40 diagram of crossing over
Diagram for Meiosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division in which a single cell undergoes division twice to produce four haploid daughter cells. The cells produced are known as the sex cells or gametes (sperms and egg). The diagram of meiosis is beneficial for class 10 and 12 and is frequently asked in the examinations. Wave flag over the head and point to the antenna or the respective line. L Raise flag and touch the top with the palm of the free hand. L Ball Touched 3 Crossing Space Faults, Ball 4 Touched an Outside Object or Foot Fault by any Player During Service Judgment Impossible 5 L Raise and cross both arms and hands in front of the chest.
Excavation of the foundation of a crossing. Notice the vertical cut on the side. Think of the final excavation as 27 forming a cup to put the base stone in. Place geotextile fabric over the cut and then place the base stone into the fabric. The fabric should extend to the top of the stone layer on the sides.
Diagram of crossing over
At each crossing we must indicate which section is "over" and which is "under", so as to be able to recreate the original knot. This is often done by creating a break in the strand going underneath. If by following the diagram the knot alternately crosses itself "over" and "under", then the diagram represents a particularly well-studied class ... Nov 9, 2020 — Download this Diagram Of Crossing Over vector illustration now. And search more of iStock's library of royalty-free vector art that features ... The second possibility is that crossing over might take place between b + and v + given eggs of two crossover classes b + v and b v + If a cross is made between fi female and a black-vestigeal male (double recessive) four categories of offspring's will be produced (Fig. 46.4).
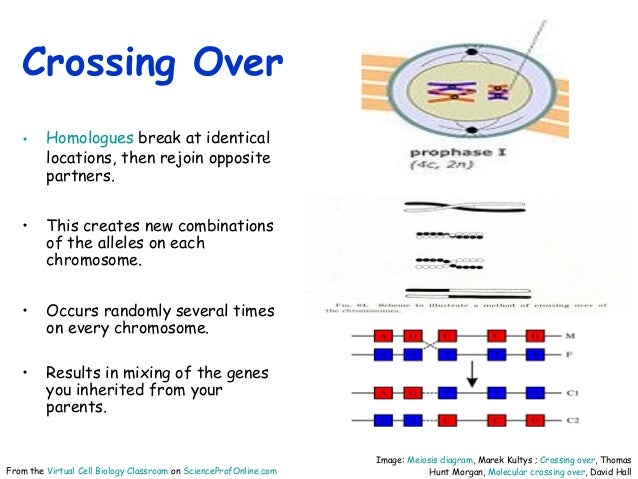
Diagram of crossing over. ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the crossing over of genes, explained with the help of suitable diagrams. The genes remain in linear order along the length of the chromosome and linkage is the physical relationship between the genes. During meiosis a physical crossover between gene pairs (Hi homologous chromosomes occur. According to […] ADVERTISEMENTS: Crossing Over on the Chromosomes: Mechanisms, Kinds, Factors and Significance! Crossing over is the process of exchange of genetic material or segments between non-sister chromatids of two homologous chromosomes. Crossing over occurs due to the interchange of sections of homologous chromosomes. ADVERTISEMENTS: Normally, if independent assortment takes place i.e. when genes are ... The crossing over of homologous chromosomes occurs in prophase I of meiosis. Prophase I of meiosis is characterized by the lining up of homologous chromosomes close together to form a structure known as a tetrad. A tetrad is composed of four chromatids. The diagram used by Morgan et al. to represent crossing over (Fig. 24 in [7]. Comment of the authors: 'At the level where the black and the white rod cross ...
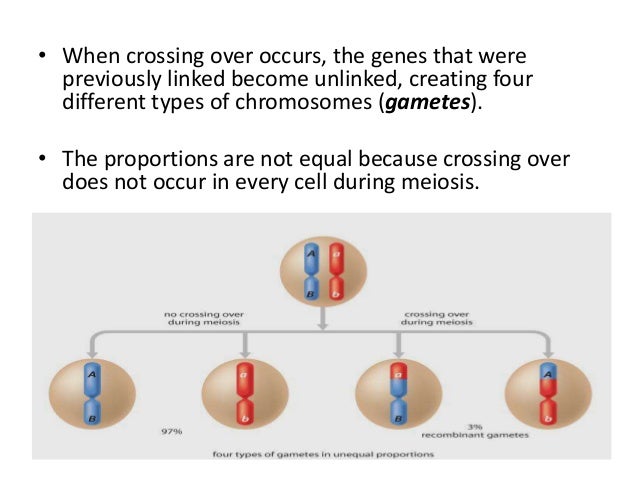
Sep 17, 2020 · Calculating the Component Values for Over Voltage Protection . If we look at the schematic, we have our mains input, which we rectify it with the help of a bridge rectifier, then we put it through a voltage divider which is made with R9, R11, and R10, then we filter it through a 22uF 63V capacitor. Significance of crossing over: 1. Crossing over leads to the production of a new combination of genes. 2. It plays an important role in the process of evolution. 3. The crossing over frequency helps in the construction of genetic maps. 4. It gives us the evidence for a linear arrangement of linked genes in a chromosome. Crossing Over · The homologous chromosomes are held together at points called chiasmata (singular: chiasma) · As a result of this exchange of genetic material, ... Chromosomal crossover, or crossing over, is the exchange of genetic material during sexual reproduction between two homologous chromosomes' non-sister chromatids that results in recombinant chromosomes.It is one of the final phases of genetic recombination, which occurs in the pachytene stage of prophase I of meiosis during a process called synapsis. ...
Display the crossing over diagram. Distribute Crossing over diagrams and markers to students. Instruct students to select two color markers for the assignment and color each of the 2 chromosomes a different color. Allow them to work independently before sharing an example of the color pattern for the 2 chromosomes. Significance of Crossing Over: 1. Crossing over provides direct proof for the linear arrangement of genes. 2. Through crossing over segments of homologous chromosomes are interchanged and hence provide origin of new characters and genetic variations. 3. Crossing over has led to the construction of linkage map or genetic maps of chromosomes. 4. Turn over (c) One way in which meiosis increases genetic variation is through crossing over. (i) The diagram below shows a pair of homologous chromosomes during meiosis. They are positioned next to each other but crossing over has not yet occurred. Complete the diagram below to show these chromosomes after crossing over has occurred. (1 ... Crossing over is the swapping of genetic material that occurs in the germ line. During the formation of egg and sperm cells, also known as meiosis, paired chromosomes from each parent align so that similar DNA sequences from the paired chromosomes cross over one another.
During meiosis, an event known as chromosomal crossing over sometimes occurs as a part of recombination. In this process, a region of one chromosome is ...
The crossing over takes place when the chromosomal threads are plectonemically arranged. Although the somatic crossing over is difficult to detect, there is no doubt that it occurs. The exact mechanism is not yet clears (Fig. 16.6). The somatic crossing over may bring several changes in the structure and physiology of the organisms.
The crossing level is the mean value of a thin vertical histogram window centered on the crossing point of the eye diagram. The eye crossing percentage is then calculated using the following equation: Eye Crossing % = 100 * [(crossing level – zero level)/(one level – zero level)] Eye crossing percentage gives an indication of duty cycle
Draw a diagram to illustrate the formation of new allele combinations as a results of crossing over. As a result of crossing over, chromatids may consist of a combination of DNA derived from both homologues - these are called recombinants (new combinations). The formation of recombinants basically makes the possible allele combinations unlimited.
Avoid lines crossing over each other while creating UML diagrams. This allows your diagrams to be more readable and understandable. If two lines must cross, use a “bridge” to show that the lines do not intersect. Try to make sure all lines go horizontally or vertically and create right angles with each other.
The diagram is missing, however, the name of process writen . already instead of image. Answer: The correct answer is - crossing over. Explanation: The crossing over is the one of the way and other words most important way of genetic recomibanation method.
Crossing over plays a critical role in increasing the genetic variation among offspring of sexual reproduction. It is important to understand how crossing over occurs and its consequences in meiosis. Look carefully at the diagrams depicting different stages in meiosis in a cell where 2n = 6.
Crossing over does not occur uniformly along a chromosome. For example, fewer crossovers occur in the area around the centromere than in other areas of the chromosome (making the loci appear closer together than they actually are). Also, the formation of one chiasma typically makes it less likely that a second chiasma will form in the immediate ...
Genetic crossing over is the process of sperm and egg cells exchanging genetic material during sexual reproduction. Explore the definition and concept of crossing over, and learn about meiosis at ...
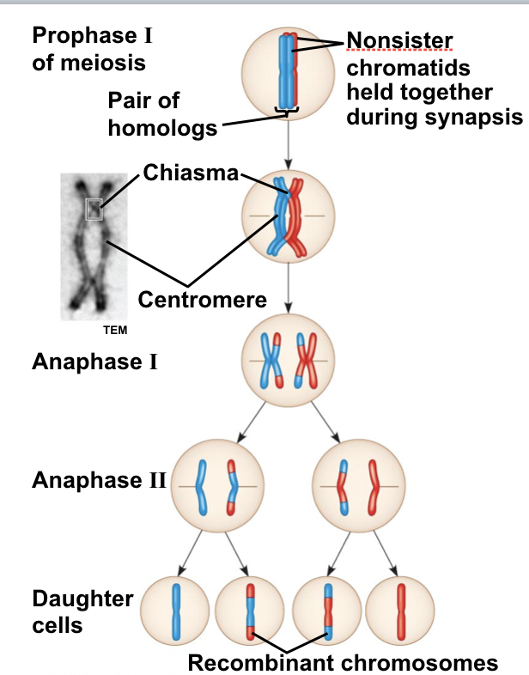
Diagram of crossing-over. Note that while crossing over is shown here, for simplicity, between only one of the two chromatids of each chromosome, each chromatid of each chromosome actually synapses with one of the chromatids of that chromosome's homolog. So crossing-over between both of the synapsed chromatid pairs does occur.
The True Location of the Red Sea Crossing. Exodus 13:17-22, "And it came to pass, when Pharaoh had let the people go that God didn't lead them by the land of the Philistines, although it was the more direct route to Canaan; for He said, 'In case the people become discouraged when they have to fight, and they return to Egypt'.So He led the them by way of the wilderness of the …
♦ Crossing over is simply the exchange of genetic material between two homologous chromosomes to give rise to recombinant chromosomes. In prophase I, homologous chromosomes align lengthwise or pair with each other, and exchange of genetic material between the two chromosomes takes place, which is known as crossing over.
In the diagram below, no crossing over has occurred. Page 9of 14 FORMATION OF NONCROSSOVER ASCI Two homologous chromosomes line up at metaphase I of meiosis. The two chromatids of one chromosome each carry the gene for tan spore color (tn) and the two chromatids of the other chromosome carry the gene
Ncert plus two biology surendran aduthila. Linkage and crossing over 1. LINKAGE AND CROSSING OVER
Some people favor one side over another, while others have a good balance. I’ve spent more than 16 years finding this balance and creating visually stimulating and informative network diagrams. In order to make quality maps, we’ll need to tap both sides to create informative, but visually appealing diagrams that everyone will want a copy of!
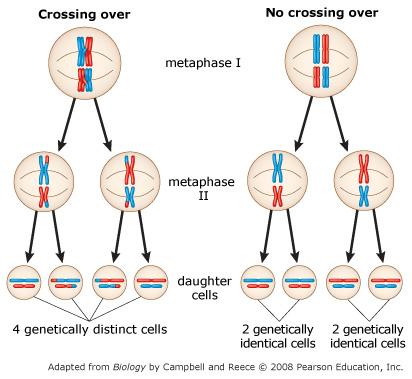
crossing over results in greater genetic variation. Tags: Question 9 . SURVEY . 30 seconds . Q. Fruit flies have 8 chromosomes in their somatic cells. The diagram below shows the results of meiosis and fertilization in fruit flies. After meiosis is complete, how many chromosomes will be in the sperm cell?
The diagram below represents a change in composition of homologous chromosomes during synapsis? (Look at quiz) Tetrads. ... Which statement best describes the process of crossing-over? It takes place between homologous chromosomes and results in new gene combinations. The formation of a tetrad during meiosis occurs as a result of.
Diagram 1. Label the side that is mitosis and meiosis. 2. Draw an arrow indicate DNA replication (S-stage). Label the place where crossing over occurs. On mitosis: label metaphase anaphase and cytokinesis. 5. Diagram 1. Label the side that is mitosis and meiosis. 2. Draw an arrow indicate DNA replication (S-stage). 3.
May 30, 2021 · Mitosis- definition, purpose, stages, application, diagram. Interphase, Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis
Crossing Over Definition. Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis, which results in new allelic combinations in the daughter cells.Each diploid cell contains two copies of every chromosome, one derived from the maternal gamete and the other from the paternal gamete. These pairs of chromosomes, each derived from ...
For crossing wires that are insulated from one another, a small semi-circle symbol is commonly used to show one wire "jumping over" the other wire (similar to how jumper wires are used). A common, hybrid style of drawing combines the T-junction crossovers with "dot" connections and the wire "jump" semi-circle symbols for insulated crossings.
Importance of crossing over is given below: (a) Crossing over provides direct evidence that the genes are arranged in a liner fashion on the chromosome. (b) Crossing over helps in the tracing of linkage groups. (c) In the construction of gene map helped by the percentage of crossing over. (d) As variation is an essential feature of evolution ...
Use the diagram to the right as a guide You now have a tetrad formed during prophase I of meiosis. First, assuming that no crossing over takes place. 3. Model the appearance of the four gamete cells that will result ... Crossing over is responsible for some of the variation seen in offspring produced by sexual reproduction. Explain what this means.
The Campbell diagram is an overall or bird's-eye view of regional vibration excitation that can occur on an operating system. The Campbell diagram can be generated from machine design criteria or from machine operating data. A typical Campbell diagram plot is shown in Figure 5-25.Engine rotational speed is along the X axis. The system frequency is along the Y axis.
Diagram of crossing-over. Note that while crossing over is shown here, for simplicity, between only one of the two chromatids of each chromosome, each.The official website of Science Olympiad, one of the largest K STEM organizations in the US. Find the latest info on events + competitive tournaments here. Start studying Prophase Diagram.
The second possibility is that crossing over might take place between b + and v + given eggs of two crossover classes b + v and b v + If a cross is made between fi female and a black-vestigeal male (double recessive) four categories of offspring's will be produced (Fig. 46.4).
Nov 9, 2020 — Download this Diagram Of Crossing Over vector illustration now. And search more of iStock's library of royalty-free vector art that features ...
At each crossing we must indicate which section is "over" and which is "under", so as to be able to recreate the original knot. This is often done by creating a break in the strand going underneath. If by following the diagram the knot alternately crosses itself "over" and "under", then the diagram represents a particularly well-studied class ...











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1048828128-157a76170f1e4ca8841bf66f0cc042e6.jpg)












0 Response to "40 diagram of crossing over"
Post a Comment