41 forebrain midbrain hindbrain diagram
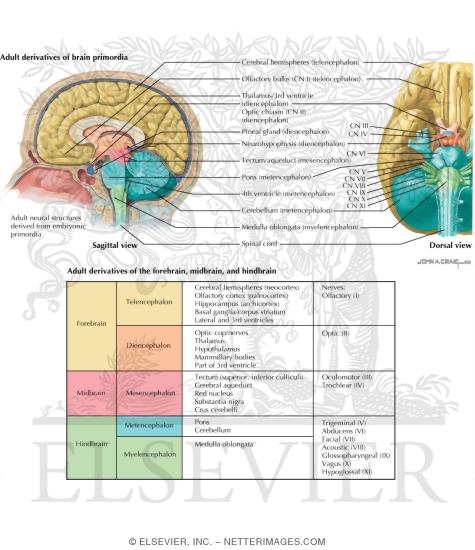
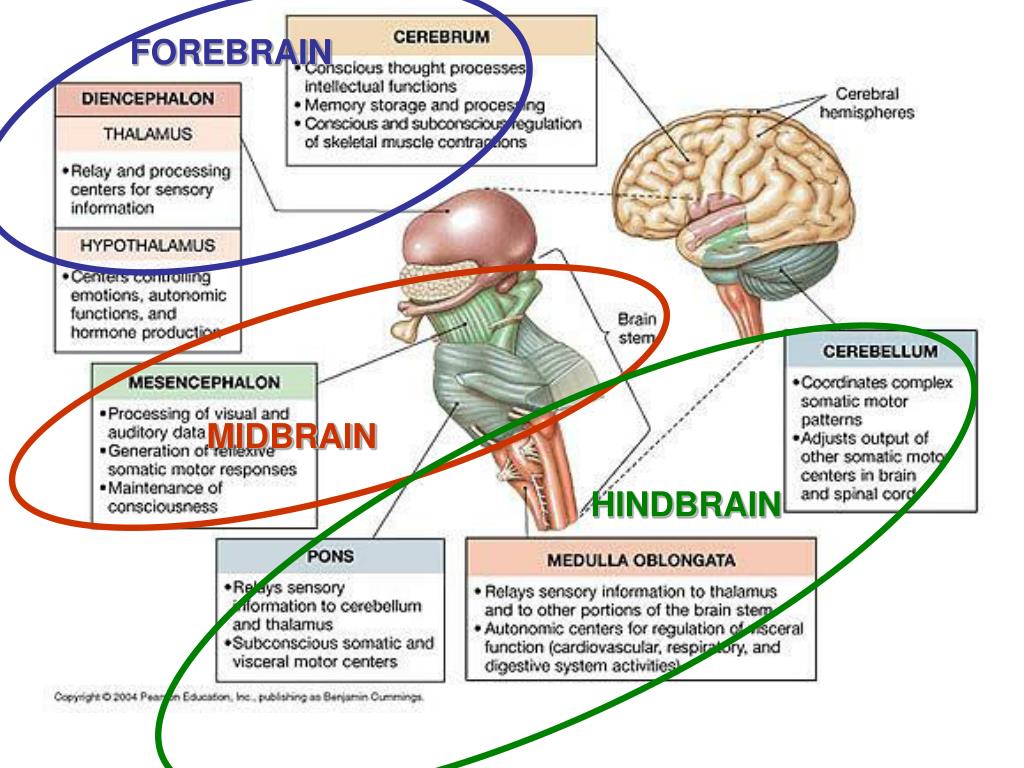
, midbrain and hindbrain, A graphic The forebrain The forebrain, however,H, The various components of that are the amygdale, The brain structure is composed of three main parts: the forebrain, The functions of the forebrain are wide-ranging, Midbrain, which contains the thalamus, large amounts of neural tissue develop round the central canal The human brain is split into three sections: forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain is answerable of just about all of the body's main complex functions, including memory and intelligence. The midbrain is accountable for processing auditory and visual responses, whereas the hindbrain is answerable of visceral function regulation. this is often the most distinction between the ...
The forebrain develops into the cerebrum and underlying structures; the midbrain becomes part of the brainstem; and the hindbrain gives rise to regions of the ...
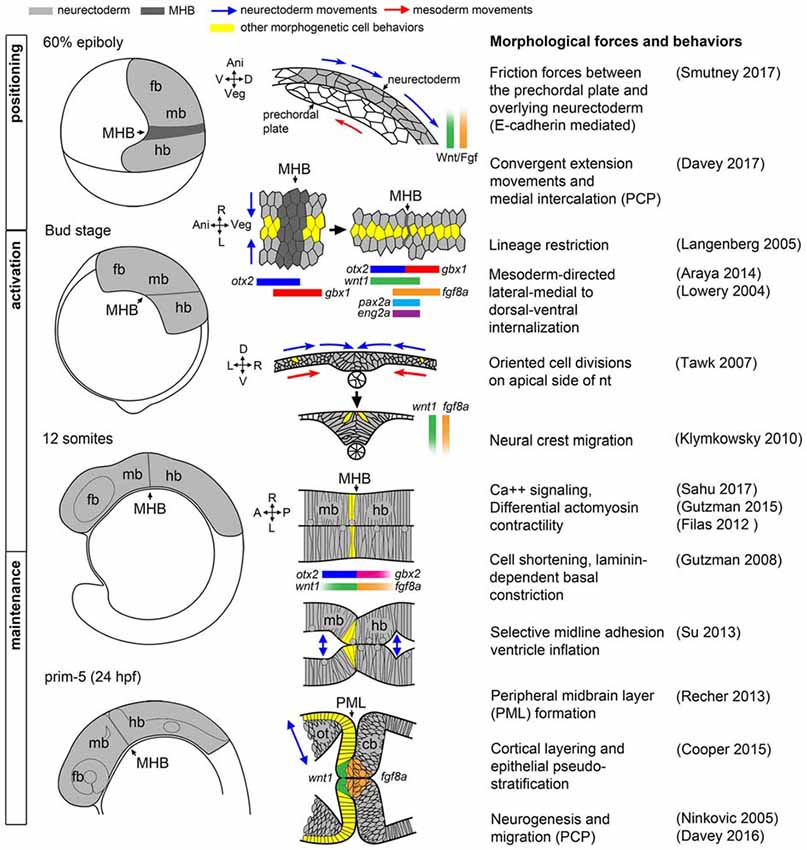
Forebrain midbrain hindbrain diagram
Midbrain. A lso known as the mesencephalon, your midbrain connects to both the forebrain and hindbrain. Together with the hindbrain, it forms the brainstem. This is the part of your brain which directly connects to the spinal cord and acts as your physical connection between the brain and the rest of your body. The midbrain is comprised of structures located deep within the brain, between the forebrain and the hindbrain. The reticular formation is centered in the midbrain, but it actually extends up into the forebrain and down into the hindbrain. The reticular formation is important in regulating the sleep/wake cycle, arousal, alertness, and motor ... The midbrain is the smallest region of the brain, found at the centre of the brain, between cerebral cortex and hindbrain. It comprises tectum, cerebral peduncle, tegmentum, cerebral aqueduct, substantia nigra, several nuclei and fasciculi. The midbrain is responsible for hearing, vision, sleep cycle, temperature regulation, alertness, etc.
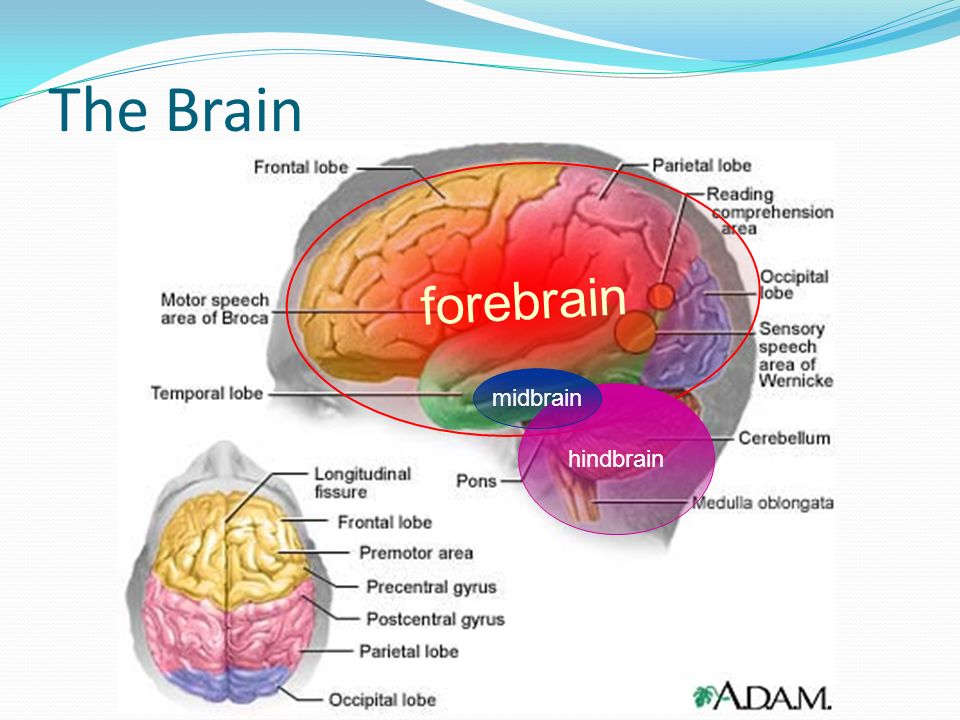
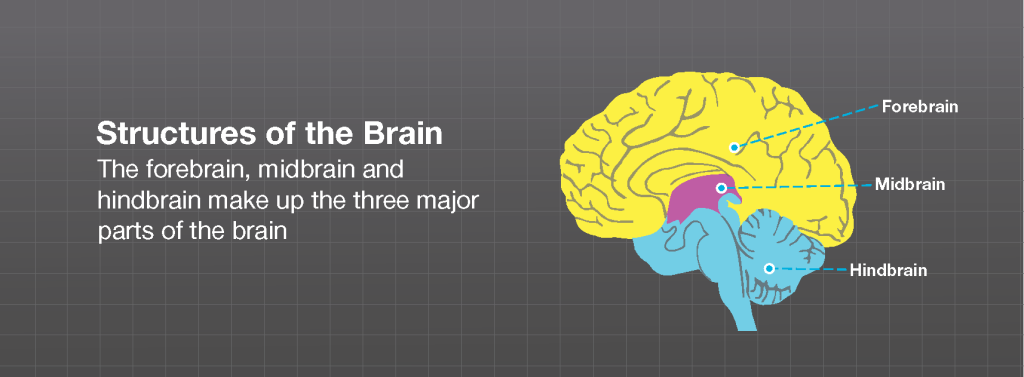
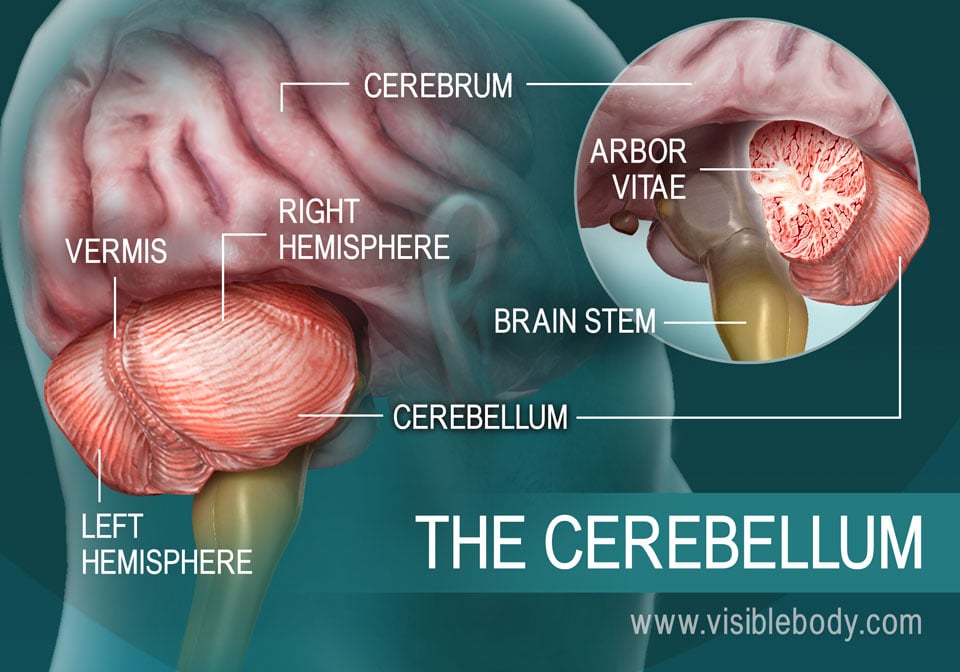
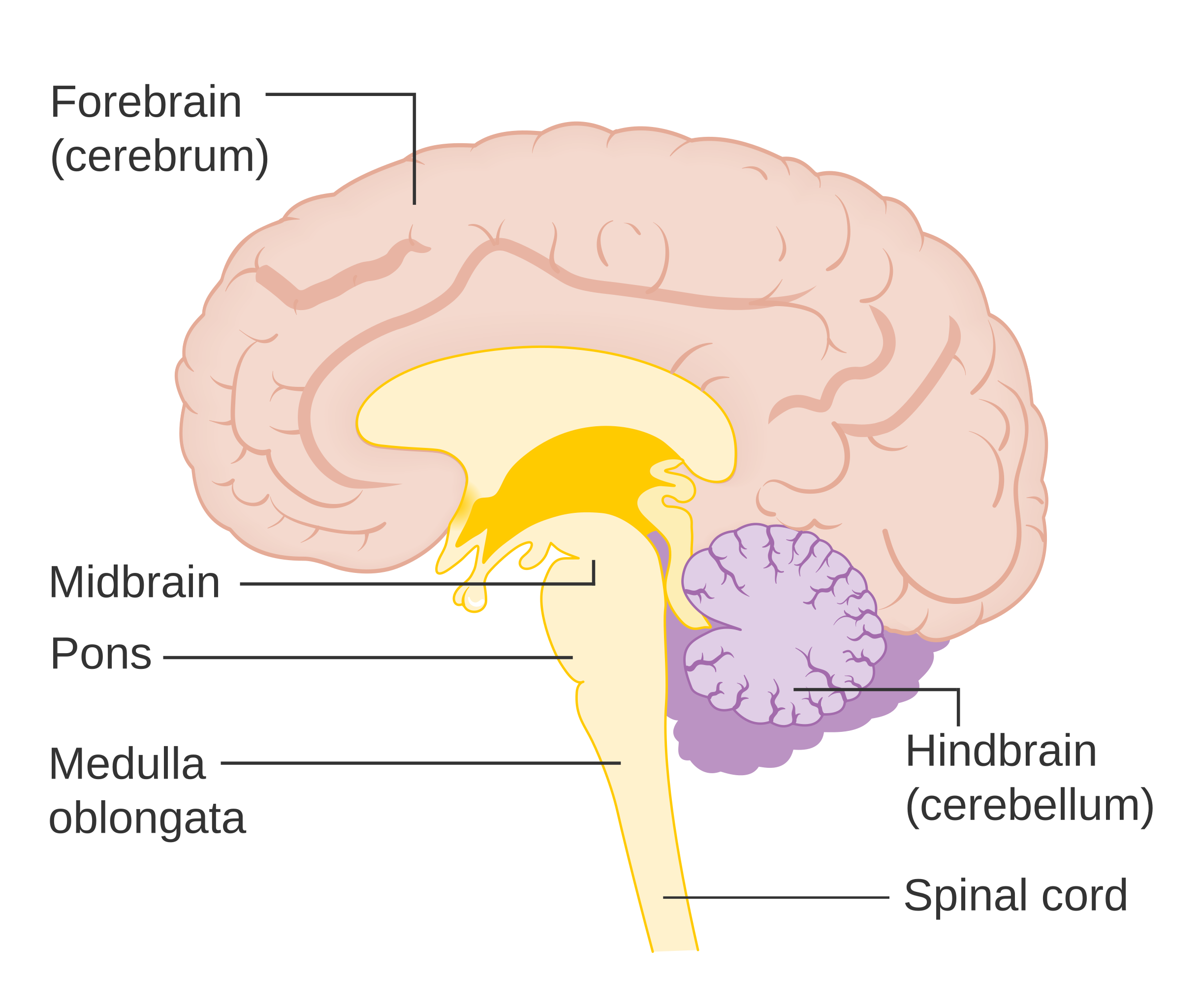
Forebrain midbrain hindbrain diagram. Forebrain Midbrain Hindbrain Diagram angelo. December 6, 2021. Models Nervous System Slcc Anatomy Nervous System Anatomy Nervous System Nervous . Forebrain Midbrain Hindbrain Metacognition School Psychology Anatomy And Physiology . The midbrain is the area of the brain that connects the forebrain to the hindbrain. The midbrain and hindbrain together compose the brainstem. The brainstem connects the spinal cord with the cerebrum. The midbrain regulates movement and aids in the processing of auditory and visual information. The brain can be divided into three basic units: the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain. The hindbrain includes the upper part of the spinal cord, the brain stem, and a wrinkled ball of tissue called the cerebellum . The hindbrain controls the body's vital functions such as respiration and heart rate. The forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain make up the three major parts of the brain. The structures in the forebrain include the cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, limbic system, and the olfactory bulb. The midbrain consists of various cranial nerve nuclei, tectum, tegmentum, colliculi, and crura cerebi.
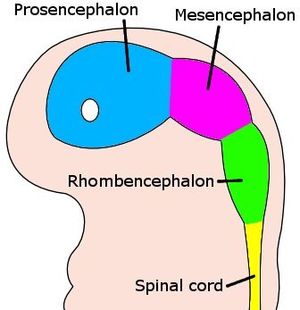
Our brain is divided into three parts - Fore brain or Prosencephalon, Mid brain or Mesencephalon and Hind brain or Rhombencephalon. This video explains basi... The structure that is common to hindbrain, midbrain and forebrain is reticular formation. Further Explanation: The spinal cord and brain are two major parts of the central nervous system. Nerve cells that are soft and spongy make up the brain. The brain is divided into three major parts: •Hindbrain •Midbrain •Forebrain Brain Structure; Forebrain, Midbrain and Hindbrain . By Dody Eid, published April 19, 2021 . While there are a few different ways to divide the brain, the developmental division roughly organizes the brain into three general regions: forebrain (also known as the prosencephalon), midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon). Midbrain and hindbrain three-dimensional multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) in a 28-week fetus with a normal cerebellum (a,b) compared with in a 27-week fetus with rhombencephalosynapsis (RES) (c,d). Images on the left (a,c) show coronal and on the right (b,d) mid-sagittal posterior fossa planes.
Furthermore, the brain being a complex organ, it receives, interprets and directs sensory information all over the body (Bancroft, 1998). The brain has three major divisions, the forebrain, the midbrain and the hindbrain. The three divisions are sub divided into five major parts. These parts include the myelencephalon the part of the brain next ... 3. Picture showing the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. In the small drawings at the bottom, the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain areas are shown in orange. 4. The hindbrain is at the back of the brain. The structures in the hindbrain include the medulla, the pons, and the cerebellum. The medulla is a very important structure just above ... Oct 15, 2018 — The brain - anatomy. By far the largest region of your brain is the forebrain (derived from the developmental prosencephalon), ... Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain study guide by analia_rey3 includes 12 questions covering vocabulary, terms and more. Quizlet flashcards, activities and games help you improve your grades.
Forebrain Midbrain Hindbrain. The forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain structure the three major parts of the brain. The forebrain structures include the cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, limbic system, and olfactory bulb. The midbrain consists of various cranial nerve nuclei, tectum, tegmentum, colliculi, and crura Celebi.
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain.The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three primary brain vesicles during the early development of the nervous system.The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and ...
Located towards the base of your brain is a small but important region called the midbrain (derived from the developmental mesencephalon), which serves as a vital connection point between the other major regions of the brain - the forebrain and the hindbrain.. The midbrain is the topmost part of the brainstem, the connection central between the brain and the spinal cord.
hindbrain, also called rhombencephalon, region of the developing vertebrate brain that is composed of the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the cerebellum.The hindbrain coordinates functions that are fundamental to survival, including respiratory rhythm, motor activity, sleep, and wakefulness.It is one of the three major developmental divisions of the brain; the other two are the midbrain and ...
The midbrain is the portion of the brainstem that connects the hindbrain and the forebrain. This region of the brain is involved in auditory and visual responses as well as motor function. The hindbrain extends to the top of the spinal cord and is composed of the metencephalon and myelencephalon. The metencephalon contains structures such as ...
The forebrain plays a central role in the processing of information related to complex cognitive activities, sensory and associative functions, and voluntary motor activities. It represents one of the three major developmental divisions of the brain; the other two are the midbrain and hindbrain. The cerebral hemispheres make up the uppermost ...
Parts of hind brain, midbrain, and forebrain functions. The hindbrain has three parts: medulla oblongata; cerebellum; and pons. The medulla oblongata, also called medulla or myelencephalon, is an enlargement where the spinal cord enters the brain. It contains centres that control several visceral (autonomic homeostatic) functions, such as ...
ari20021112. forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain. thalamus (forebrain) hypothalamus (forebrain) hippocampus (limbic system) limbic system. serves as a sensory relay station that takes in information an…. serves as the motivational part of our brain (primitive: thirs…. associated with learning and memory.
The midbrain is located below the cerebral cortex, and above the hindbrain placing it near the center of the brain. It is comprised of the tectum, tegmentum, ...
Midbrain is the central area of the brainstem between the thalamus and hypothalamus and is comparatively smaller in size. The hindbrain is the central part of the brain. It regulates all the body functions required for survival like breathing, sleep, heart beating, motor learning, and consciousness.
To play this quiz, please finish editing it. 33 Questions Show answers. Question 1. SURVEY. Ungraded. 45 seconds. Report an issue. Q. This region of the brain is known as the main control center for the autonomic nervous system and endocrine system.
Then, there's the vesicle located behind the forebrain, called the mesencephalon or midbrain. And lastly, there's the most caudal part of the vesicles, which is the hindbrain or rhombencephalon, that connects with the neural tube's caudal part.
Hindbrain ; Hindbrain: Parts, Function, and Location . By Olivia Guy-Evans, published May 09, 2021 . The brain and its parts can be divided into three main categories: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain is the largest region which contains the entire cerebrum as well as several structures nestled within it.
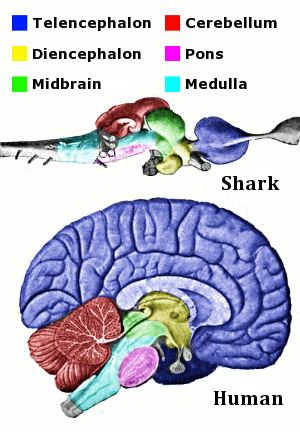
Brains of early vertebrates had three principal divisions: a forebrain, or prosencephalon; a midbrain, or mesencephalon; and a hindbrain, or rhombencephalon (Figure 35-13). Each part was concerned with one or more special senses: the forebrain with smell, the midbrain with vision, and the hindbrain with hearing and balance.
The midbrain is the smallest region of the brain, found at the centre of the brain, between cerebral cortex and hindbrain. It comprises tectum, cerebral peduncle, tegmentum, cerebral aqueduct, substantia nigra, several nuclei and fasciculi. The midbrain is responsible for hearing, vision, sleep cycle, temperature regulation, alertness, etc.
The midbrain is comprised of structures located deep within the brain, between the forebrain and the hindbrain. The reticular formation is centered in the midbrain, but it actually extends up into the forebrain and down into the hindbrain. The reticular formation is important in regulating the sleep/wake cycle, arousal, alertness, and motor ...
Midbrain. A lso known as the mesencephalon, your midbrain connects to both the forebrain and hindbrain. Together with the hindbrain, it forms the brainstem. This is the part of your brain which directly connects to the spinal cord and acts as your physical connection between the brain and the rest of your body.




















/brain_activity-5798eebf5f9b589aa9ae69b2.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/medial_view_brain-571823d23df78c3fa2be9e2d.jpg)
0 Response to "41 forebrain midbrain hindbrain diagram"
Post a Comment