39 galilean telescope ray diagram
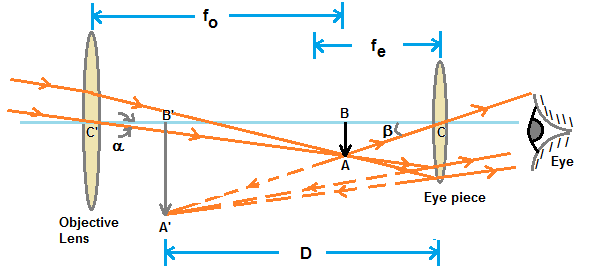
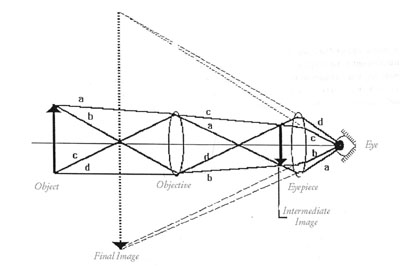
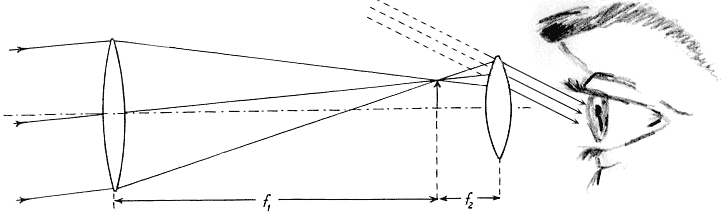
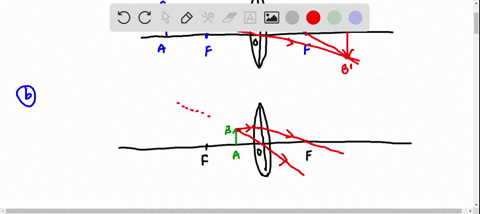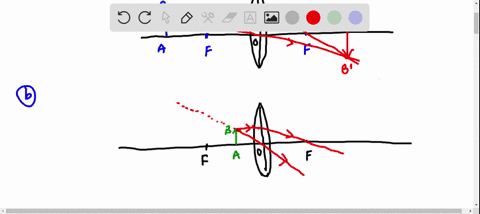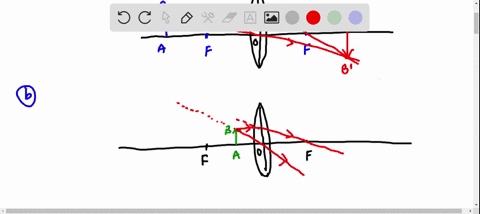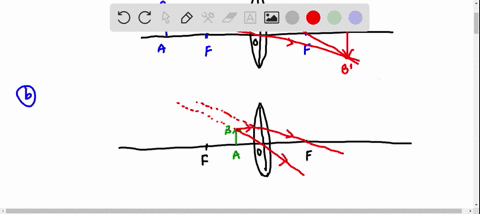
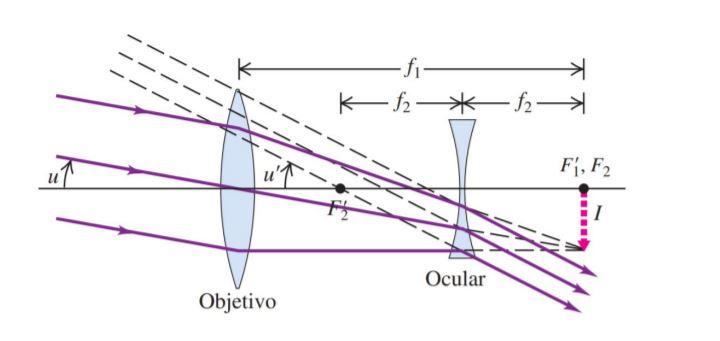
astronomical telescope, if it is negative it is a Galilean telescope. Astronomical telescopes produce inverted images and Galilean telescopes produce erect images. Image formation is shown in the diagrams below. The angular magnification of either kind of telescope can be calculated from the equation M=-Focular/Fobjective=pE/pE', Refracting Telescope Ray Diagram. Here we make a Keplerian telescope from simple elements and explain its operation using a ray diagram. This page supports the multimedia tutorial. The refracting telescope works by bending light with lenses. the eyepiece lens and the objective lens are set to coincide (see diagram below).
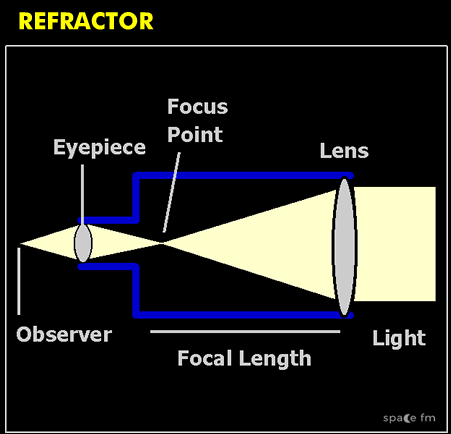
Galileo's refracting telescope (). Diagram illustrating the basic optical design of Galileo's reracting telescope. Galileo's refractor used two lenses to. Amateur astronomers use two main types of telescopes: reflecting and refracting. A reflecting telescope uses mirrors to focus light from a distant object, while a.
Galilean telescope ray diagram
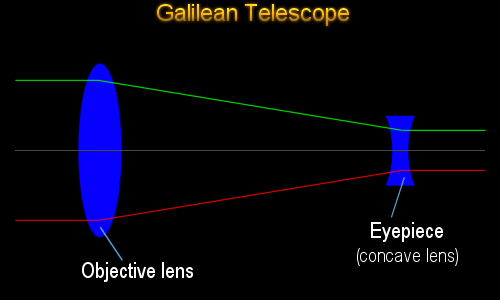
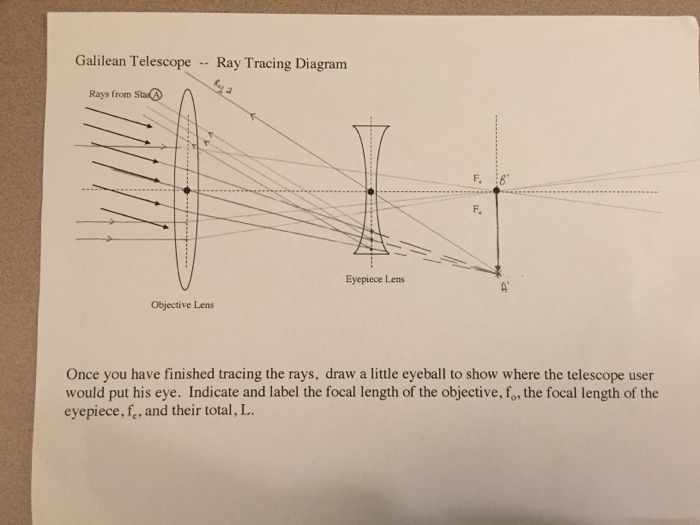
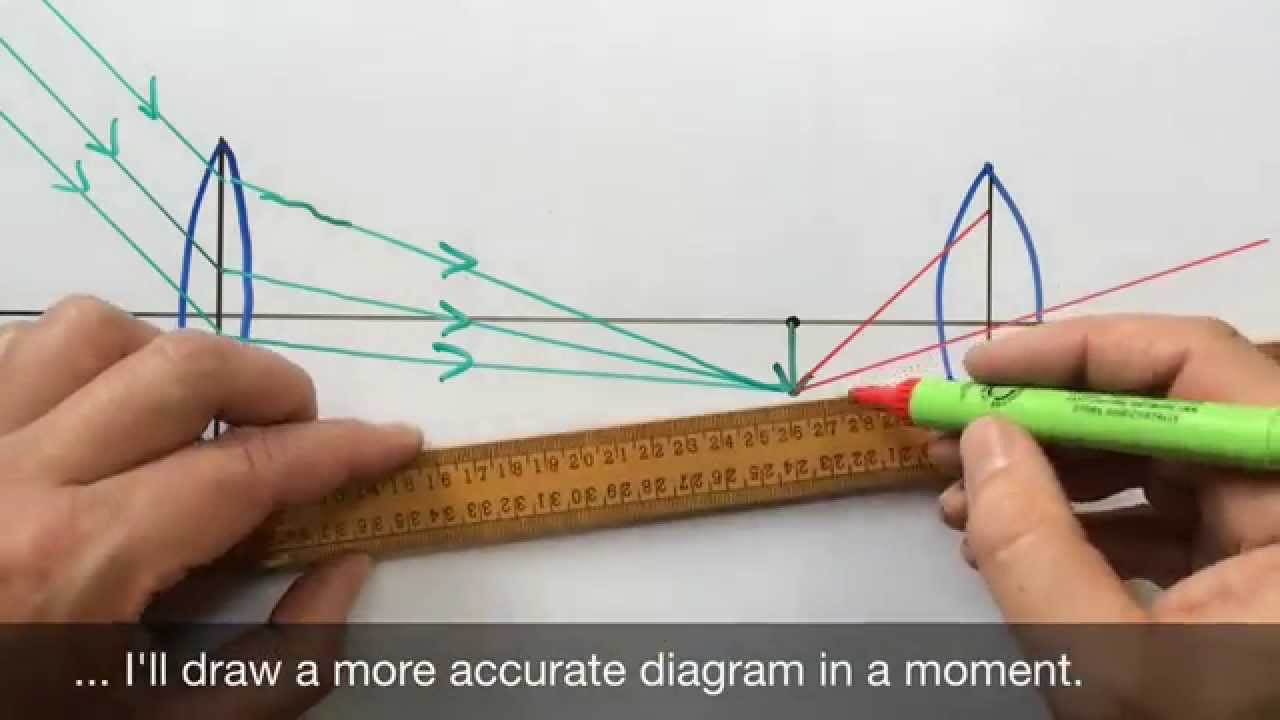
The Galilean telescope (fig. 1) consists of a converging lens (plano-convex or biconvex) serving as objective, and a diverging lens (plano-concave or biconcave) serving as eyepiece. The eyepiece is situated in front of the focal point of the objective, at a distance from the focal point equal to the focal length of the eyepiece. Telescopes of this design are called Galilean telescopes and to understand how they work it is necessary to understand a little about lenses. There are two main types of lens: a converging lens , shown in the top of the diagram above, causes parallel light rays from a distant object, shown in red, to bend so that they converge at point known as ... The final image can be formed at infinity as shown in the ray diagram below. enter image description here . f1 if the focal length of the ...4 answers · Top answer: The angular magnification of a telescope M is defined as the ratio of the angle subtended ...
Galilean telescope ray diagram. telescope is a Keplerian or Astronomical telescope4.1 (a). If the , shown in Fig. eyepiece has negative power, the telescope is a Galilean telescope, shown in Fig. 4.1 (b). Note that in both cases the distance between the two elements is equal to the sum of the focal lengths of the elements (positive or negative signs taken into account). In its present stage of development, POV-Ray is able to treat lenses and mirrors with a great deal of realism. In POV-Ray's virtual world a lens will refract ... This requires increasing the total length of the telescope. Indicate, with a ray diagram, how this can be done. (8) Use the mathematical theory of these telescopes to predict how the light efficiency of a Galilean telescope compares with that of an astronomical telescope of the same power and the same objective lens diameter. Galilean Telescope. The Galilean or terrestrial telescope uses a positive objective and a negative eyepiece. It gives erect images and is shorter than the astronomical telescope with the same power. It's angular magnification is -f o /f e.. The image below shows parallel rays from two helium-neon lasers passing through a Galilean telescope made from an objective with f=30cm and an eyepiece ...
The incident rays from a distinct object falls on the objective as a beam of parallel rays at an angle " a " and after refraction from objective lens these rays ... Refracting telescopes, including Keplerian telescopes or Galilean telescopes, use lenses to produce inverted, magnified, virtual images. Here we make a Keplerian telescope from simple elements and explain its operation using a ray diagram. This page supports the multimedia tutorial Geometrical Optics. Refracting telescope and schematic. A simple Galilean telescope also consists of 2 lenses, one with a positive focal length and one with a ... And looking at the Ray Fan Diagrams, we can see that the spherical aberrations are well balanced. Using a bi-convex or achromatic lens can bring the spot diagram closer to or well within the diffraction have a magnification of 25 times, which is comparable to Galileo's best telescope and ... LABEL THE THREE RAYS (I, II, and III) IN THE DIAGRAM BELOW:.11 pages
The final image can be formed at infinity as shown in the ray diagram below. enter image description here . f1 if the focal length of the ...4 answers · Top answer: The angular magnification of a telescope M is defined as the ratio of the angle subtended ... Telescopes of this design are called Galilean telescopes and to understand how they work it is necessary to understand a little about lenses. There are two main types of lens: a converging lens , shown in the top of the diagram above, causes parallel light rays from a distant object, shown in red, to bend so that they converge at point known as ... The Galilean telescope (fig. 1) consists of a converging lens (plano-convex or biconvex) serving as objective, and a diverging lens (plano-concave or biconcave) serving as eyepiece. The eyepiece is situated in front of the focal point of the objective, at a distance from the focal point equal to the focal length of the eyepiece.
Draw A Ray Diagram Of Astronomical Telescope And Derive The Formula Of Its Magnifying Power When Final Image Is Formed At The Least Distance Of Distin Physics Topperlearning Com Ypy0tyy
What Is The Magnifying Power Of The Galilean Telescope And What Were The Details Of Its Components Quora

Galileo S Telescope He Called It A Cannocchiale Eye Tube Is Sketched In Fig 1 97 As In The Telescope The Second Focus Of The Objective Coincides With The First Focus Of The

What Galileo Saw In 1609 Word Reached Galileo That A New Optical Device Was Being Shown In Northern Europe One That Showed A Magnified Image Of Distant Objects He Quickly Figured Out How To Make Such A Device And Created The Instrument That We Now














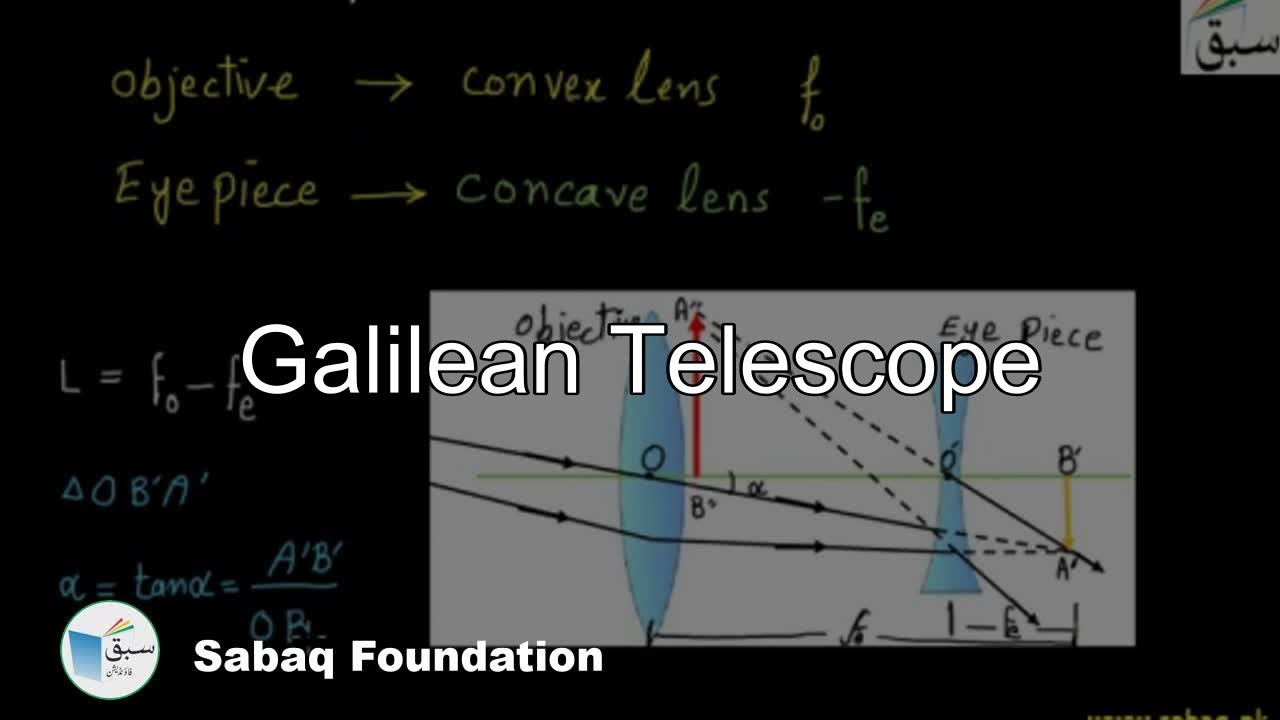
0 Response to "39 galilean telescope ray diagram"
Post a Comment