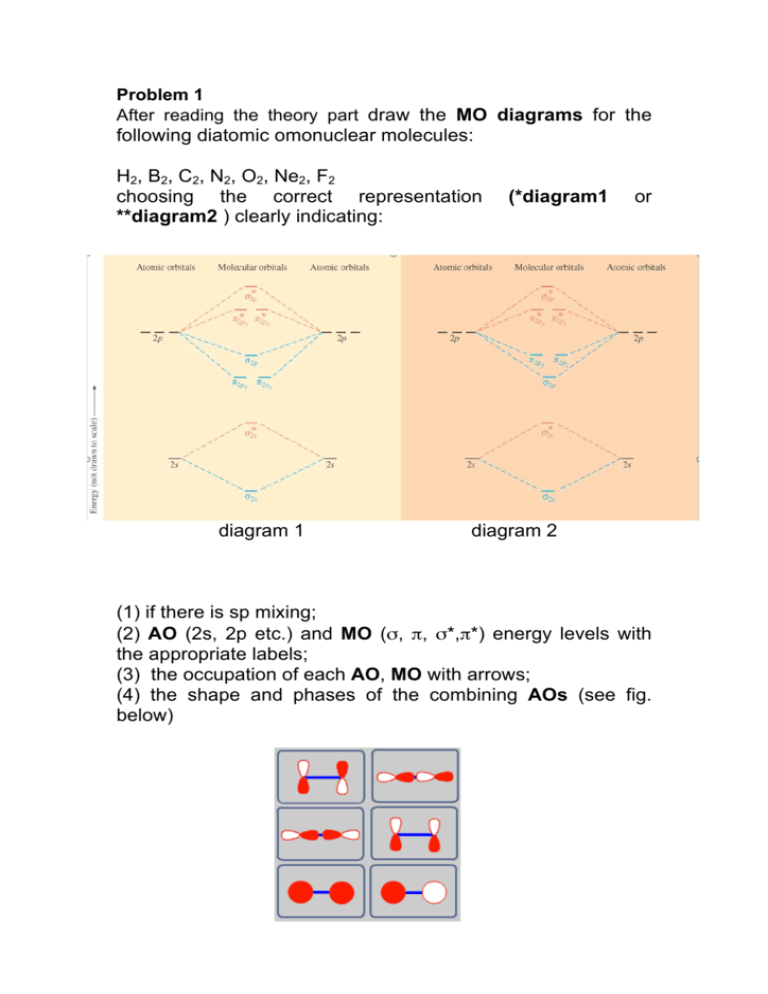
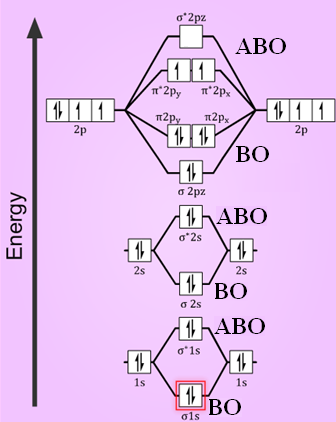
42 molecular orbital diagram for o2 2
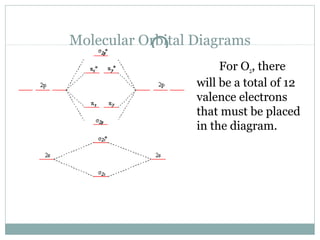
Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram of O2, Видео, Смотреть онлайн • Molecular Orbital Diagram for Oxygen Gas (O2). Fill from the bottom up, with 12 electrons total. Bonding Order is 2, and it is Paramagnetic. sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),sigma2p(2),pi2p(4),pi2p*(2). MO Diagrams | Molecular Orbital Diagram Maker A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
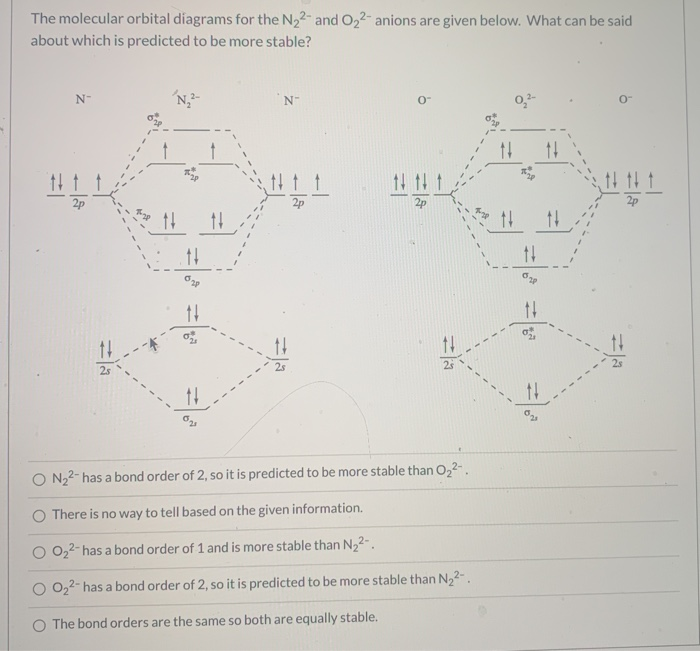
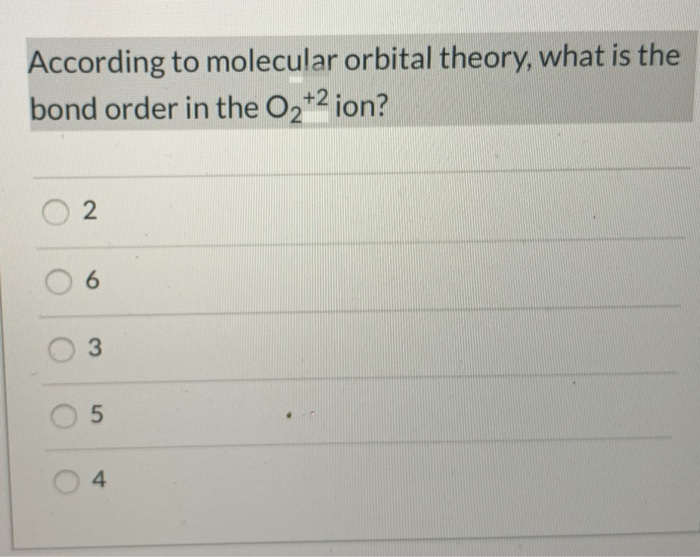
Chapter 9 Molecular Orbitals in Chemical Bonding (Midterm) | Quizlet molecular orbital diagram for N2. number of electrons in the sigma2p molecular orbital is. which response lists all the following diatomic molecules and ions that are paramagnetic (Be2, B2, B2+2, C2+2, C2-2, O2-, O2-2).

Molecular orbital diagram for o2 2
Tutorial on Chemical Bonding, Part 8 of 10 (Molecular orbitals) The diagram shows how the molecular orbitals in lithium hydride can be related to the atomic orbitals of the parent atoms. Notice that the relative energies of the 2p-derived σ and π bonding molecular orbitals are reversed in O2 and F2. This is attributed to interactions between the 2s orbital each atom... 8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 8). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
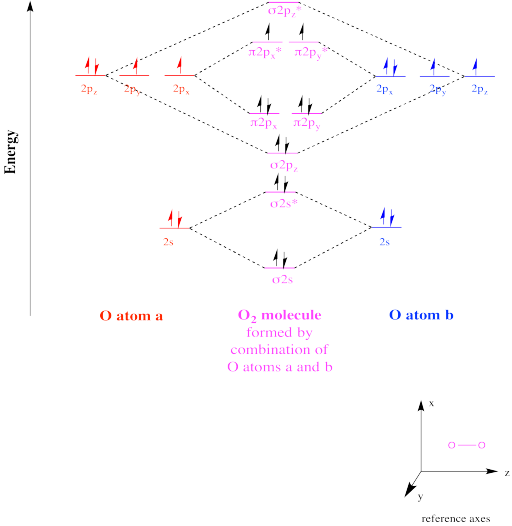
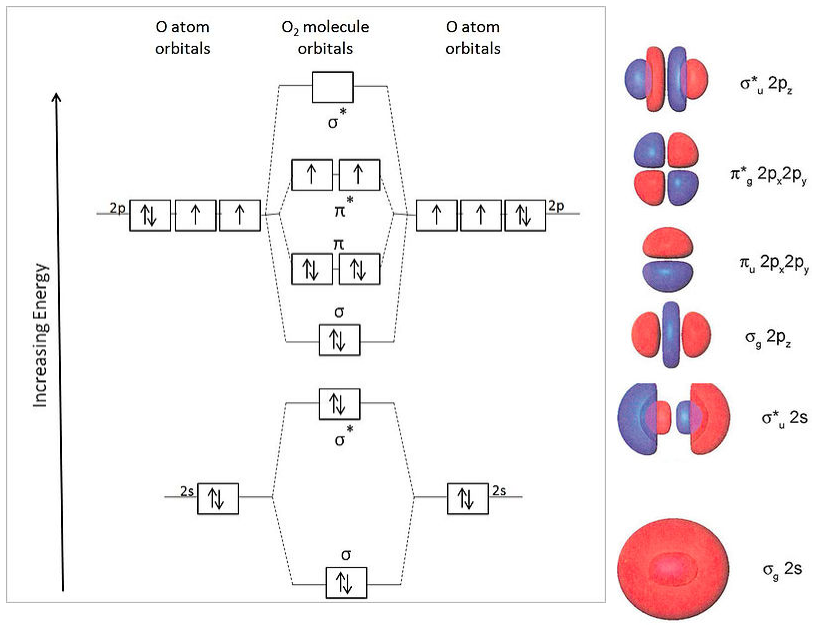
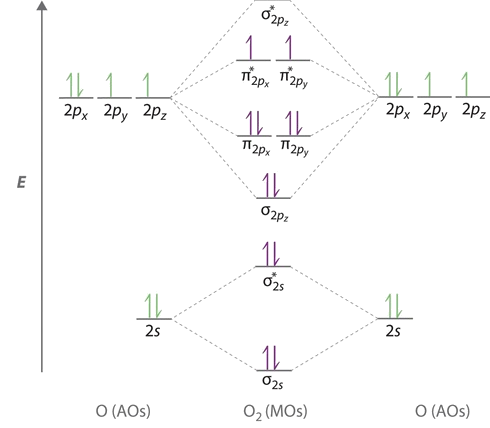
Molecular orbital diagram for o2 2. Explain the formation of O2 molecule using molecular orbital theory. The molecular orbital energy level diagram of oxygen molecule is given as follows : Bond order 2Nb −Na =28−4 =2 Thus, oxygen molecule has two bonds. i.e., one is bond and one p bond. The last two electrons in p2px∙ and p2py∙ orbitals will remain unpaired. Therefore, oxygen molecule has... PDF Figure 9.32: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for • The following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the... PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory.ppt... - MO diagrams for Inorganic complexes. • It is a waste of both the lecturers and students time if the tutorial to ends up being a lecture covering questions. 5. An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory. Figure 4: Schematic of the 'O2' molecular orbital diagram. The figure... Download scientific diagram | Schematic of the 'O2' molecular orbital diagram. The orange area represents the oxygen-2p band. Note that (a) (O2)4− molecular ion is not stable (number of bonding electrons=number of antibonding electrons), but it represents the corresponding diagram for a pair of...
Molecular orbital diagram - WikiMili, The Best Wikipedia Reader A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms. Molecular orbital diagram - Infogalactic: the planetary knowledge core A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals - Chemical Bonding and... 3) If Nb = Na ,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals. Diagram for O2+ is wrong because 2p atomic orbital of 2nd O atom will have only 3 e Molecular Orbital Theory : chemhelp Molecular Orbital Theory. I'm having a lot of trouble with this stuff. I don't really know how to start these questions (such as how to draw a correlation diagram) Well, this stuff is pretty hard to explain in text alone but I'll give it a go. Feel free to ask clarification questions. I'll use your example of O2
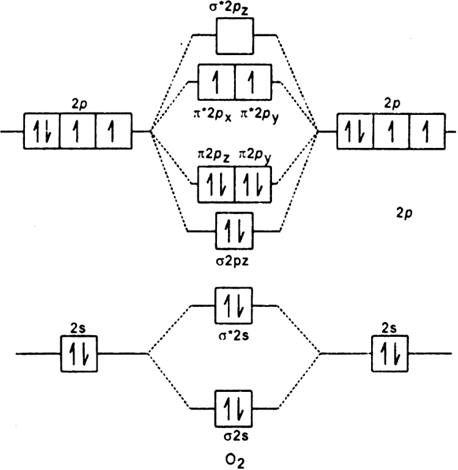
Why is the molecular orbital diagram for O₂ different from N₂? - Quora If we compare such diagrams for the diatomic molecules on the Second Period (Li₂, Be₂, B₂, C₂, N₂, O₂, and F₂), the resulting pattern looks like this: When it comes to O₂ and N₂, I think there are two things to point out: the energies of the starting atomic orbitals are different , due to different fundamental... Asked for: "skewed" molecular orbital energy-level diagram, bonding... Figure 4.10.1: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules.(a) For F 2 , with 14 valence electrons (7 from each F To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for O 2 , we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram... 8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. English: Molecular orbital energy diagram for O2 File:Oxygen molecule orbitals diagram.JPG. From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. Jump to navigation Jump to search. DescriptionOxygen molecule orbitals diagram.JPG. English: Molecular orbital energy diagram for O2. Date. 19 March 2008, 03:01:58.
Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry | Socratic Molecular Orbital theory starts by assuming that the three atomic p orbitals on the O atoms overlap to form three molecular π orbitals that extend over the whole molecule. We end up with two electrons in a bonding π orbital; two electrons in a nonbonding #π^n# orbital; and no electrons in an antibonding...
PDF Character Tables | Valence Orbital Ionization Energies, eV General Features of MO Diagrams. Bonding MOs are found at low energy Non-bonding or lone-pair MOs are at higher energy Antibonding MOs are usually The water HOMO-1 has A1 symmetry This is a bonding MO with the O 2pz orbital mixing with the bonding MO of H2. 5.03 Inorganic Chemistry.
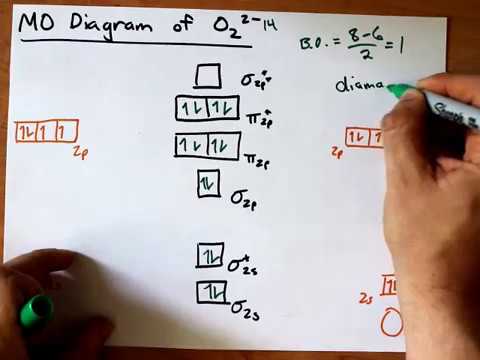
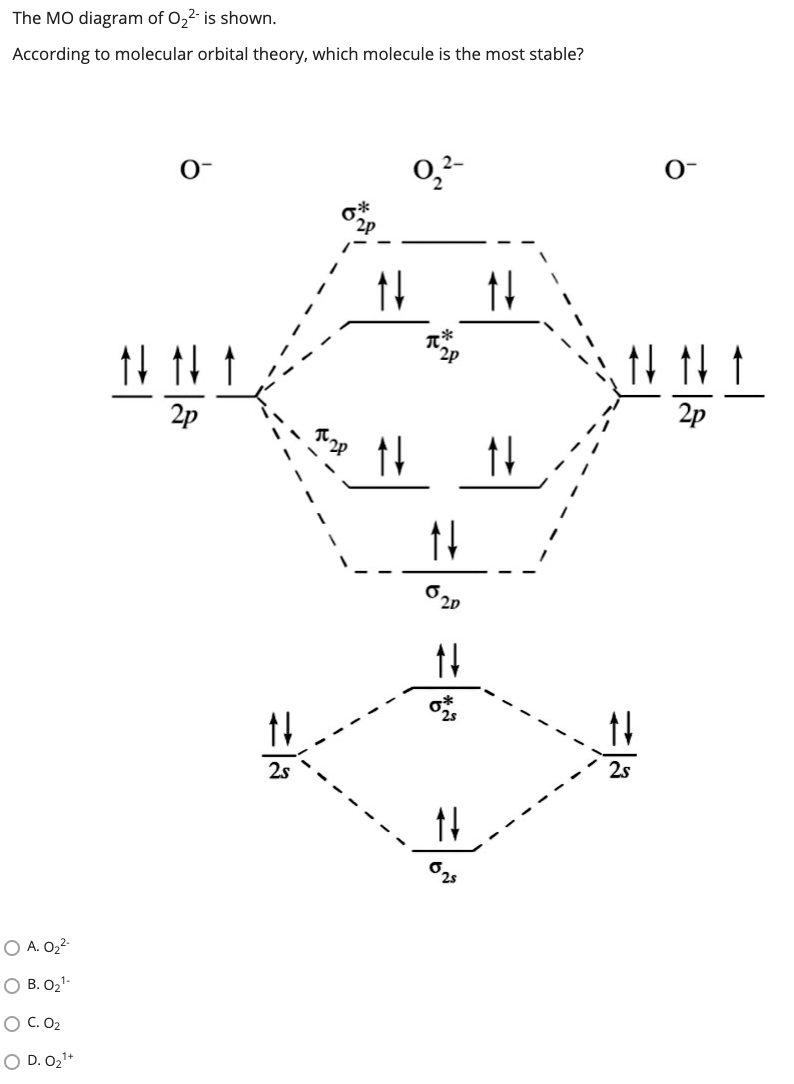
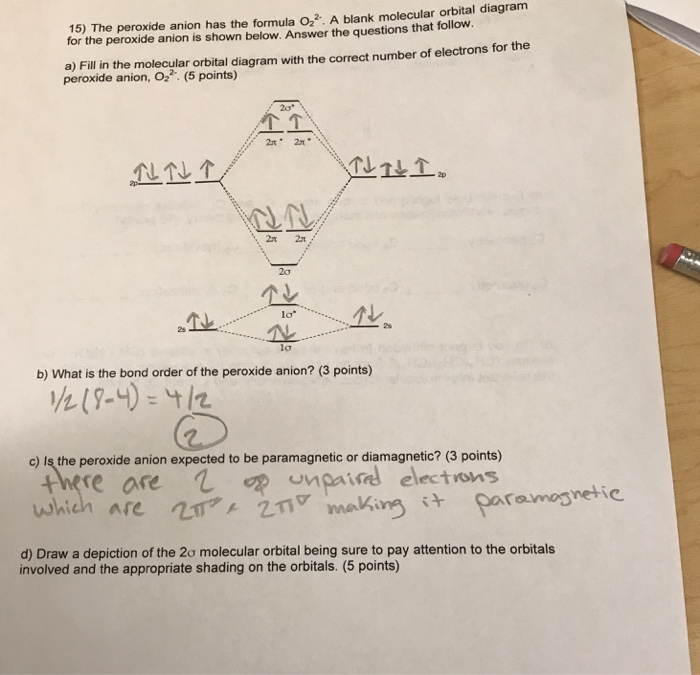
Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram for O2(2-) - YouTube This is the peroxide ion, O2(2-), so you KNOW it's going to be stable.It has a bond order of 1, which also makes sense. Draw the Lewis diagram of hydrogen...
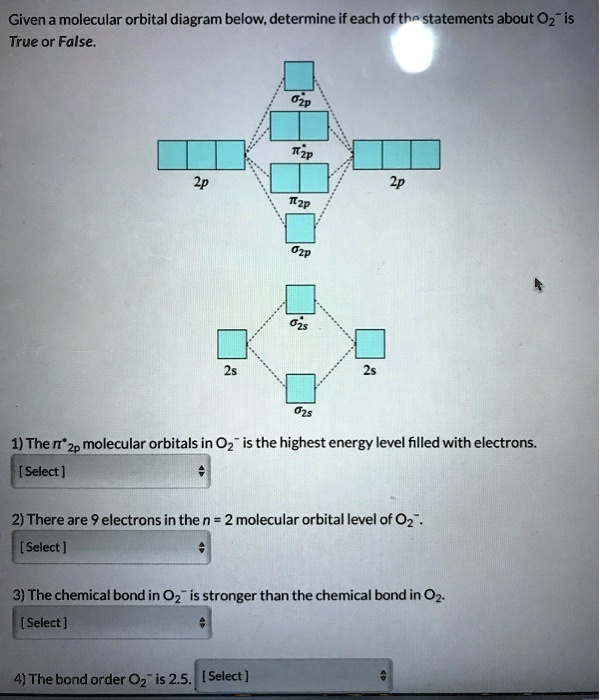
What is the molecular orbital diagram of O2 and F2? - Answers So, since oxygen has two unpaired electrons in the molecular orbital diagram it will have the strongest mass shift on a magnetic susceptibility balance. No, it is not correct to say that the bond energy always decreases when a diatomic molecule loses an electron. F2 and O2 are counterexamples to...
Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT), Chemistry Study... | eMedicalPrep The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. This kind of mixing of orbitals or symmetry interaction is not applicable for O 2 and F 2 molecule formation because of larger energy gap between 2s and 2p orbitals for these atoms.
Molecular Orbital Theory The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2pz orbitals on the adjacent...
Atomic and Molecular Orbital Diagram for Oxygen/O2 Describe molecular bonding using molecular orbital theory, compare/contrast with VESPR and Lewis theory. Molecular Diagram of B C N (Vs) O F Ne, how to draw & fill diagrams. Understand how to represent electron densities for sigma, pi bonding & anti-bonding molecular orbitals.
Molecular Orbital Theory | Boundless Chemistry In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as the difference, divided by two, between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons; this This MO diagram depicts the molecule H2, with the contributing AOs on the outside sandwiching the MO. The bonding level (lower level) is completely...
Chemical Forums: Molecular Orbital Diagram of O2. I thought I understood the molecular orbital theory but this practice question is making me confused. Include labels for molecular orbitals. --- -> For this, I drew the MO diagram but was wondering, since it says 'valence' MO diagram, do I...
PDF lecture_6 Molecular orbital 'resembles' the atomic orbital to which it lies closest in energy. Always break MO diagrams down into components based on symmetry. Walsh diagrams summarise changes in MO diagram wrt structure note a combination of first and second order effects.
Solved: Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For... | Chegg.com How Many Electrons Are In The Molecular Orbital? 4 3 1 Zero 2. Assuming that the sigma 2p molecular orbital is from the 2pz atomic orbitals and that the two pi 2p orbitals are from the 2px and 2py atomic orbitals.
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 8). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right.
Tutorial on Chemical Bonding, Part 8 of 10 (Molecular orbitals) The diagram shows how the molecular orbitals in lithium hydride can be related to the atomic orbitals of the parent atoms. Notice that the relative energies of the 2p-derived σ and π bonding molecular orbitals are reversed in O2 and F2. This is attributed to interactions between the 2s orbital each atom...

















0 Response to "42 molecular orbital diagram for o2 2"
Post a Comment