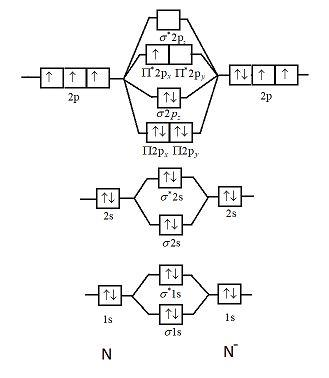
41 n22- molecular orbital diagram
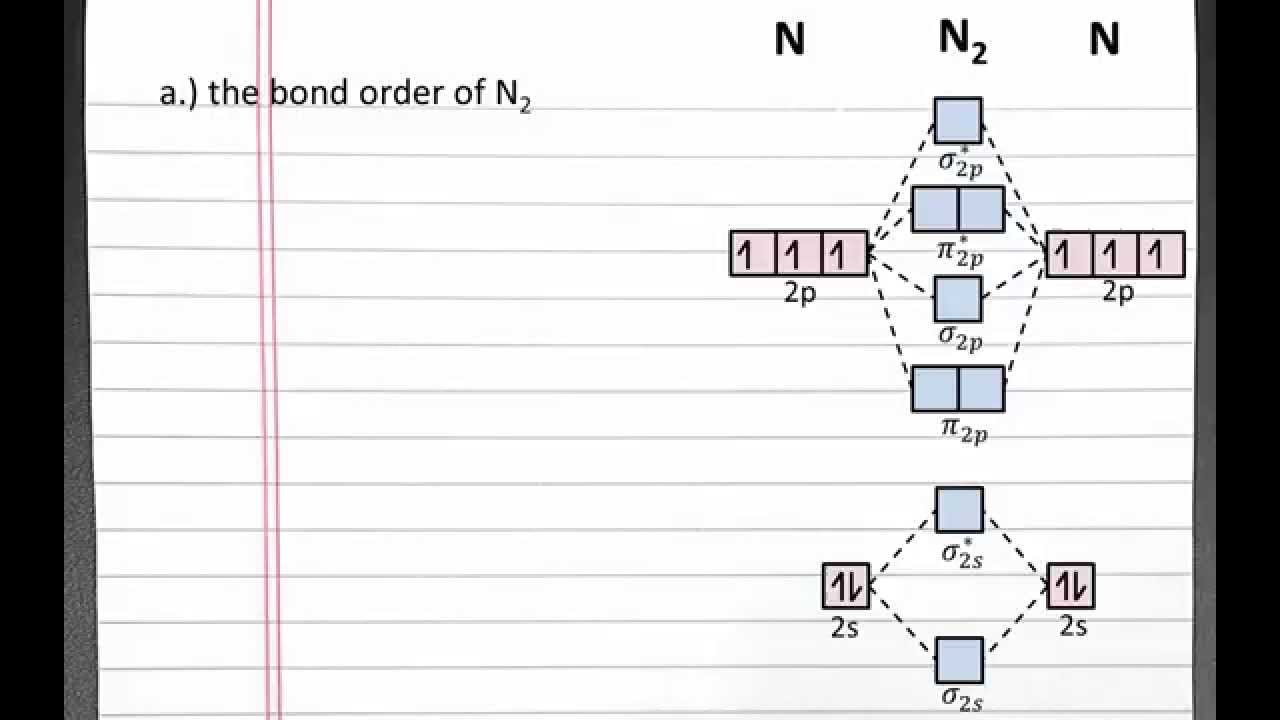
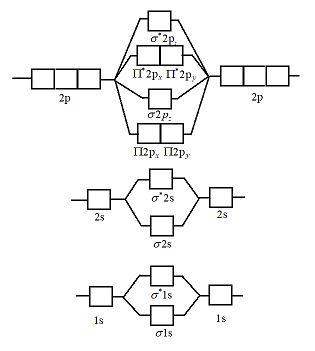
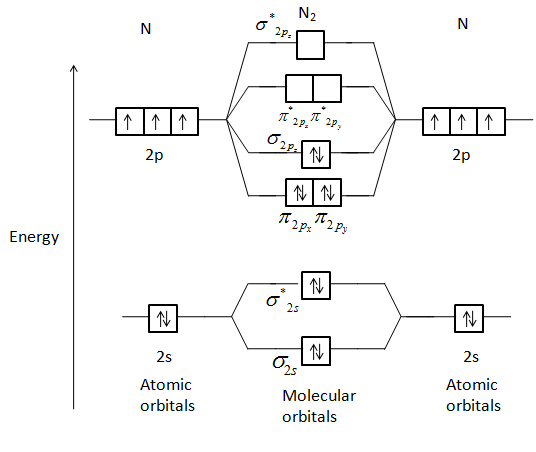
Molecular orbital diagram of N 2 BO = [Nb-Na] = [10-4] = 3 Since all the electrons in nitrogen are paired, it is diamagnetic molecule. Answered by | 13th Jun, 2016, 04:45: PM. Concept Videos. Molecular Orbital Theory - Part 1.
N22+ B22+ B B2 CeV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of the lowest energy molecular orbital with respect to the 3s orbital of sulfur. This lowest energy orbital is .
Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ...
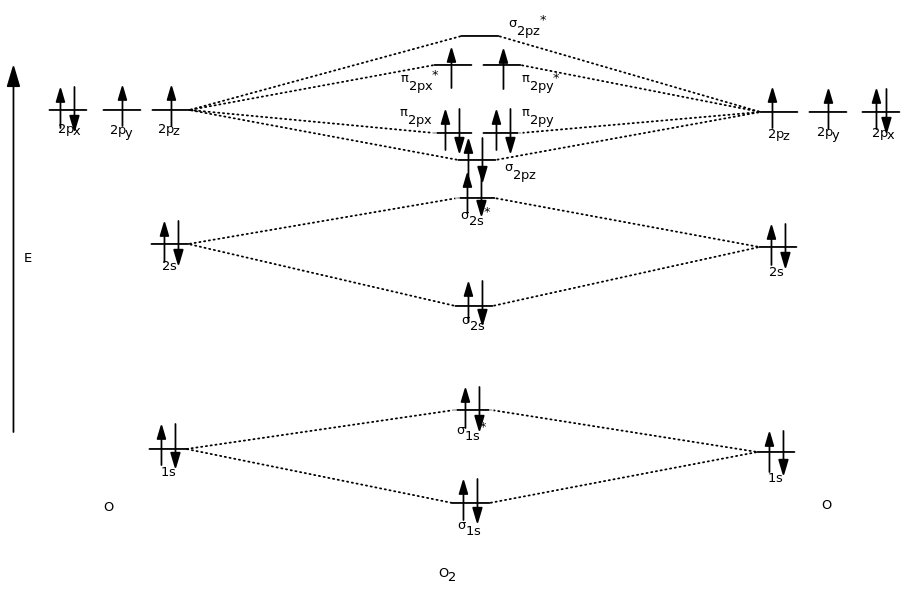
N22- molecular orbital diagram
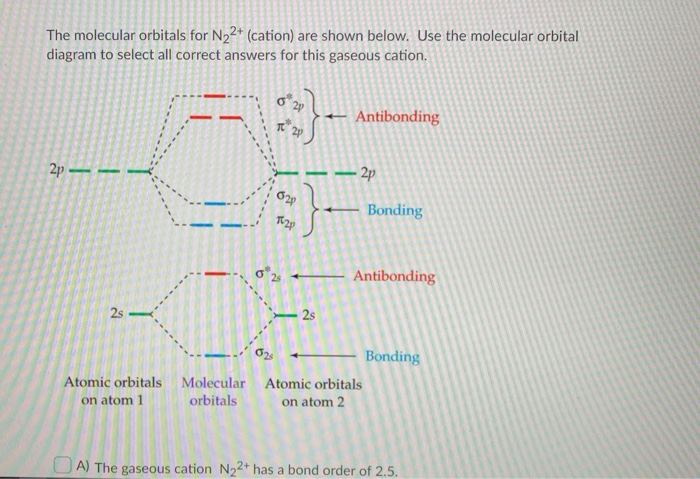
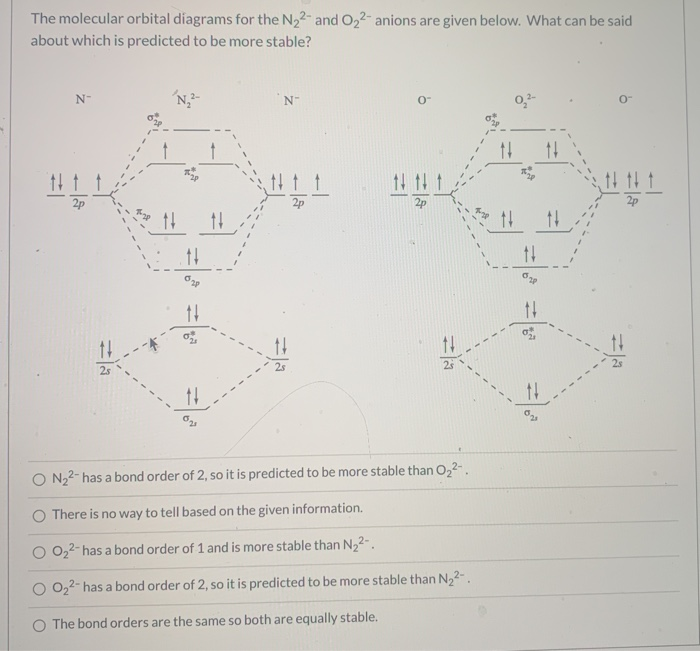
The molecular orbital diagrams for the N22-and 0,2- anions are given below. What can be said about which is predicted to be more stable? N- N, 2- N- 0- 0" + 11 11 * 14 11 2p 2th 1 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 25 11 O The bond orders are the same so both are equally stable. O 022-has a bond order of 1 and is more stable than N2+.
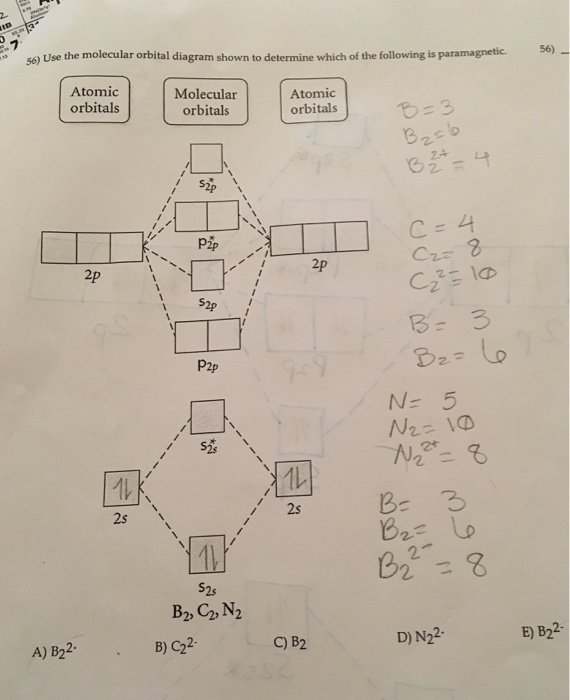
Sign In to Writing (Essays) Science. Chemistry Q&A Library Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B22+, B2, C22-, B22-, and N22+. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B22+, B2, C22-, B22-, and N22+. Start your trial now!
Hint: First draw a molecular orbital diagram (MOT) where the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The total electrons associated with the molecules are filled in the MOT diagram. To solve this question, we need to write the molecular orbital configuration. To find out the bond order from the molecular orbital configuration is:
N22- molecular orbital diagram.
the pi(2p) bonding orbitals are LOWER than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals.N2(2-) has a bonding order of 2, which predicts that there will be a stable double ...
C o22 use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. Molecular orbital diagram. Periodic trends determine. A n22 b b2 c b22 d c22 e c22. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. Molecular Orbital Theory
The molecular orbital diagram for H2+ is given in Fig 30. Fig 30 Molecular Orbital Diagram For H2+ ion. The Bond Order for H2+ ion can be calculated as given below : Bond Order = ½ [Nb Na] = ½ [1 0 ] = ½ Since there is an unpaired electron in H2+ion so that it is expected to be paramagnetic. This fact has been confirmed experimentally.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic.Answer options:B2B22+N22+C22-B22-Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic.Answer options:B2B22+N22+C22-B22-
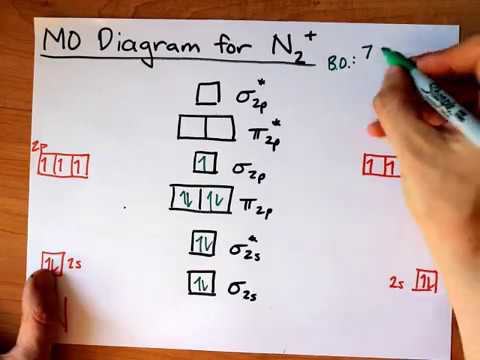
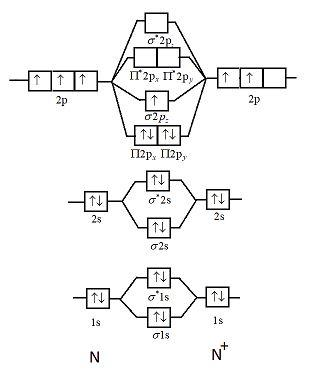
N 2+ ion is formed by the loss of one electron from the N 2 molecule. This lost electron will be lost from σ (2p z) orbital. Hence, the electronic configuration of N 2+ ion will be N 2+ = KK [σ (2s)] 2 [σ* (2s)] 2 [π (2p x )] 2 [π (2p y )] 2 [σ (2p z )] 1 Here, N b =7, N a =2 so that
This picture shows the molecular orbital diagram of N 2 + . Orbitals represented by ∗ are antibonding orbitals and the orbitals without ∗ are bonding orbitals. Bond order can be calculated by the formula: Bond order = bonding electrons - antibonding electrons 2
1. The electron-pair and molecular geometries are tetrahedral. The C atom is sp3 hybridized. Three of these hybrid orbitals each overlap with a chlorine 3p orbital to form three C—Cl sigma bonds. One hybrid orbital overlaps with a hydrogen 1s orbital to from a C—H sigma bond. 2. Answers: (a) BBr 3 trigonal planar trigonal planar sp2 (b) CO
Which statement is true? a. The total number of molecular orbitals formed doesn't always equal the number of atomic orbitals in the set. b. When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular orbital will be higher in energy than the separate atomic orbitals.
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
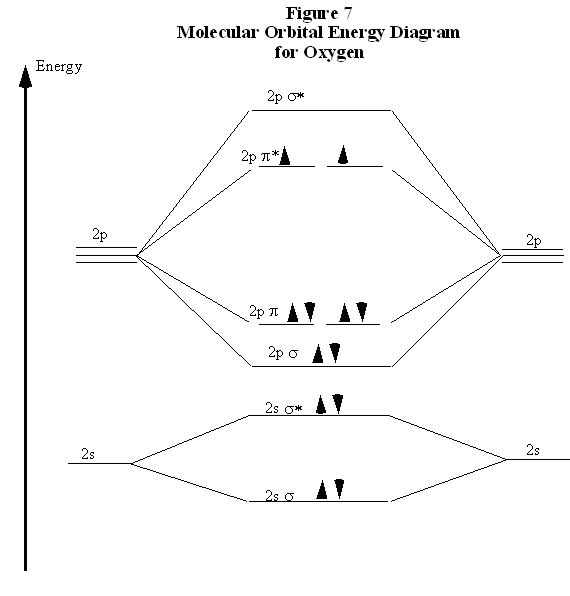
The bond length in the oxygen species can be explained by the positions of the electrons in molecular orbital theory. To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for O 2, we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure 9.10.1 . We again fill the orbitals according to Hund's rules ...
Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons . Number of electrons present in the bonding orbitals is represented by N b and the number of electrons present in antibonding orbitals by Na.. 1) If N b > Na,the molecule is stable because greater number of bonding orbitals are occupied than ...
Use molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which is most stable a o22 bf2 c f22 d f22 e ne22 a. A asdfasdf b asdfasdf c asdf d f2 2 e none of the above are paramagnetic. Label each and each and every molecular orbital with its call sigma pi and position the accessible electrons interior the perfect atomic orbitals and molecular orbitals.
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start...
If we build the MO diagram for "N"_2, it looks like this: First though, notice that the p orbitals are supposed to be degenerate. They weren't drawn that way on this diagram, but they should be. Anyways, for the electron configurations, you would use a notation like the above. g means "gerade", or even symmetry upon inversion, and u means "ungerade", or odd symmetry upon inversion.
molecular orbital diagram for F2. number of elections in the sigma*2p molecular orbital is. 0. the total numbers of electrons in the pi2p molecular orbital of B2 is. 2. the total numbers of electrons in the pi*2p molecular orbitals of F2 is. 4. what is the bond order for B2. 1.
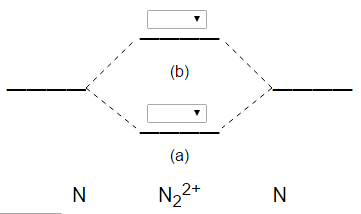
Answer to: Given N22-, using molecular orbital and valence bond theory: a) Write the molecular orbital configuration. b) Determine the bond order....
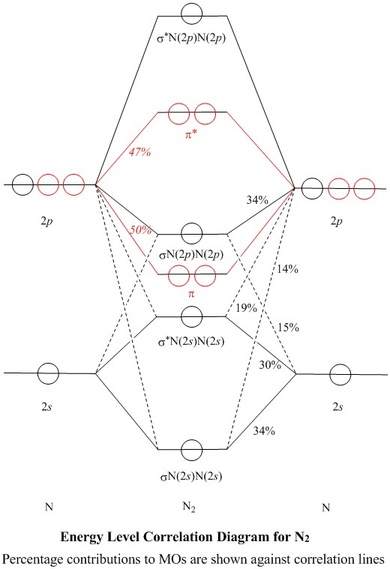
N2 2- Molecular orbital Diagram. molecular orbital mo diagram of n2 molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas n2 use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you sigma2s 2 sigma2s 2 pi2p 4 mo diagram for n2 molecular orbital there are two mo diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms n2 o2 ne2 etc e is for the elements up to nitrogen the other is for after
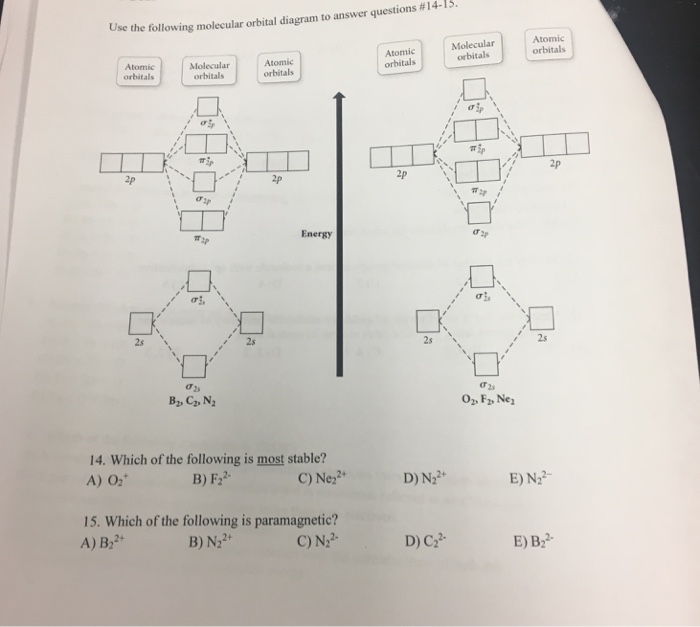
Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.A) N22+ B) B2C) B22+D) C22-E) C22+ FREE Expert Solution Show answer Answer:
How to Make the Molecular Orbital Diagram for B2- (Bond Order, Paramagnetic or Diamagnetic). Principia. Principia. 1 answerThe MO diagram of the NF molecule can be drawn as below. The energies of the atomic orbital of N and F are different. The atomic orbital s of F are.... 1918 (Venn's diagram is from 1904), named for English logician John Venn (1834-1923) of Cambridge, who explained them in ...
Bond Order: Bond order is a measurement of electrons that participate in bond formation. It shows a chemical bond is stable. If the value of a bond order is high, the atom contains a strong bond.
Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ...
Show activity on this post. I have been taught that the MO diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. For N X 2 the orbitals in increasing energy are: σ 1 s < σ 1 s ∗ < σ 2 s < σ 2 s ∗ < π 2 p x, π 2 p y < σ 2 p z < π 2 p x ∗, π 2 p y ∗ < σ 2 p z ∗ ...
Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.a. F22+b. Ne22+c. F22-d. O22+e. F2 FREE Expert Solution Recall that the bond order t ells us the strength and length of a bond: a higher bond order means the bond is stronger and shorter.








![Solved] Using Figures 9.35 and 9.43 as guides, draw the ...](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.question.images/image/images11/876-(557)-1.png)



![Best Answer] draw the molecular orbital diagram of N2 and ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d20/b492acf8cb9ff01954c3929a3b7a93c7.jpg)








0 Response to "41 n22- molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment