38 molecular orbital diagram practice problems with answers
PDF Orbitals and Quantum Numbers Practice Questions Orbitals and Quantum Numbers Practice Questions 1. What are the shapes of s, p, and d orbitals respectively? s= spherical p = dumbbell d = cloverleaf 2. How many 1s orbitals are there in an atom? 4p orbitals? 4d orbitals? 1s: 1 4p: 3 4d: 5 3. What is the maximum number of orbitals with: n = 4 l = 1 3 (the 4p orbitals) n = 2 l = 2 none (l must ... Quiz & Worksheet - Molecular Orbital Theory | Study.com This lesson will help you: Understand the molecular orbital theory. Explain the assumption behind the theory. Identify how to determine the shape of electron orbitals. Describe how carbon can bond ...
PDF Molecular Orbital Diagram Practice Problems With Answers molecular orbital diagram practice problems with answers chembook co uk chemistry in perspective for bored and. four letter course codes undergraduate academic catalogs. martindale s clinical physical examinations amp clinical. study guide and solutions manual to accompany t w graham. chemistry page 2 www 101science com. what makes a good ...
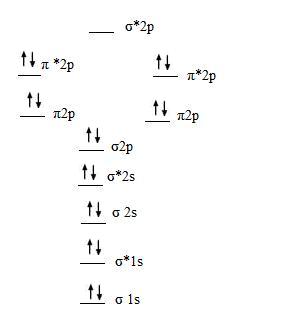
Molecular orbital diagram practice problems with answers
PDF Molecular orbital theory practice problems with answers Molecular orbital theory practice problems with answers Antibonding orbitals have the effect of destabilizing any bonding that has occurred. Answer Bonding orbitals have electron density in close proximity to more than one nucleus. As a result, the H2 molecule is more stable than a pair of isolated atoms. Molecular Structure Practice Problems Chemistry 401 Intermediate Inorganic Chemistry University of Rhode Island Practice Problems Molecular Structure and Covalent Bonding. 1. Write Lewis structures for (a) XeF 4, (b) PF 5, (c) BrF 3, (d) TeCl 4, (e) ICl 2 -.Give the formal charge and oxidation number for each atom. PDF Answers to Practice Test Questions 3 Molecular Orbital ... Answers to Practice Test Questions 3 . Molecular Orbital Theory: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules . 1. (a) 1The electron configuration for 𝐻𝐻 is 1𝑠𝑠, so 𝐻𝐻 has 1 valence electron. The electron configuration for 𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻 is 1𝑠𝑠2, so 𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻 has 2 valence electrons.
Molecular orbital diagram practice problems with answers. PDF Answers to Practice Test Questions 2 Molecular Orbital ... Answers to Practice Test Questions 2 . Molecular Orbital Theory: Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules . 1. Note that the bond dissociation energy (a positive value since energy is required to break a bond) is equal to the difference between E = 0 and the lowest energy vibrational energy PDF Problem Set 1 - University of Delaware (Circle your answer.) trigonal planar trigonal pyramidal (b) Draw both molecular orbital diagrams to explain your answer to part (a). You may ignore the core electrons and only show the orbitals where the valence electrons reside plus the LUMO (you do not need to show the higher, unoccupied molecular orbitals). PDF Molecular Orbital Diagram Practice Problems With Answers Molecular Orbital Diagram Practice Problems With Answers Chemistry Wikipedia. Sites to help students practice skills needed for the. Genetic Algorithms and Evolutionary Computation. What Makes A Good Nucleophile Master Organic Chemistry. Alkene Reactivity Department of Chemistry. Oxygen Wikipedia. chembook co uk CHEMISTRY IN PERSPECTIVE FOR ... CHE 110 Molecular Orbital Practice Problems Answers | PDF ... These problems are for practice in drawing your molecular orbital diagrams, molecular electron configurations and determining bond order. The following questions pertain to the F2 molecule: A) Draw the molecular orbital energy diagram for this molecule. Label all of the orbitals specifically. *2px
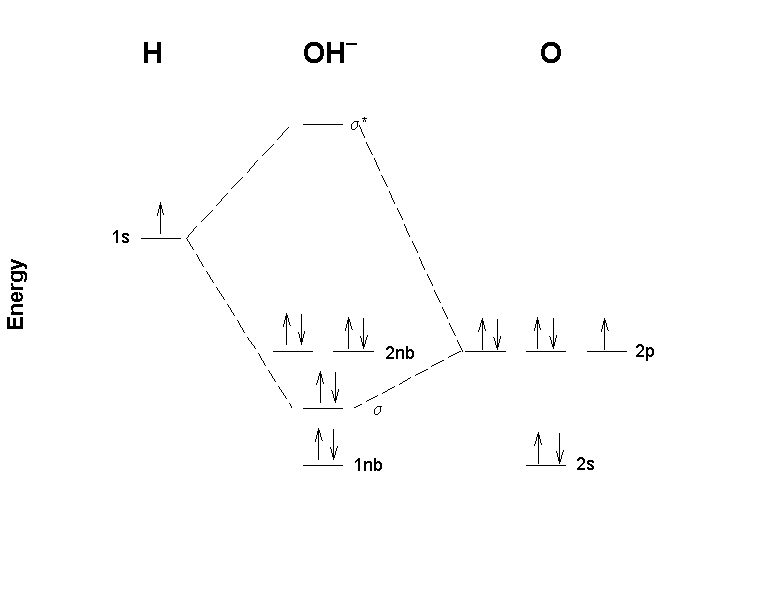
Molecular Orbitals - Problems - McMaster University Recall that the 2p atomic orbitals on C and O may form molecular orbitals of both s and p symmetry. 9. The correlation diagram in Problem 7 correlates the separated atom orbitals for R = ¥ with the molecular orbitals at R e, the equilibrium internuclear distance in the molecule. Continue the correlation of the orbitals to the limiting case of ... Molecular Structure Practice Problems Answers The molecular orbital diagram for ClO - is given below: The basis orbitals for Cl are 3s and 3p and for O are 2s and 2p. Z* for O 2s and 2p orbitals are similar so the AOs start at nearly the same energy. For the Cl 3s and 3p orbitals the two Z* values are quite different so the initial energies are more separated. PDF Molecular Orbital Diagram Practice Problems With Answers Molecular Orbital Diagram Practice Problems With Answers Materials Science and Engineering an Introduction 9th. UpToDate. Polytechnic Diploma in Computer Engineering first Semester. Martindale s Clinical Physical Examinations amp Clinical. 19 TAC Chapter 112 Subchapter C Texas Education Agency. Heating and Cooling Curves AP Chemistry. Oxygen ... PDF Worksheet 14 - Hybridization molecular orbitals atomic ... In atoms with n=3 or larger, the d orbitals can also be hybridized. In molecules with five molecular orbitals, five atomic orbitals are mixed: This will give trigonal bipyramidal geometry and is called dsp3 hybridization. Finally, molecules with octahedral geometry, will have ____ molecular orbitals. This hybridization is called _____ . Shown below is a portion of the chart from Worksheet 13.
Answer: Complete the molecular orbital dia... | Clutch Prep All Organic Chemistry Practice Problems Molecular Orbitals Practice Problems Q. Draw a molecular orbital energy diagram when the 1s orbitals of two hydrogen atoms combine to form a hydrogen molecule.In your drawing, label the... Molecular Orbital Theory Practice Problems - XpCourse Answers to the Practice Problem Set: 1. The electron-pair and molecular geometries are tetrahedral. The C atom is sp3 hybridized. Three of these hybrid orbitals each overlap with a chlorine 3p orbital to form three C—Cl sigma bonds. One hybrid orbital overlaps with a hydrogen 1s orbital to from a C—H sigma bond. 2. Molecular Orbital Theory - Texas A&M University (c) Molecular orbitals are generally described as being more delocalized than hybridized atomic orbitals. (d) One of the shortcomings of molecular orbital theory is its inability to account for a triple bond in the nitrogen molecule, N 2. (e) One of the shortcomings of valence bond theory is its inability to account for the paramagnetism of the ... PDF Chapter 11 Answers Practice Examples Chapter 11 Answers Practice Examples 1a. There are three half-filled 2p orbitals on N, and one half-filled 5p orbital on I. Each half-filled 2p orbital from N will overlap with one half-filled 5p orbital of an I. Thus, there will be three N—I bonds. The I atoms will be oriented in the same direction as the three 2p orbitals of N: toward the x ,y, and z-directions of a Cartesian coordinate ...
Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds.
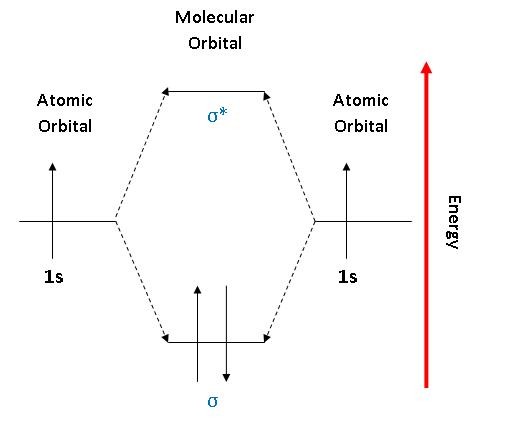
PDF Molecular Orbital Practice Answers Molecular Structure Practice Problems Answers A molecular orbital can hold two electrons, so both electrons in the H 2 molecule are in the σ 1s bonding orbital; the electron configuration is [latex]{\left({\sigma}_{1s}\right)}^{2}.[/latex] We represent this configuration by a molecular orbital energy diagram (Figure 10) in which a single
[Solved] Show the molecular orbital diagram and determine ... The number of electrons on H 2, H 2+, and H 22+ are 2, 1, and 0 respectively. These can be arranged in the molecular orbitals as follows: The bond order can be determined by the division of difference in bonding and anti bonding orbital electrons by two. The orbital with star (*) are the antibonding orbitals, and orbitals without star are ...
PDF Molecular Orbital Diagram Practice Problems With Answers molecular orbitals problems, molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet with answers, chem 131 name 100 points part 0 warmup 4 points each, lesson 3 chemical bonding molecular orbital theory, four 3 three 2 p sp university of illinois, vsepr and molecular geometry rules examples and practice, molecular orbital diagram practice daytonva150 ...
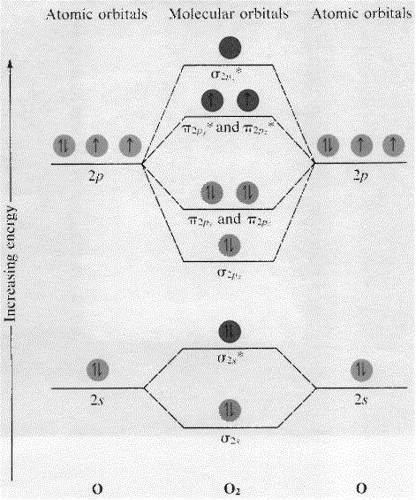
Molecular Orbital Theory - Purdue University Practice Problem 9: Construct a molecular orbital diagram for the O 2 molecule. Click here to check your answer to Practice Problem 9 . Bond Order. The number of bonds between a pair of atoms is called the bond order. Bond orders can be calculated from Lewis structures, which are the heart of the valence-bond model. ...
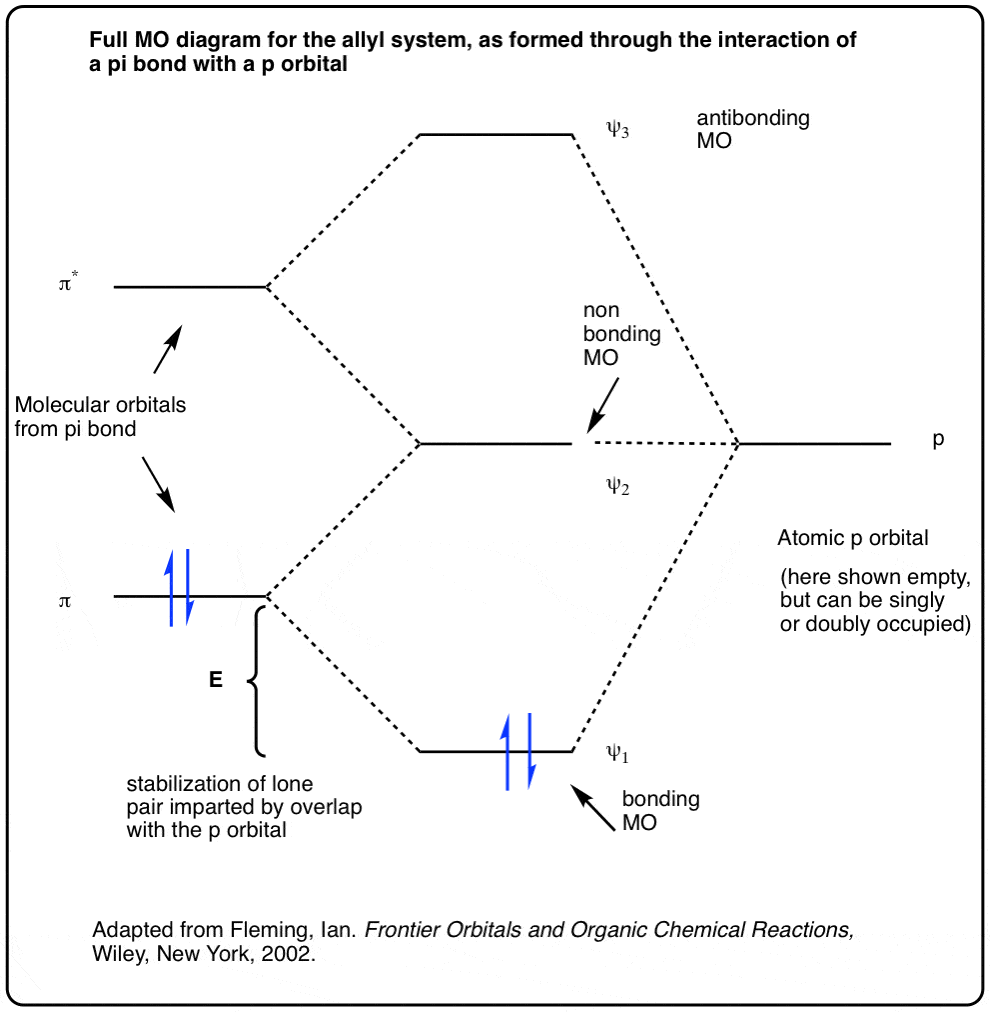
DOC Molecular Orbital Worksheet - Mr. Lee's 10th Grade ... Six overlapping p orbitals must form six molecular orbitals . Three will be bonding, three antibonding . Lowest energy MO will have all bonding interactions, no nodes . As energy of MO increases, the number of nodes increases . System symmetric so 2 pairs of degenerate orbitals . 6 atomic orbitals - 6 molecular orbitals
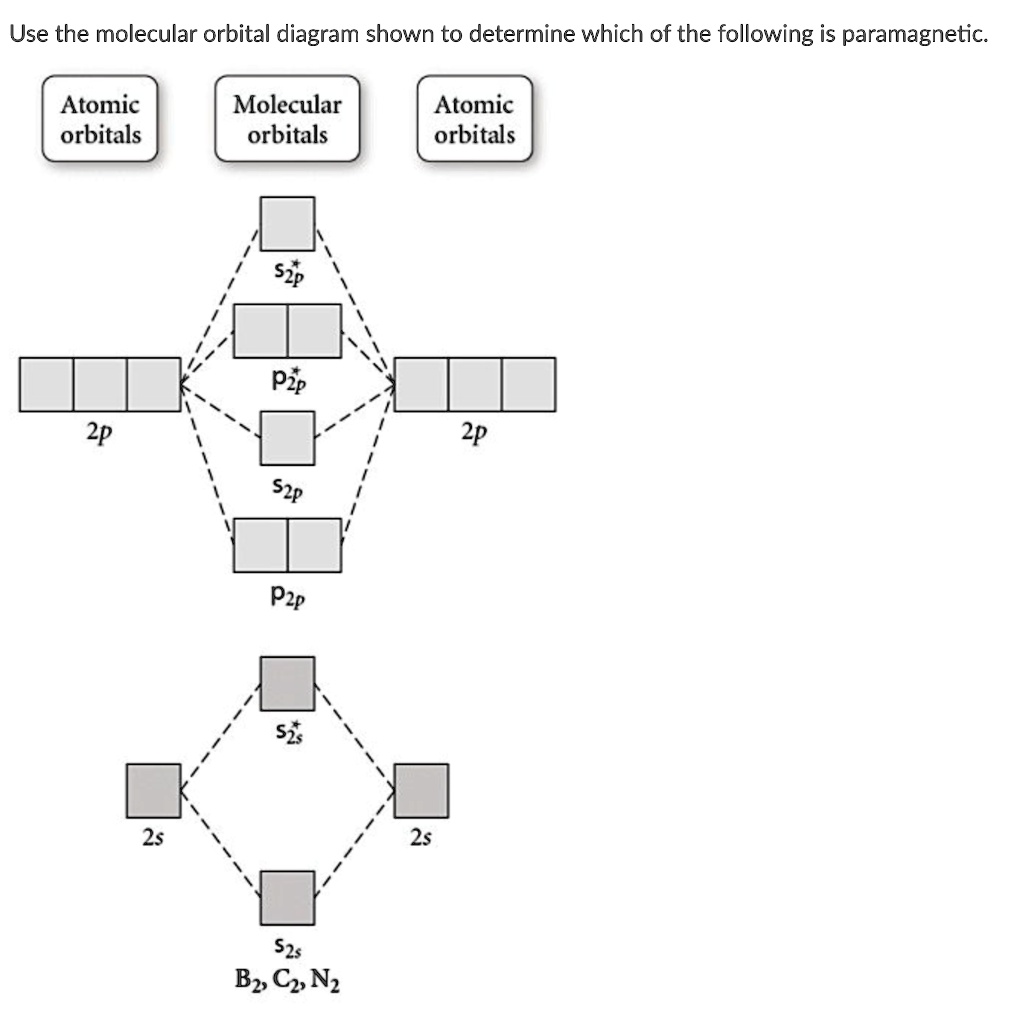
Molecular Orbitals: Problems and Solutions | SparkNotes By constructing a molecular orbital picture for each of the following molecules, determine whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. a. B 2 b. C 2 c. O 2 d. NO e. CO a. B 2 is paramagnetic because it has two unpaired electrons, one in each of its p orbitals. b. C 2 is diamagnetic because all of its electrons are paired.
8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science 8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams. Abstract (TL;DR) Molecular orbital diagrams are a fantastic way of visualizing how molecular orbitals form using what we already understand about sigma and pi bonds. Depending on if it is a homonuclear case, where the bonding atoms are the same, or a heteronuclear case, where the bonding atoms are ...
Molecular Orbital Theory Practice Questions - chem-textbook Solution. (a) Similarities: Both are bonding orbitals that can contain a maximum of two electrons. Differences: σ orbitals are end-to-end combinations of atomic orbitals, whereas π orbitals are formed by side-by-side overlap of orbitals. (b) Similarities: Both are quantum-mechanical constructs that represent the probability of finding the ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram Practice | Chem 251 February 15, 2015. By Marsha Massey. University of Sydney has created a practice website for reviewing different parts of molecular orbital diagrams. Using this resource you can add pieces to pre-drawn MO diagrams for over 20 different molecules. The site includes opportunities to practice filling in electrons, attaching the names/symbols of ...
Answer: Consider the molecular orbital dia... | Clutch Prep Problem: Consider the molecular orbital diagram for a 2nd row diatomic molecule (X 2) shown below. The labels a, b, and c are placed in three of the molecular orbitals. What are the names of these three orbitals?1. σ*2p, π2p, σ*1s2. π*2p, σ*2p, σ1s3. σ*2p, π2p, σ*2s4. π*2p, σ2p, σ1s5. π*2p, σ2p, σ*2s FREE Expert Solution Show answer
PDF Answers to Practice Test Questions 3 Molecular Orbital ... Answers to Practice Test Questions 3 . Molecular Orbital Theory: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules . 1. (a) 1The electron configuration for 𝐻𝐻 is 1𝑠𝑠, so 𝐻𝐻 has 1 valence electron. The electron configuration for 𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻 is 1𝑠𝑠2, so 𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻 has 2 valence electrons.
Molecular Structure Practice Problems Chemistry 401 Intermediate Inorganic Chemistry University of Rhode Island Practice Problems Molecular Structure and Covalent Bonding. 1. Write Lewis structures for (a) XeF 4, (b) PF 5, (c) BrF 3, (d) TeCl 4, (e) ICl 2 -.Give the formal charge and oxidation number for each atom.
PDF Molecular orbital theory practice problems with answers Molecular orbital theory practice problems with answers Antibonding orbitals have the effect of destabilizing any bonding that has occurred. Answer Bonding orbitals have electron density in close proximity to more than one nucleus. As a result, the H2 molecule is more stable than a pair of isolated atoms.
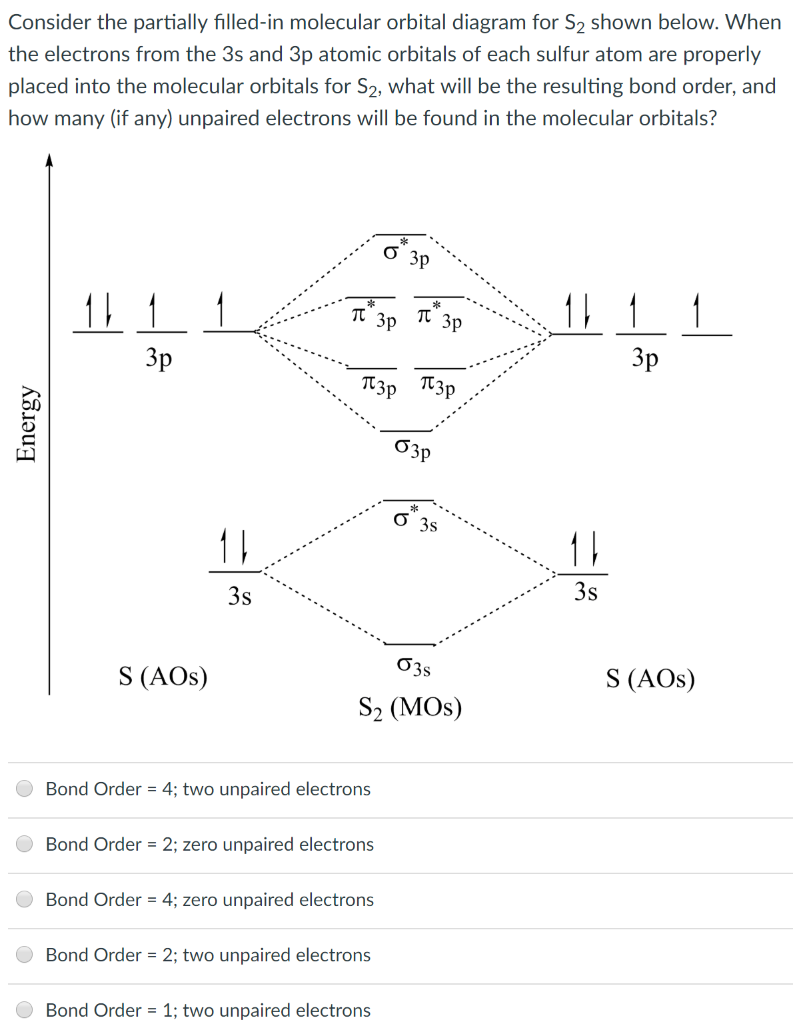

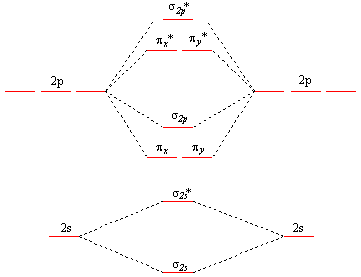


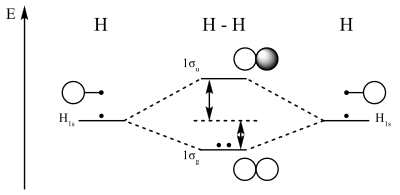





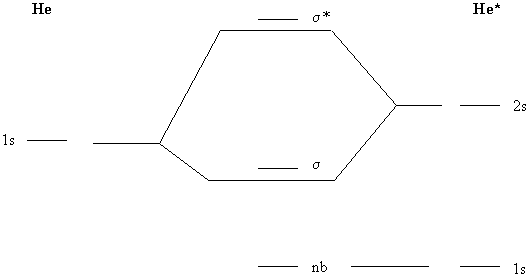
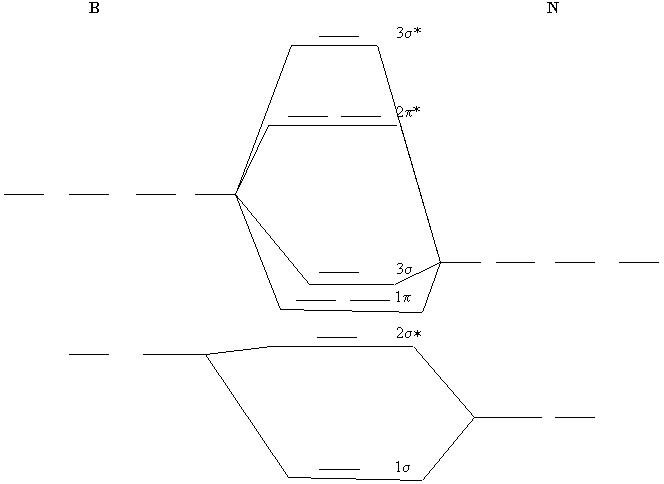
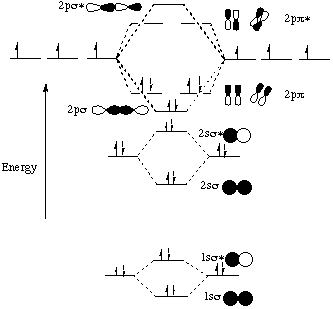
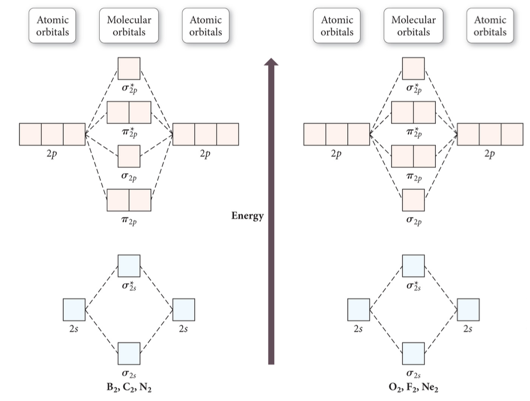

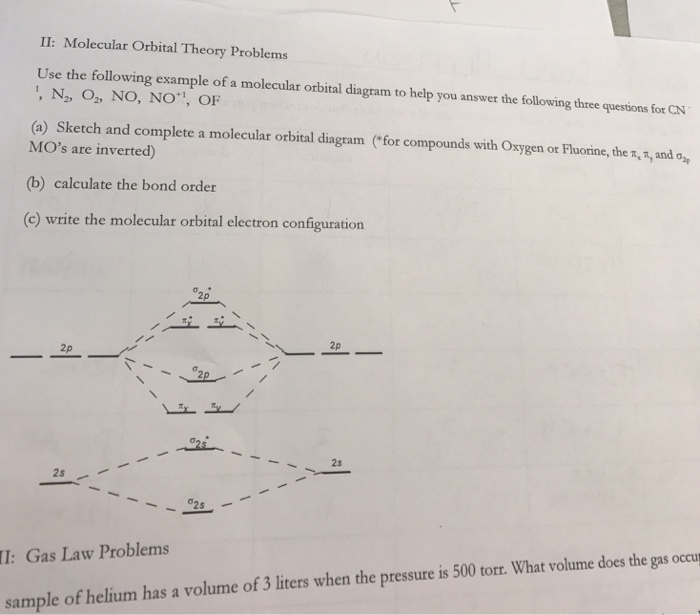
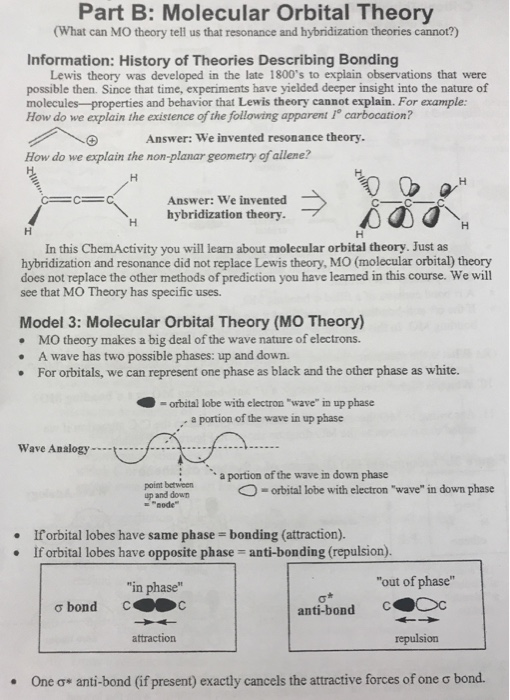




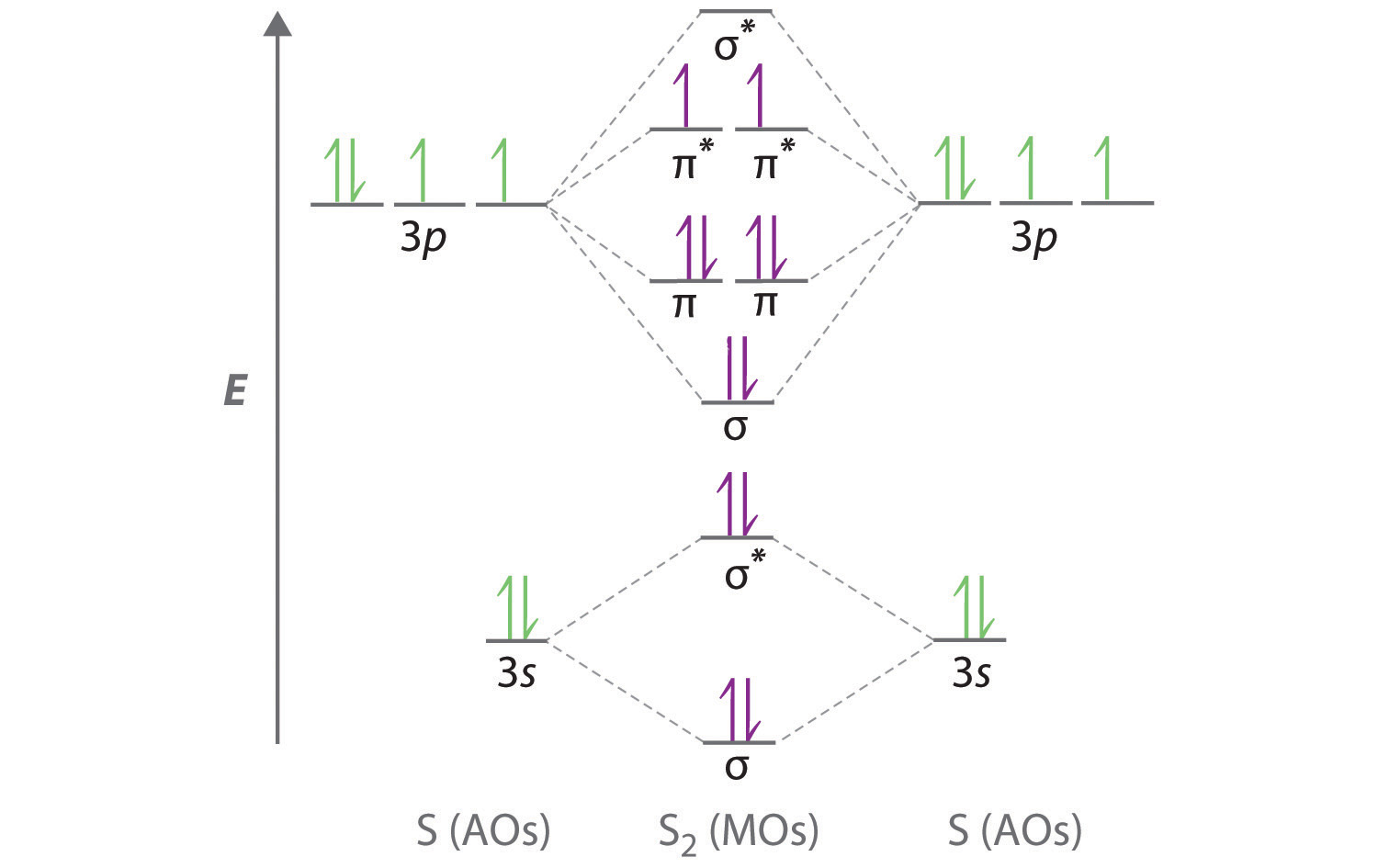

0 Response to "38 molecular orbital diagram practice problems with answers"
Post a Comment