38 identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - Physics Classroom Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. OneClass: Your physics textbook is sliding to the right ... Your physics textbook is sliding to the right across the table. Identify all the forces acting on the object and draw a free-body diagram. Draw the force vectors with their tails at the dot. The orientation of your vectors will be graded. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded.
SOLVED:Describe a situation. For each, identify all forces ... Problem 25 Easy Difficulty Describe a situation. For each, identify all forces acting on the object and draw a free-body diagram of the object. An ice hockey puck glides across frictionless ice. Answer normal force upwards and gravitational force downwards in vertical direction. View Answer Discussion You must be signed in to discuss.
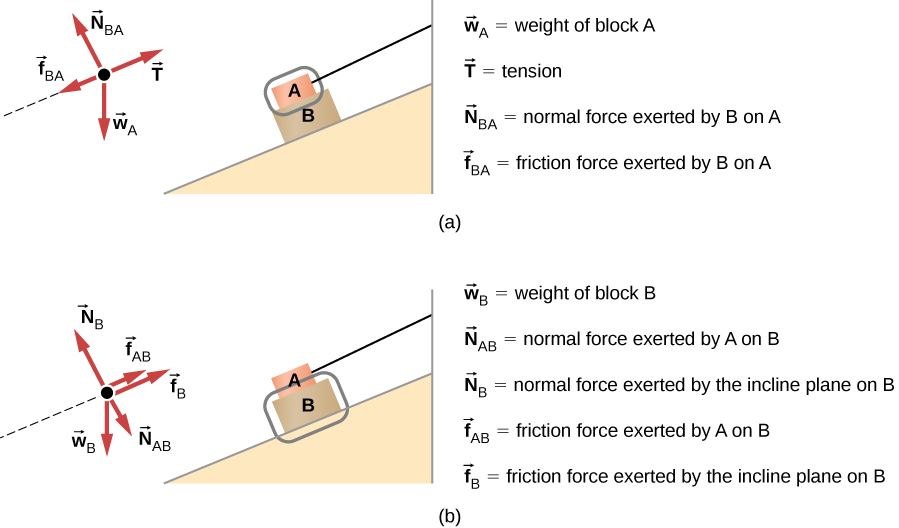
Identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram.
What are some examples about free body diagram ... How do free body diagrams solve force problems? The free body diagram is a pictorial representation used to analyze the forces acting on a body. The purpose of a free body diagram is to show all the forces acting on a body due to contact with other objects, and/or due to body forces acting on the body (such as gravity or magnetic fields). PDF Concept of Force and Newton's Laws of Motion Treat each object in the system as a point-like object Identify all forces that act on that object, draw a free body diagram Apply Newton's Second Law to each body Find relevant constraint equations Solve system of equations for quantities of interest TACTICS BOX 53 Drawing a freebody diagram 1 Identify all ... TACTICS BOX 5.3 Drawing a freebody diagram 1. Identify all forces acting on the object. This step was described in Tactics Box 5.2. 2. Draw a coordinate system. Use the axes defined in your pictorial representation. If those axes are tilted, for motion along an incline, then the axes of the freebody diagram should be similarly tilted. 3.
Identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram.. Your car is accelerating to the right from a stop ... July 29, 2017August 29, 2020Answers Your car is accelerating to the right from a stop.Identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram.Draw the force vectors with their tails at the dot. The orientation of your vectors will be graded. Also, the relative length of one vector to the other will be graded. Management Free Body Diagrams, Tutorials with Examples and Explanations The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in the direction of the force to be drawn. 1 Draw a free body diagram of object 1 or 2 and the book 2 ... Draw a free body diagram of object (1 or 2) and the book. 2. Label all the forces acting on the object. 3. At the angle just before the blocks begins to move, the forces are in equilibrium, and thus the net force is zero. Write two equations (x component & y components or components along the slope and perpendicular to the slope) of equilibrium. 4. 2 Identify all the forces acting on the object and their ... ANSWER: Correct Now that you have identified the forces acting on the piano, you should draw the free-body diagram. Draw the length of your vectors to represent the relative magnitudes of the forces, but you don't need to worry about the exact scale. You won't have the exact value of all of the forces until you finish solving the problem.
SOLVED:For each problem, identify all the forces acting on ... SOLVED:For each problem, identify all the forces acting on the object and draw a free-body diagram of the object. A box is being dragged across the floor at a constant speed by a rope pulling horizontally on it. Friction is not negligible. Get the answer to your homework problem. Try Numerade Free for 7 Days Jump To Question SOLVED:Describe a situation. For each problem identify all ... The free body diagram off a system shows all the forces acting on the system. So in this question, it is given that there is a elevator hanging from a cable and this elevator is moving upwards and there is good and this is speed is reducing. So we can say that the weight off the Liberator is acting downwards. PDF Free-body diagrams - ParishPhysics 1. Draw the free body diagram of the object. 2. Name all the forces. 3. Set the net force to zero, taking account of +/- directions. 4. Solve for the unknown force. 2F!mg=0 Solving equilibrium problems PDF Draw free Body Diagram - Department of Physics Determine (a) the angle θ and (b) the tension in the string. Example #4-73 Two objects connected by a massless string Draw free body diagrams Apply Newton's Laws separately to each object The magnitude of the acceleration of both objects will be the same The tension is the same in each diagram Solve the simultaneous equations
Statics Free body diagram - scientific sentence 2. Drawing free-body diagram, the steps. Draw a picture of the situation, that is the motion diagram, Isolate the system (the object) of interest by drawing a closed curve around, Identify all forces acting on the object, Draw a coordinate system (x, y, z) axis, Represent the object as a dot at the origin of the coordinate axes, Draw vectors ... 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - General Physics Using ... We must draw a separate free-body diagram for each object in the problem. A free-body diagram is a useful means of describing and analyzing all the forces that act on a body to determine equilibrium according to Newton's first law or acceleration according to Newton's second law. Solved TACTICS BOX 5.3 Drawing a free-body diagram - Chegg Question: TACTICS BOX 5.3 Drawing a free-body diagram Identify all forces acting on the object. This step was described in Tactics Box 5.2.Draw a coordinate system. Use the axes defined in your pictorial representation. If those axes are tilted, for motion along an incline, then the This problem has been solved! See the answer SOLVED:For each problem, identify all the forces acting on ... and this problem. We are asked to identify all of the forces acting on an object and to draw a free body diagram of that object. So in this situation we have an ascending elevator that is hanging from the cable and coming to a stop. So we have an elevator from the table and this is its direction of motion.
Answered: Identify all the forces acting on the… | bartleby Question Identify all the forces acting on the object and draw a free-body diagram of the object. The light turns green and you accelerate rapidly forward so that you and your passenger feel "thrown back" into your seat. Consider your passenger to be the object. Expert Solution Want to see the full answer? Check out a sample Q&A here See Solution
Chapter 5, Force and Motion Video Solutions, Physics for ... For each, identify all forces acting on the object and draw a free-body diagram of the object. A steel beam is being lifted straight up at steady speed by a crane. Vipender Y.
Free Body Diagram - Definition, Examples, Solved Problems ... Here, we are only interested in determining the forces acting on our object. 3. Draw a coordinate system and label positive directions. 4. Draw the contact forces on the dot with an arrow pointing away from the dot. The arrow lengths should be relatively proportional to each other. Label all forces. 5. Draw and label our long-range forces.
For the problem, identify all the forces acting on the ... For the problem, identify all the forces acting on the objec | Quizlet Explanations Question For the problem, identify all the forces acting on the object and draw a free-body diagram of the object. An ascending elevator, hanging from a cable, is coming to a stop. Explanation Create a free account to see explanations
Force Diagram instructions Force Diagrams (Free-body Diagrams) A force diagram is simply a diagram showing all the forces acting on an object, the force's direction and its magnitude. It is a simplification of the picture that shows just the forces. In the example below, the first image is a picture of a climber on the side of a cliff.
PDF Free-Body Diagrams: the Basics The equilibrium equation (1.1) is used to determine unknown forces acting on an object (modeled as a particle) in equilibrium. The first step in doing this is to draw thefree-body diagramof the object to identify the external forces acting on it. The object's free-body diagram is simply a sketch of the objectfreedfrom its surroundings showingall
How to Draw a Free Body Diagram: 10 Steps (with Pictures) A free-body diagram is a visual representation of an object and all of the external forces acting on it, so to draw one you'll have to have this information calculated. They are very important for working in engineering or physics problem solving since drawing them helps you to understand what is going on in a problem.
PDF Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of Motion Forces and Free Body Diagrams -Example 4.2 ketchup-slide • Like the previous example, we account for the forces and draw a free body diagram. • Again, in this case, the net horizontal force is unbalanced. • In this case, the net horizontal force opposes the motion and the bottle slows down (decelerates) until it stops. 2− 0 2=2𝑎 − 0
length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative ... Part A Identify all forces acting on the object. Check all that apply. ANSWER: ANSWER: Normal force, \vec{n} Air resistance, \vec{D} Thrust, \vec{F}_{\rm thrust} Tension, \vec{T} Kinetic friction force, \vec{f}_k Weight, \vec{w} Correct Part B Draw a freebody diagram of the car. Suppose that the car is moving to the right. Draw the vectors ...
TACTICS BOX 53 Drawing a freebody diagram 1 Identify all ... TACTICS BOX 5.3 Drawing a freebody diagram 1. Identify all forces acting on the object. This step was described in Tactics Box 5.2. 2. Draw a coordinate system. Use the axes defined in your pictorial representation. If those axes are tilted, for motion along an incline, then the axes of the freebody diagram should be similarly tilted. 3.
PDF Concept of Force and Newton's Laws of Motion Treat each object in the system as a point-like object Identify all forces that act on that object, draw a free body diagram Apply Newton's Second Law to each body Find relevant constraint equations Solve system of equations for quantities of interest
What are some examples about free body diagram ... How do free body diagrams solve force problems? The free body diagram is a pictorial representation used to analyze the forces acting on a body. The purpose of a free body diagram is to show all the forces acting on a body due to contact with other objects, and/or due to body forces acting on the body (such as gravity or magnetic fields).

0 Response to "38 identify all forces acting on the object and draw the free-body diagram."
Post a Comment