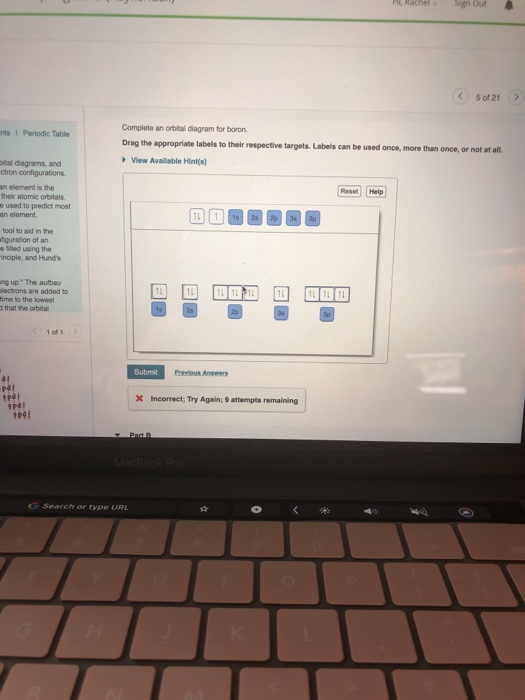
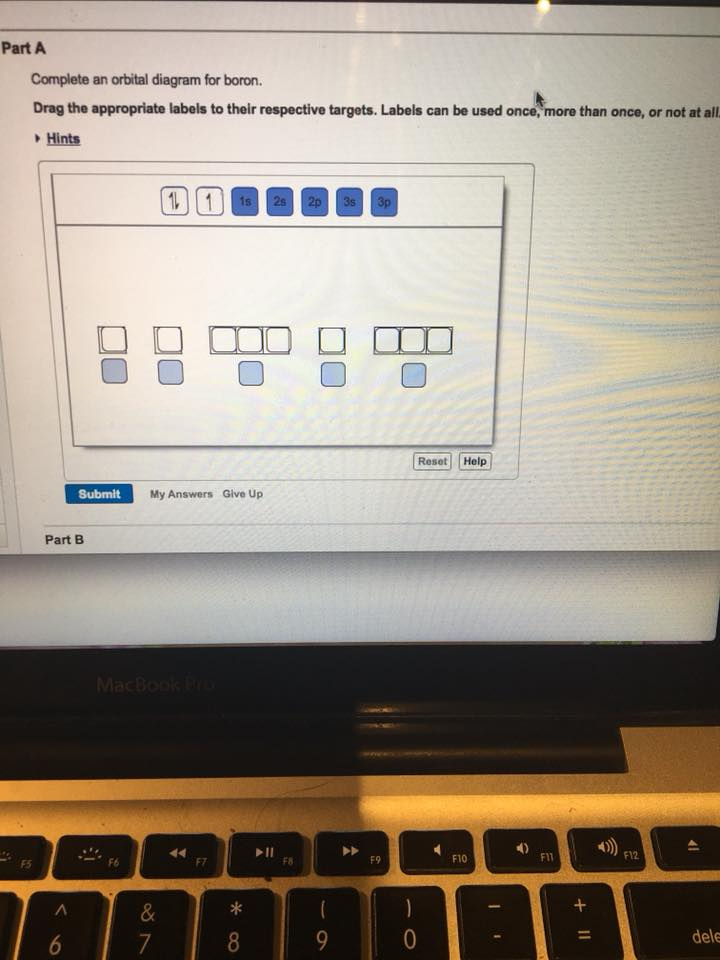
40 complete an orbital diagram for boron
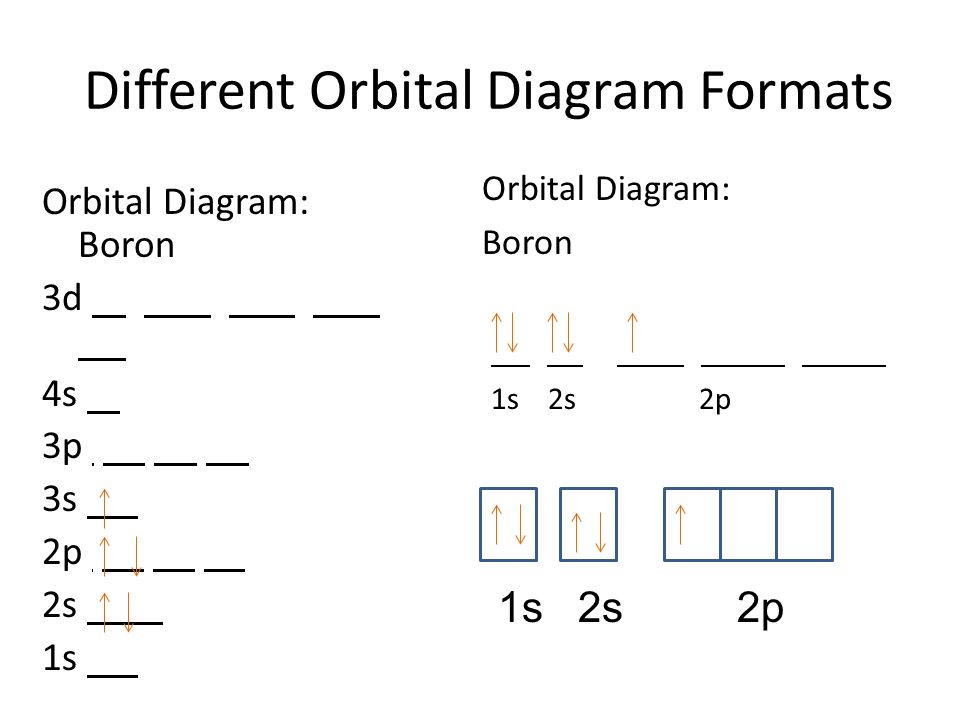
orbital diagram (orbital box diagram) : 1s box has 2 arrows (as per helium above), 2s box has 2 arrows as per boron above, but now we see that there are 3 orbitals that make up the p-subshell (p x, p y, p z), into which we need to place 2 arrows. So, we apply Hund's Rule so that we maximise the number of unpaired electrons in all the 2p orbitals, and, we give those electrons parallel spin ... The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment.After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg.
An orbital diagram is similar to electron configuration, except that instead of indicating the atoms by total numbers, each orbital is shown with up and down. 1s2, 2s2, 2p1 Boron 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d1. Scandium. Answer to Draw an orbital diagram for boron. Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Draw an orbital diagram for ...
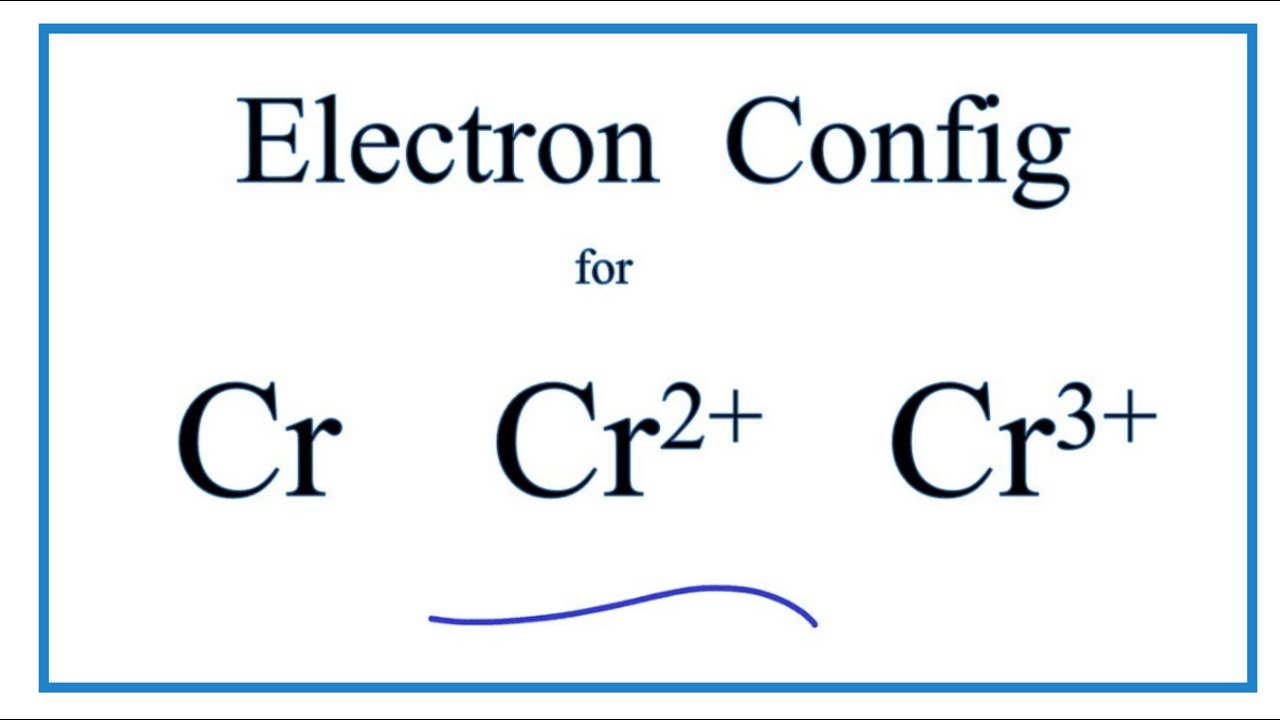
Complete an orbital diagram for boron
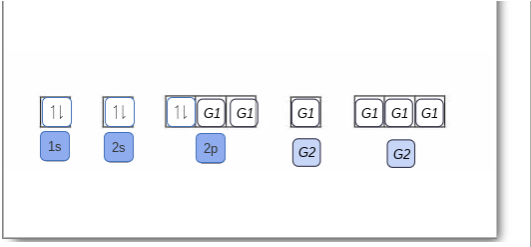
5 B Boron 10.81; 6 C Carbon 12.011; 7 N Nitrogen 14.007; 8 O Oxygen 15.999; 9 F Fluorine 18.998; 10 Ne Neon 20.180; 3. 11 Na Sodium 22.990; 12 Mg Magnesium 24.305; 13 Al Aluminium 26.982; 14 Si Silicon 28.085; 15 P Phosphorus 30.974; 16 S Sulfur 32.06; 17 Cl Chlorine 35.45; 18 Ar Argon 39.948; 4. 19 K Potassium 39.098; 20 Ca Calcium 40.078; 21 Sc Scandium 44.956; 22 Ti Titanium 47.867; 23 V ... Solved Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Drag the | Chegg.com. Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Complete an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc). Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. 1s: 2 arrows 2s: 2 arrows 2p: 1 arrow in the first orbital (leave the rest empty) Complete an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc).
Complete an orbital diagram for boron. You can complete the orbital diagrams of Boron (B) and Scandium (Sc) by referring to the periodic table, locating the position of each element in it, and ...16 Sep 2020 FREE Answer to Complete an orbital diagram for boron Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can...1 answer · Top answer: Part A Complete an orbital diagram for boron Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not ... Boron ends in 2p1. In group 4A or 14, all elements end in p2. And so it goes. For the transition metals, groups 3-12, there are many exceptions. The general rule is that the element's electron configuration ends in d and whatever place they are in. Scandium would end in 3d1, titanium in 3d2, etc. The transition metals are behind by one period because the d electrons are high in energy. For the ... Neon electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6.The symbol for neon is ‘Ne’ and it is an inert element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of neon(Ne) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of neon, application of different principles. The tenth element in the periodic table is neon.
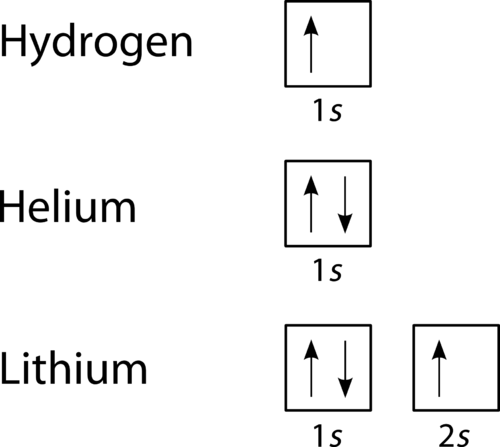
The 1s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2s and then 2p, 3s, and 3p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more influence on energy than the increasing l value for small atoms. However, this pattern does not hold for larger atoms. The 3d orbital is higher in energy than the 4s orbital. Such ... Orbital Diagram of All Elements Diagrams; 1: Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine ... Description. The sun, which drives the water cycle, heats water in the ocean and seas. Water evaporates as water vapor into the air.Some ice and snow sublimates directly into water vapor. Evapotranspiration is water transpired from plants and evaporated from the soil. The water molecule H 2 O has smaller molecular mass than the major components of the atmosphere, nitrogen (N Problem: Part A. Complete an orbital diagram for boron.Draw orbital diagrams, and use them to derive electron configurationsTo understand how to draw orbital diagrams, and how they are used to write electron configurations.The electron configuration of an element is the arrangment of its electrons in their atomic orbitals. Electron configurations can be used to predict most of the chemical ...
In writing the electron configuration for Boron the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for ...24 Oct 2016 · Uploaded by Wayne Breslyn Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add %(8). Question: Orbital Diagrams Draw an orbital diagram for boron. Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons. Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Therefore the b electron configuration will be 1s22s22p1. Lower energy subshells fill before higher energy subshells. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. 4 answersHello. How are you doing here? Was supposed to give the orbital notation for phosphors, boron, sodium and oxygen. You're going to do this using a periodic ...
10.02.2020 · By having 2 in the s sub-orbital and 2 in each of the 3 p sub-orbitals, this makes the L orbital complete. This applies to the M orbital as well. This is referred to as the Octet Rule. Find the Valency Number. Use the periodic table to find the atomic number. For the first example, let’s use carbon. The atomic number is 6, which means 6 protons and 6 electrons. The inner orbital of …
This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Complete an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc). Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
01.11.2021 · Atomic no. Protons, Neutrons and Electrons of all the Elements: Shell Diagram: 1: Hydrogen has 1 proton, 0 neutron and 1 electron: 2: Helium has 2 protons, 2 neutrons and 2 electrons: 3: Lithium has 3 protons, 4 neutrons and 3 electrons: 4: Beryllium has 4 protons, 5 neutrons and 4 electrons: 5: Boron has 5 protons, 6 neutrons and 5 electrons: 6: Carbon has 6 protons, 6 neutrons and 6 electrons
Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Part a complete an orbital diagram for boron. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. Therefore the b electron configuration will be 1s22s22p1. Click within the orbital to add electrons. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for b goes in the 2s orbital.
The two elements that most commonly fail to complete an octet are boron and aluminum; they both readily form compounds in which they have six valence electrons, rather than the usual eight predicted by the octet rule. While molecules exist that contain atoms with fewer than eight valence electrons, these compounds are often reactive and can react to form species with eight valence electrons ...
Boron electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1.The period of boron is 2 and it is a p-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of boron(B) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of boron, application of different principles.. The fifth element in the periodic table is the boron(B).
Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. 1s: 2 arrows 2s: 2 arrows 2p: 1 arrow in the first orbital (leave the rest empty) Complete an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc).
Solved Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Drag the | Chegg.com. Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Complete an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc). Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
5 B Boron 10.81; 6 C Carbon 12.011; 7 N Nitrogen 14.007; 8 O Oxygen 15.999; 9 F Fluorine 18.998; 10 Ne Neon 20.180; 3. 11 Na Sodium 22.990; 12 Mg Magnesium 24.305; 13 Al Aluminium 26.982; 14 Si Silicon 28.085; 15 P Phosphorus 30.974; 16 S Sulfur 32.06; 17 Cl Chlorine 35.45; 18 Ar Argon 39.948; 4. 19 K Potassium 39.098; 20 Ca Calcium 40.078; 21 Sc Scandium 44.956; 22 Ti Titanium 47.867; 23 V ...

Review I Constants I Periodic Table Learning Goal Complete An Orbital Diagram For Boron To Understand How To Draw Homeworklib

Structure And Bonding In Boron Carbide The Invincibility Of Imperfections New Journal Of Chemistry Rsc Publishing
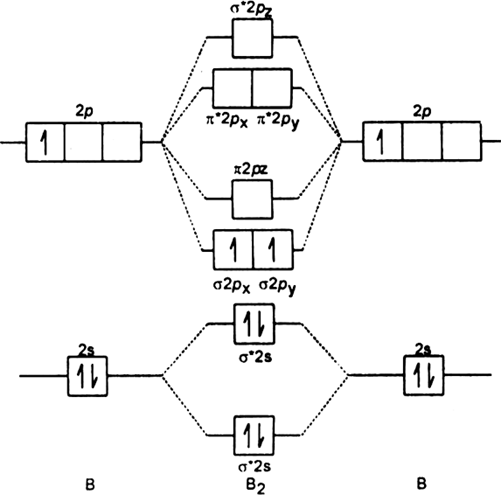
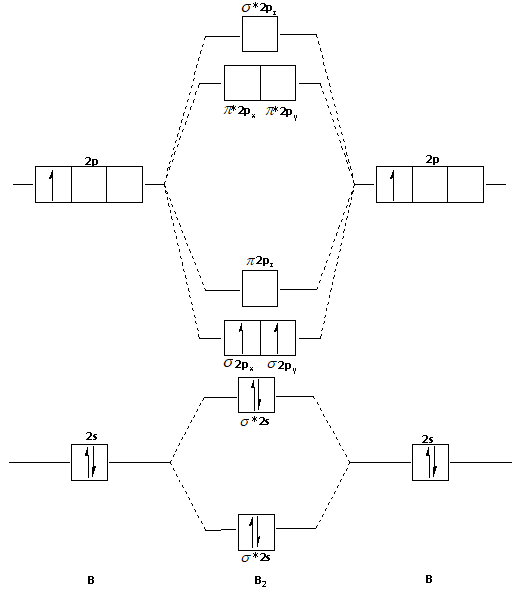
Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For I Be2 Ii B2 And Predict Bond Order And Magnetic Properties From Chemistry Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Class 11 Haryana Board English Medium

Complete An Orbital Diagram For Boron Drag The Appropriate Labels To Their Respective Targets Labels Can Homeworklib



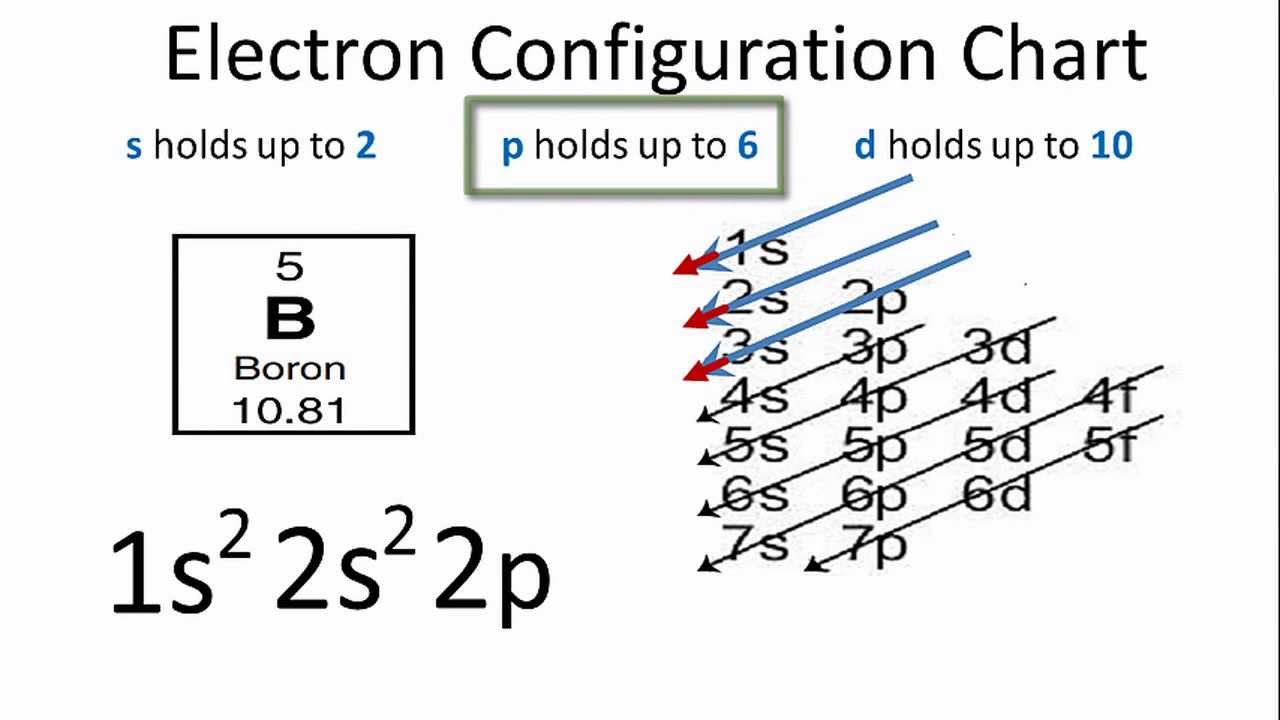















0 Response to "40 complete an orbital diagram for boron"
Post a Comment