie on the main sequence in our H-R diagram. Our models and our observations agree. What about the other stars on the H-R diagram—the giants and supergiants, and the white dwarfs?
Around 90 percent of the stars in the Universe are main-sequence stars, ... Therefore blue giant simply refers to stars in a particular region of the HR diagram rather than a specific type of star. An example of a blue/white giant star is Alcyone in the constellation Taurus. -a diagonal area on an H-R diagram that includes -more than 90 percent of all stars. shooting star. another name for a meteor. red giant. A large, bright, cool star, late in it's life cycle ... Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, a graph that shows the relationship between magnitudes and temperature. ... A star/supernova that has collapsed under its ... Describe: More than 90 percent of all stars in the universe, including the Sun, are main sequence stars. As main sequence stars age, they move up and to the right on the H-R diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer parts expand outwards. 48.In the H-R diagram, 90 percent of all stars fall Ahow fast the star is moving Bthe strength of the light emanating from the star Cthe distance from us to the star Dthe amount and kind of obstacles between us and the star 49.The apparent brightness of an object such as a star does not depend on.
On the H-R diagram, 90 percent of all stars are. on the main sequence. The hydrogen lines in spectral type A stars. are most narrow for supergiants. In an H-R diagram, stars with the smallest radius are found in the ____ of the diagram. lower left corner.
The sun is in the main sequence of the HR diagram with 90% of other stars. It is also the same size and color as other stars, and is middle aged. 90 percent of the stars in space are what kind of ...
In the H-R diagram, 90 percent of all stars are. a. in the giant region. b. in the supergiant region. c. among the B stars. d. among the G stars. e. on the main sequence. 6. We know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the sun because. a. they are more luminous but have about the same temperature. ...
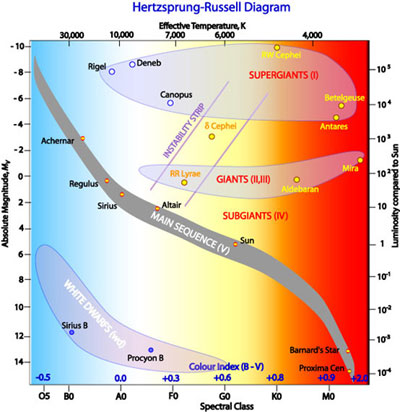
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram plots stars according to their luminosity and temperature, which is also associated with spectral class. Stars with the highest temperatures appear towards the right side of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram plots stars according to their size and shape. The Sun's high temperature ...
12.4M people helped. Answer: main-sequence stars. Explanation: Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram shows the relation between temperature of stars and their luminosity. It shows the position of stars in its life-cycle. Star takes birth in nebula and moves to main-sequence. When the fuel finishes, it forms red-giant or super-giant depending on the ...
(Note that his arrow only applies to main sequence stars, but that is over 90% of stars.) (DONE) Figure 1: Conceptual HR Diagram. L T R M. The “brightest stars” are putting out a very large amount of energy. By putting out a large amount of energy the stars are able to shine brightly, more so than the more common stars.
Simple Sequence Repeats Drive Genome Plasticity And Promote Adaptive Evolution In Penaeid Shrimp Communications Biology
The main reason that the HR Diagram is so useful and important to scientists is, you can tell the size of the star by plotting it on the HR Diagram. The different sizes of stars form a pattern on the HR diagram.
In the H-R diagram, 90 percent of all stars fall. answer choices . in the Red Dwarf region. in the Supergiant region. among the White Dwarfs. on the Main Sequence. Tags: Question 5 . SURVEY . 120 seconds . Q. Which of the following stars is least bright? answer choices . the sun. a blue supergiant. a white dwarf.
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is one of the most important tools in the study of stellar evolution.Developed independently in the early 1900s by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, it plots the temperature of stars against their luminosity (the theoretical HR diagram), or the colour of stars (or spectral type) against their absolute magnitude (the observational HR diagram, also known ...
The only stars which could fall in this region of the HR diagram would be very small stars. And when I write, "very small", I mean "much, much, MUCH smaller than ordinary stars." Just how small would they have to be? Look at Russell's diagram: there is one dot at ... most stars -- about 90 percent -- fall on the main sequence, with about 10 ...
5. Describe: More than 90 percent of all stars in the universe, including the Sun, are main sequence stars. As main sequence stars age, they move up and to the right on the H-R diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer parts expand outwards.
About 90 percent of the stars in the universe, including the sun, are main sequence stars. ... This understanding lead to the creation of a plot known as the Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram, a ...
In a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where are the stars with the smallest radius found? a. in the upper left corner b. in the upper right corner *c. in the lower left corner d. in the lower right corner 9. In a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where are 90 percent of all the stars found? a.
In the H-R diagram, 90 percent of all stars are Select one: a. among the G stars. b. in the supergiant region. c. among the B stars. d. on the main sequence. e. in the giant region. d. on the main sequence. Stars on the main sequence with the greatest mass Select one: a. are spectral type M stars.
Depending on the type of H-R diagram, any and all stars should fit somewhere on the graph. When plotting an H-R diagram any star in the galaxy could be measured for its brightness and temperature ...
Figure is a schematic H-R diagram for a large sample of stars, drawn to make the different types more apparent. Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) Schematic H-R Diagram for Many Stars. Ninety percent of all stars on such a diagram fall along a narrow band called the main sequence.
H R Diagram Use The H R Diagram Below To Answer Questions Throughout This Activity 1 What Are The Spectral Type Temperature Absolute Magnitude Course Hero
Describe: More than 90 percent of all stars in the universe, including the Sun, are main sequence stars. As main sequence stars age, they move up and to the right on the H-R diagram and become giants or supergiants What are the characteristics of giants? _____ What are the characteristics of Supergiants?

Pdf Open Clusters Iii Fundamental Parameters Of B Stars In Ngc 6087 Ngc 6250 Ngc 6383 And Ngc 6530 B Type Stars With Circumstellar Envelopes
On A Hertzsprung Russell Diagram Where Would We Find Stars That Are Cool And Dim Wiring Site Resource

Overfishing Drives Over One Third Of All Sharks And Rays Toward A Global Extinction Crisis Sciencedirect

Impact Of The Galactic Disk And Large Magellanic Cloud On The Trajectories Of Hypervelocity Stars Ejected From The Galactic Center Iopscience

Stars Earth Science Mr Foster Why Do Stars Exist Stars Exist Because Of Gravity Two Opposing Forces In A Star Are Gravity Contracts Thermal Ppt Download







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ESO_-_The_Carina_Nebula_1600-592b92875f9b58595034906c.jpg)








0 Response to "40 in the hr diagram 90 percent of all stars are"
Post a Comment