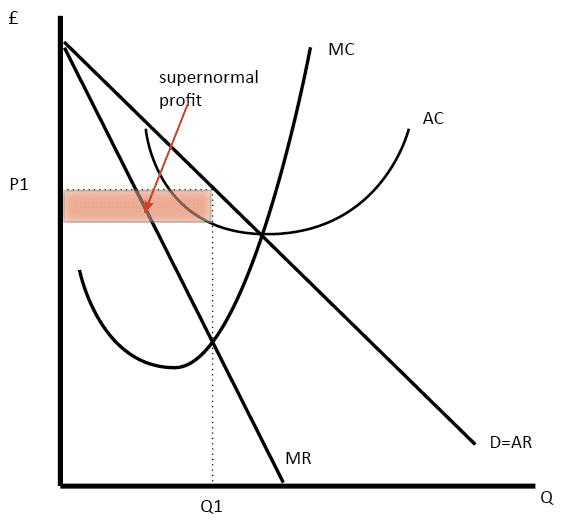
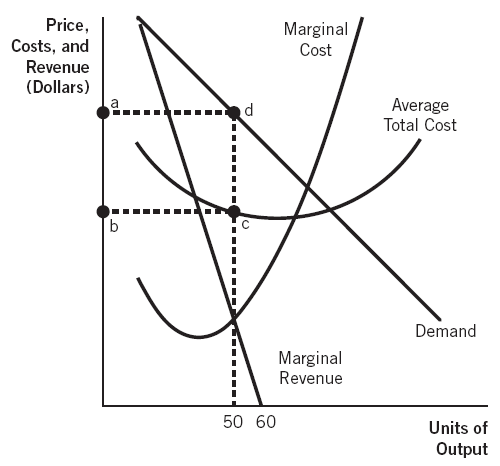
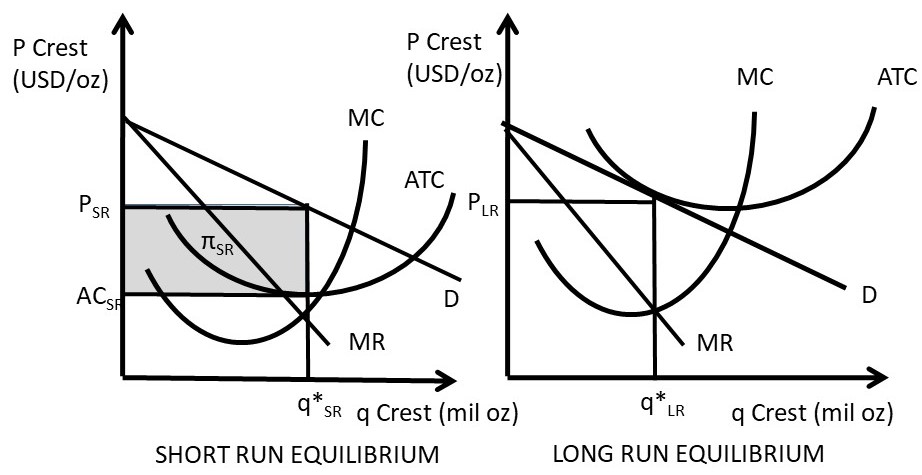
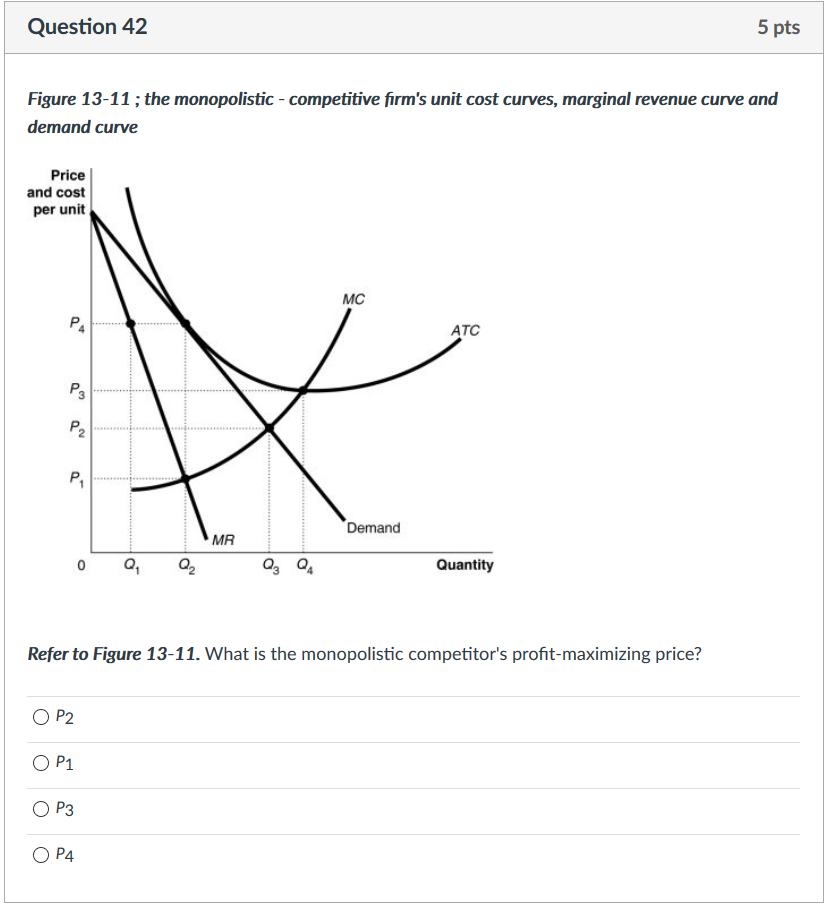
39 refer to the diagram to the right. what is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output?
21)In monopolistic competition, in the short run a firm maximizes its profit by selecting an output at which marginal cost equals A)price. B)marginal revenue. C)zero. D)average total cost. 21) 22)If a monopolistically competitive firm's marginal cost curve shifts upward, then its level of output A)will decrease. Refer to the diagram to the right. What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output? A. Q_1 units B. Q_2 units C. Q_3 units D. Q_4 units ; Question: Refer to the diagram to the right. What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output? A. Q_1 units B. Q_2 units C. Q_3 units D. Q_4 units
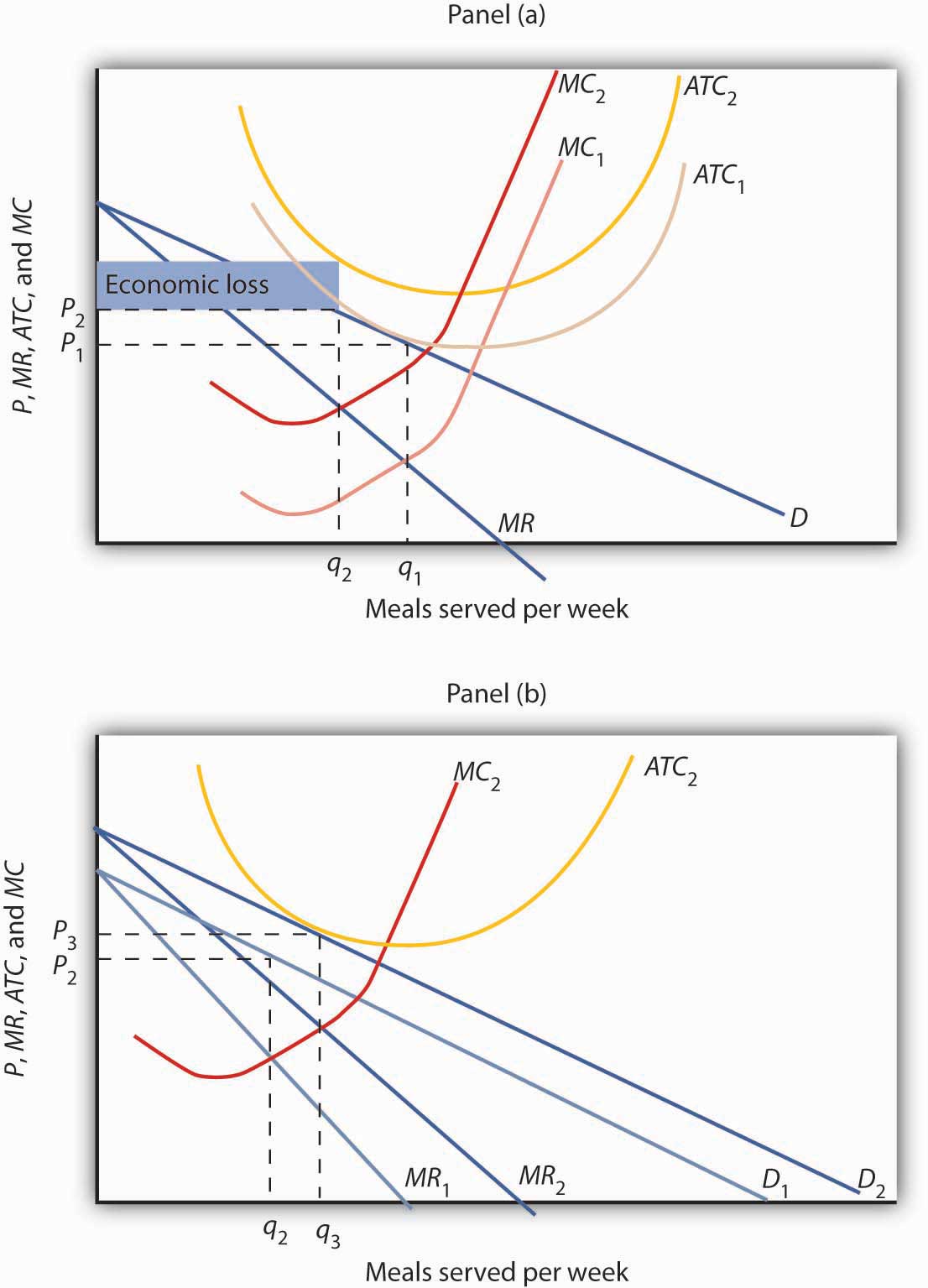
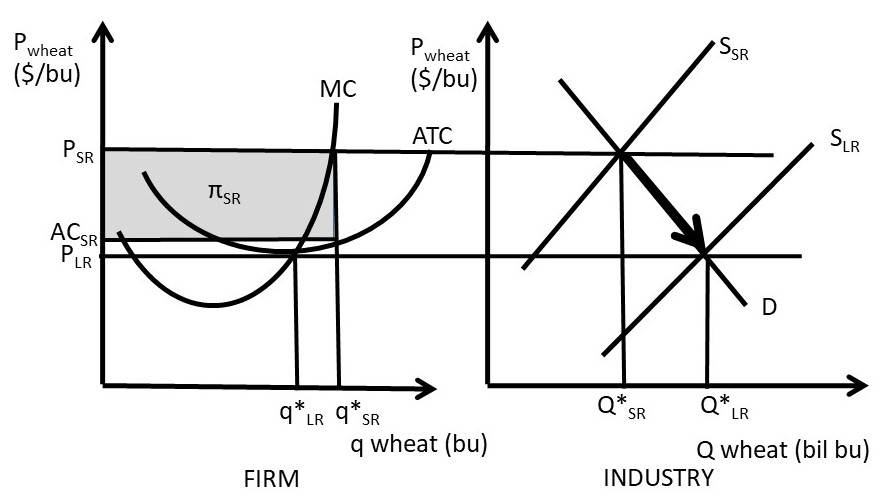
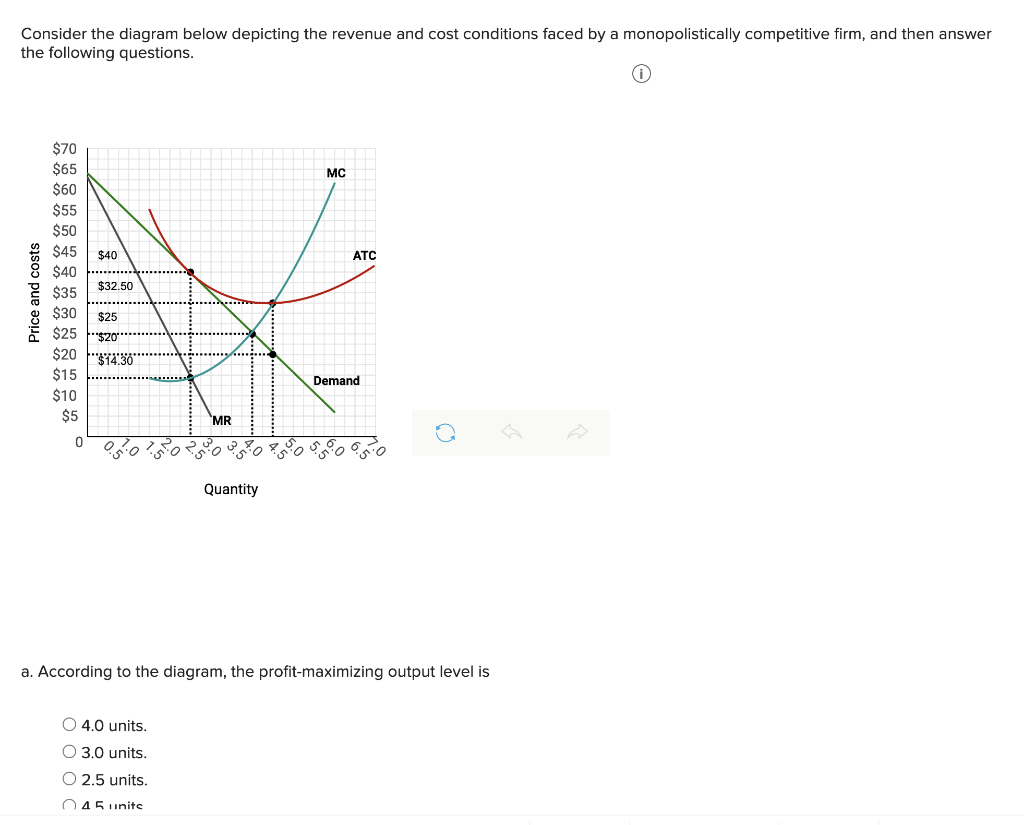
On a diagram, draw the marginal cost curves for the two factories, the average and marginal revenue curves, and the total marginal cost curve (i.e., the marginal cost of producing Q = Q 1 + Q 2). Indicate the profit-maximizing output for each factory, total output, and price. The average revenue curve is the demand curve, P = 700 - 5Q.
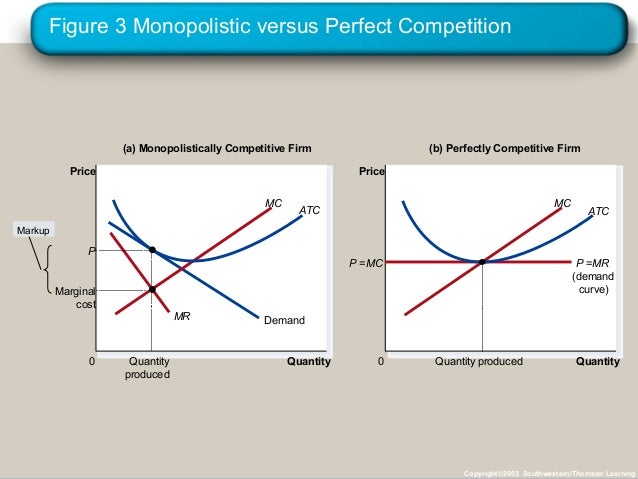
Refer to the diagram to the right. what is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output?
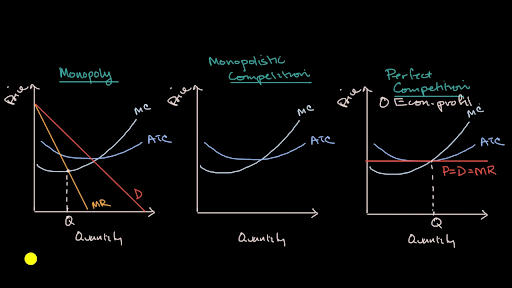
Monopolistic competition and economic profit. AP.MICRO: PRD‑3 (EU) , PRD‑3.B (LO) , PRD‑3.B.10 (EK) Transcript. In this video we explore why it is hard for a monopolistic competitor to make economic profit in the long run. Refer to Figure 13-11. What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output? Q2 units. 11) Refer to Figure 13 -5. The candy store represented in the diagram is currently selling Q a units of candy at a price of P a . Is this candy store maximizing its profit and if it is not, what would you recommend to the firm? 11) A) Yes, it is maximizing its profit by charging the highest price possible.
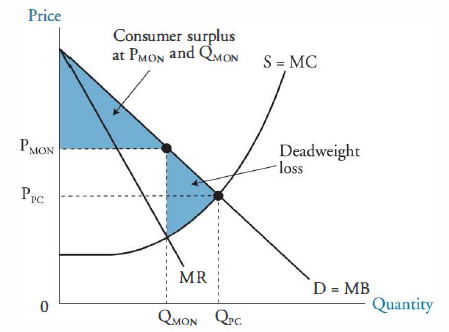
Refer to the diagram to the right. what is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output?. Profit Maximization. The monopolist's profit maximizing level of output is found by equating its marginal revenue with its marginal cost, which is the same profit maximizing condition that a perfectly competitive firm uses to determine its equilibrium level of output.Indeed, the condition that marginal revenue equal marginal cost is used to determine the profit maximizing level of output of ... In Step 1, the monopoly chooses the profit-maximizing level of output Q 1, by choosing the quantity where MR = MC. In Step 2, the monopoly decides how much to charge for output level Q 1 by drawing a line straight up from Q 1 to point R on its perceived demand curve. Thus, the monopoly will charge a price (P 1 ). The profit maximizing output level and price of a monopolist can be determined through two approaches: the TR-TC method and the MR-MC method, same as in case perfect competition. However, unlike perfect competition, there is no need to carry out analysis at two levels, firm and industry since there is a single producer. A) The profit maximizing output is the one at which marginal revenue and marginal cost are equal. B) Average revenue equals price. C) The profit maximizing output is the one at which the difference between total revenue and total cost is largest. D) The monopolist's demand curve is the same as the market demand curve.
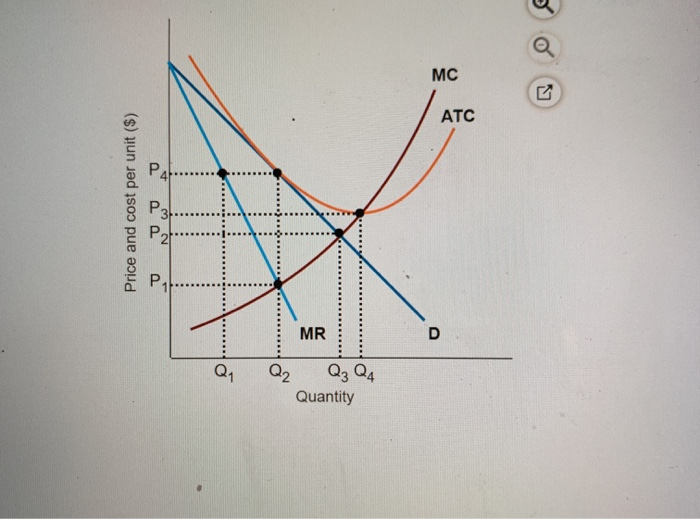
24) Long-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition is similar to that under perfect competition in that A) firms produce at the minimum point of their average cost curves. B) 24) price equals marginal revenue. A monopolistically competitive firm earning profits in the short run will find the demand for its product decreasing and becoming more elastic in the long run as new firms move into the industry until the firm's demand curve is tangent to its average total cost curve. Refer to the diagram to the right. The firm represented in the diagram makes Refer to the diagram to the right. What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output? Q2 units. C) The demand curve will shift to the right and became more elastic. D) The demand curve will shift to the right and became less elastic. Figure 13-11 . 43) Refer to Figure 13-11. What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output? A) Q1 units. B) Q2 units. C) Q3 units. D) Q4 units . 44) Refer to Figure 13-11.
How a Profit-Maximizing Monopoly Decides Price In Step 1, the monopoly chooses the profit-maximizing level of output Q 1, by choosing the quantity where MR = MC. In Step 2, the monopoly decides how much to charge for output level 1 by drawing a line straight up from Q 1 to point R on its perceived demand curve. B) In seeking the profit-maximizing output the pure monopolist underallocates resources to its production. C) The pure monopolist maximizes profits by producing that output at which the differential between price and average cost is the greatest. D) Purely monopolistic sellers earn only normal profits in the long run. 24) Refer to Figure 13-11. What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing price? A) P1 . B) P2 . C) P3 . D) P4 . 25) Refer to Figure 13-11. The firm represented in the diagram . A) should expand its output to take advantage of economies of scale. B) should exit the industry. C) makes zero accounting profit. D) makes zero economic profit. A perfectly competitive firm produces 3,000 units of a good at a total cost of $36,000. The price of each good is $10. Calculate the firm's short run profit or loss. Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the cost and demand curves for a profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market.
Solution for Practice question: 20 According to the figure above, what is the monopolistic competitor's profit-maximizing output? Group of answer choices Q3…
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A monopolistically competitive industry that earns economic profits in the short run will. A) continue to earn economic profits in the long run. B) experience the exit of old firms out of the industry in the long run.
Refer to the diagram to the right which shows short run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches. If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units, what is the price charged?
A. The demand curve will shift to the right and became less elastic. ... What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output? A. Q1 units
What is the long-run result for the monopolistic competitor indicated by the above diagram? A) economic loss and subsidization. B) economic profit
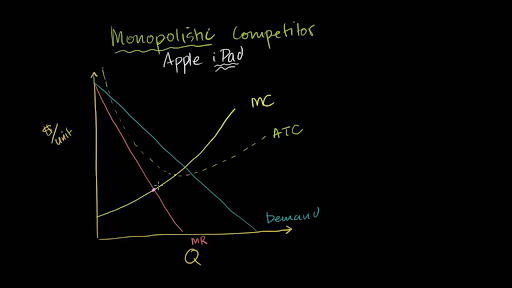
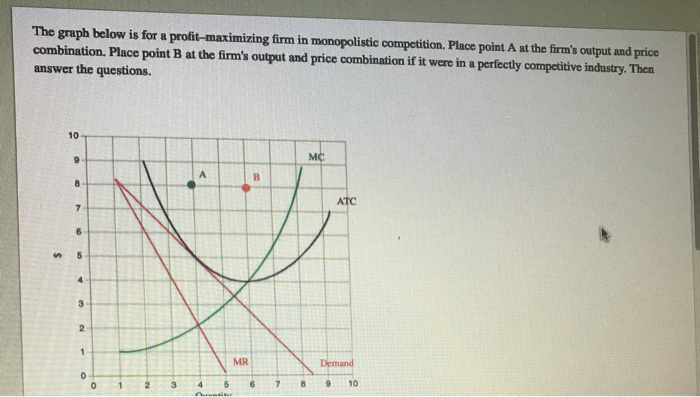
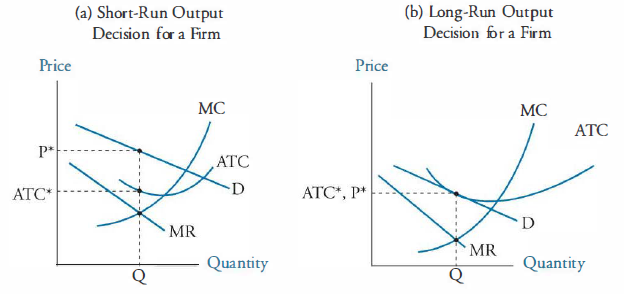
How a Monopolistic Competitor Chooses its Profit Maximizing Output and Price. To maximize profits, the Authentic Chinese Pizza shop would choose a quantity where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, or Q where MR = MC. Here it would choose a quantity of 40 and a price of $16.
58) Refer to Figure 13-16. Figure 13-16 depicts a monopolistically competitive barber shop. Use the diagram to answer the following questions. a. Suppose the average variable cost of production is $15 when output equals 110 haircuts and $15.25 when output equals 140 haircuts.
8. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: A. 0AHE. B. 0BGE. C. 0CFE. D. ABGE. A. 0AHE. 9. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize: A. a loss equal to BCFG. B. a loss equal to ACFH. C. an economic profit of ACFH. D. an economic profit of ABGH. D. an economic ...
Answer to Solved Refer to the diagram to the right. What is the ... What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing price? ... firm produces that level of ...
Rogers decides what price to charge. When the firm has determined its profit-maximizing quantity of output, it will behave like a monopoly and charge the maximum it can at the quantity. On the graph, this process can be shown as a vertical line reaching up through the profit-maximizing quantity until it hits the firm’s perceived demand curve.
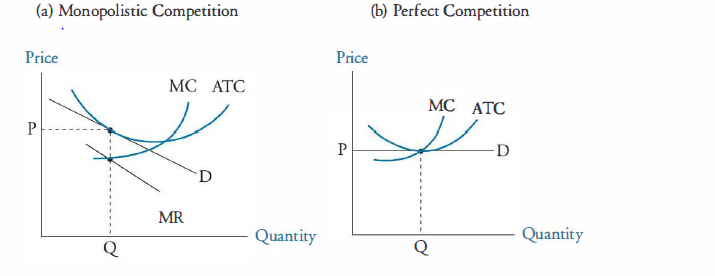
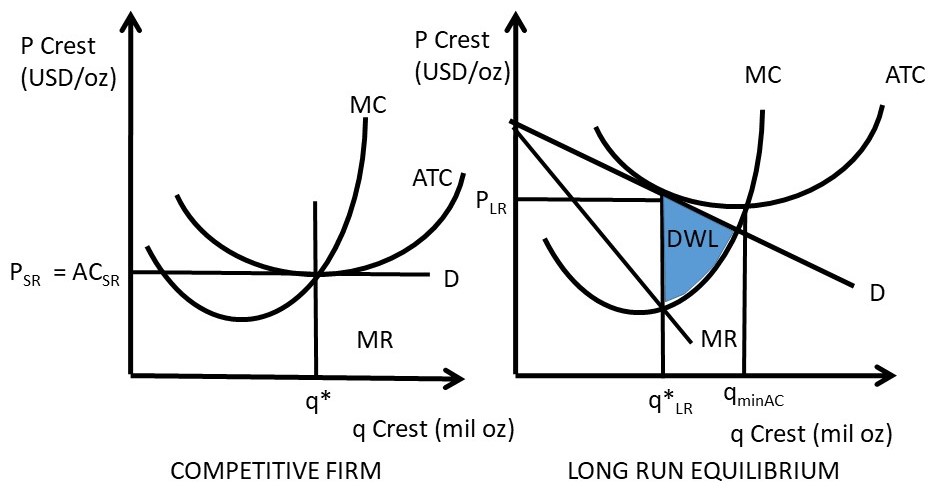
The below mentioned article provides an overview on the Theory of Excess Capacity. The doctrine of excess (or unutilized) capacity is associated with monopolistic competition in the long-run and is defined as "the difference between ideal (optimum) output and the output actually attained in the long-run.". Under perfect competition, however, the demand curve (AR) is tangential to the long ...
181. Refer to the above diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission were to set a maximum price of P3, the monopolist would: A. maximize profits. B. increase output beyond the profit-maximizing level. C. reduce output below the profit-maximizing level. D. be unable to make a normal profit. 182.
See Page 1. 7) A monopolistically competitive firm earning profits in the short run will find the demand for its product decreasing and becoming more elastic in the long run as new firms move into the industry until A) the original firm is driven into bankruptcy. B) the firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic.
Refer to Table 13-3. What is the amount of the firm's loss at its optimal output level? ... What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing price?
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be: The demand curve faced by a nondiscriminating pure monopoly is; Suppose a pure monopolist is faced with the demand schedule; Refer to the diagram. a shift of the aggregate demand curve from ad1 to ad0 might be caused by a(n) Refer to the diagram to the right. the firm ...
14. Refer to Exhibit 14-2. In Graph A, a profit-maximizing (loss-minimizing) firm will experience a ____ at output quantity ____. a. loss; q 1 b. loss; q 2 c. profit; q 1 d. profit; q 2 15. In the long run, a monopolistic competitor: a. earns a normal rate of return. b. sells a level of output at which marginal revenue is less than price.
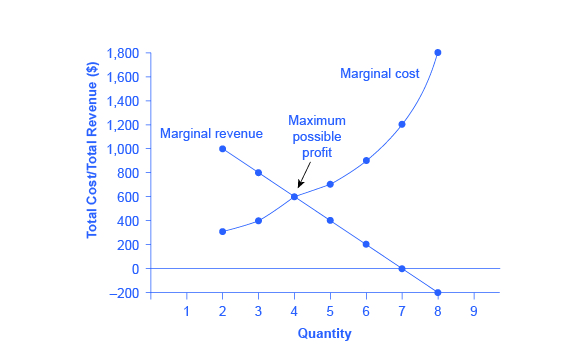
C) an industry that sells all its output to one buyer. D) a firm that sells all its output to one buyer. Answer: A Use the following information to solve the next 4 questions about a monopolistic market. The demand for a good is given by: P = 10 - Q. A monopolist's costs are given by: TC = 2 + 4Q. 7.
Refer to the diagram to the right. What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing price? OA, SP B.. SP Ос.SP3 MC 2 ATC 2 P MR Quanity ; Question: Refer to the diagram to the right. What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing price? OA, SP B.. SP Ос.SP3 MC 2 ATC 2 P MR Quanity
11) Refer to Figure 13 -5. The candy store represented in the diagram is currently selling Q a units of candy at a price of P a . Is this candy store maximizing its profit and if it is not, what would you recommend to the firm? 11) A) Yes, it is maximizing its profit by charging the highest price possible.
Refer to Figure 13-11. What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output? Q2 units.
Monopolistic competition and economic profit. AP.MICRO: PRD‑3 (EU) , PRD‑3.B (LO) , PRD‑3.B.10 (EK) Transcript. In this video we explore why it is hard for a monopolistic competitor to make economic profit in the long run.
















0 Response to "39 refer to the diagram to the right. what is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output?"
Post a Comment