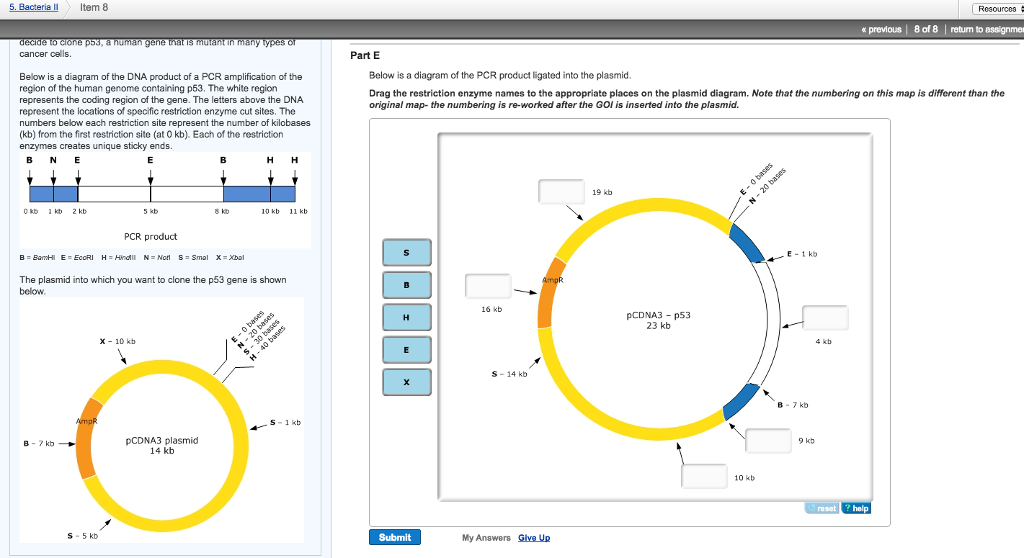
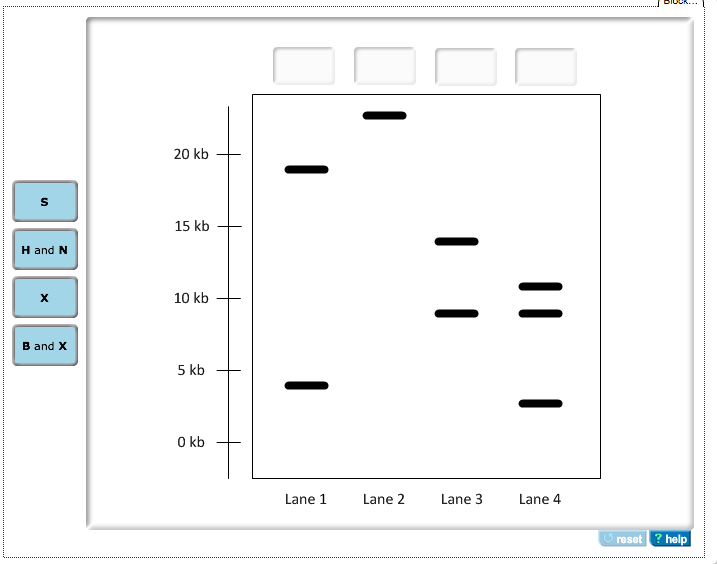
41 below is a diagram of the pcr product ligated into the plasmid.
by VK Chaudhary · 2014 · Cited by 12 — Therefore, only ligation of an insert carrying compatible ends allows directional cloning of the insert to the vector to generate a ... substrate called X-gal and cleave the β-1,6 linkage to form a product that is bright blue. For each of the following sequences found on pBlue, list the step or steps (1-7 above) for which that sequence is ... you decide to use Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) to amplify the psy2 coding sequence based on the flanking ... PCR fragment into vector ...
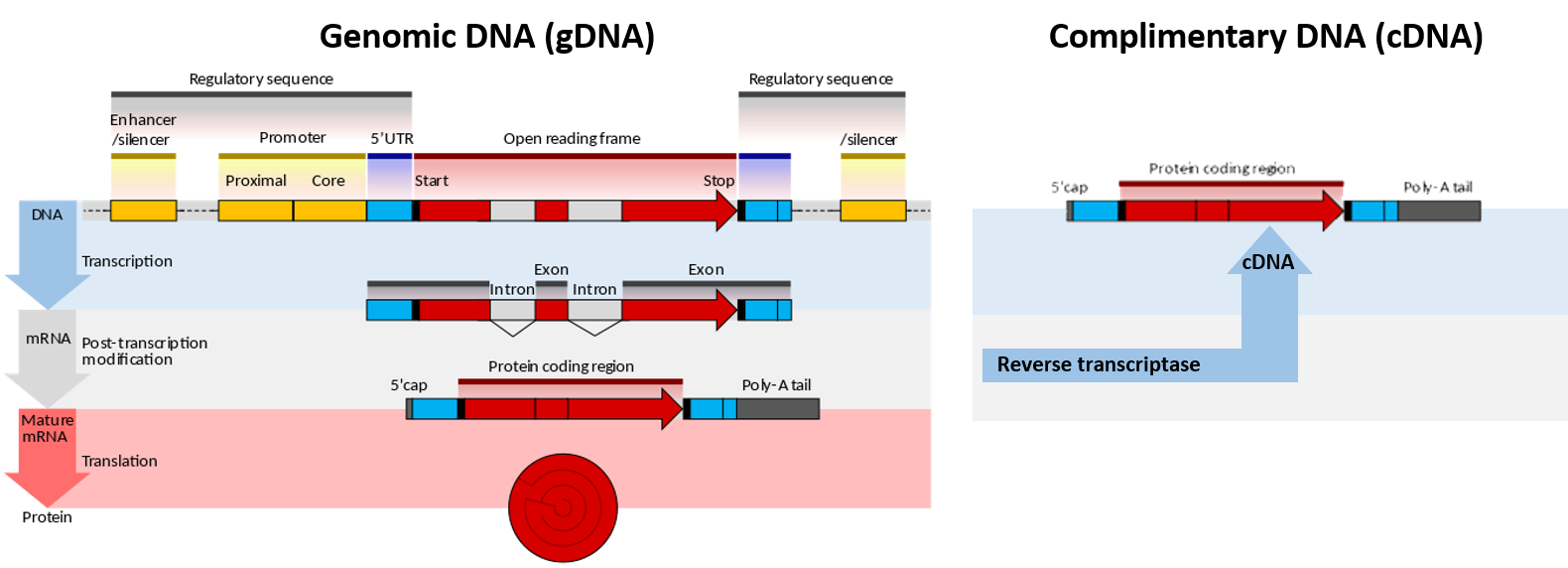
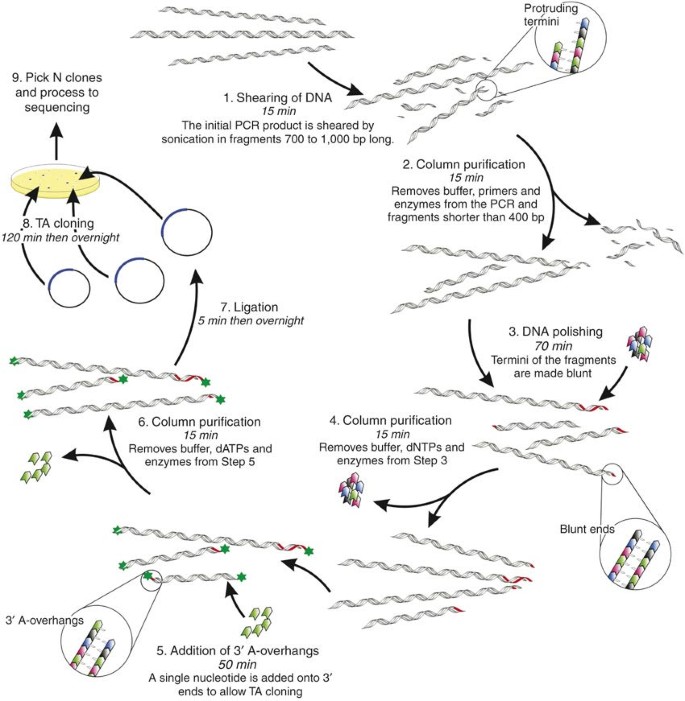
Figure 7.04. TA Cloning. When Taq polymerase amplifies a piece of DNA during PCR, the terminal transferase activity of Taq adds an extra adenine at the 3′ end of the PCR product. The TA cloning vector was designed so that when linearized it has single 5′ thymidine overhangs at each end. The PCR product can be ligated into this vector without the need for special restriction enzyme sites.
Below is a diagram of the pcr product ligated into the plasmid.
(bp) in length for best results. Below is a typical workflow for cloning and sequencing a gene. The steps that the Ligation and Transformation module ... † Ligation of PCR product into pJet1.2 plasmid † Transform ligated plasmid into bacteria ... to the size of the PCR fragment ligated into the plasmid. Finally, the DNA To clone your gene of interest into pCR ® 2.1, you must first generate a PCR product. The PCR product is ligated into pCR ® 2.1 and transformed into competent cells. Since the PCR product can ligate into the vector in either orientation, individual recombinant plasmids need to be analyzed to confirm proper orientation. When PCR was in its infancy, researchers found that subcloning PCR products by simple blunt-ended ligation into blunt-ended plasmid cloning vectors was not easy. Part of the challenge is thermostable DNA polymerases, like Taq DNA polymerase, add a single nucleotide base extension to the 3´ end of blunt DNA in a template-independent fashion ...
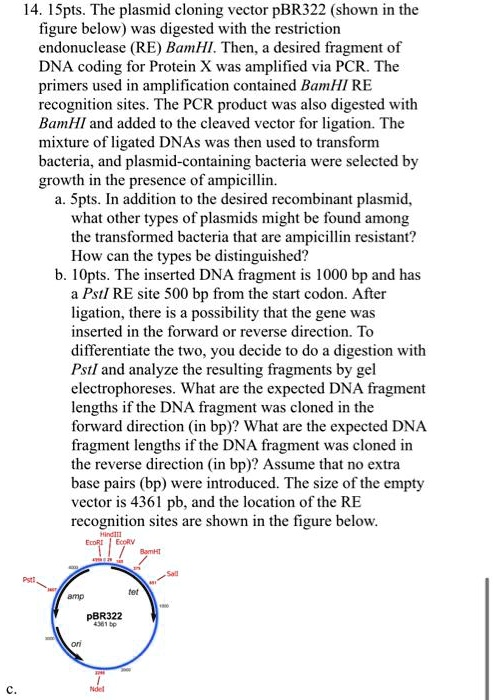
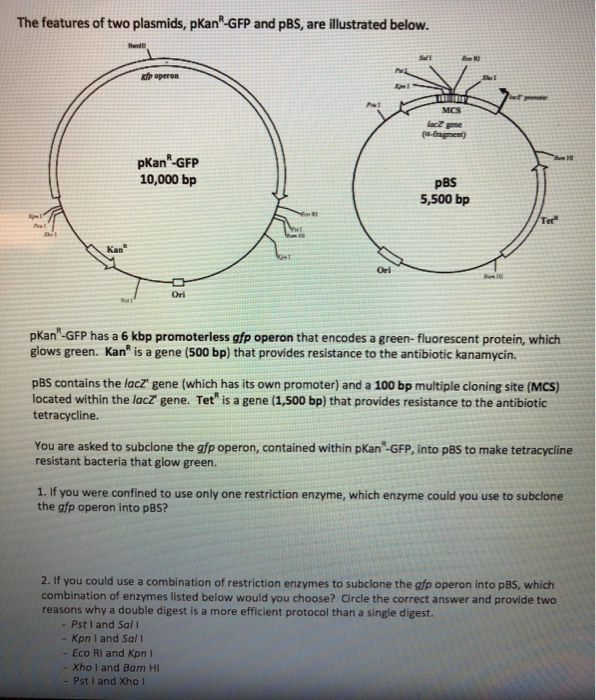
Below is a diagram of the pcr product ligated into the plasmid.. Shown below is a diagram for a plasmid vector you want to use to clone a gene. The diagram shows the location of the recognition sites for four restrictions enzymes, BamHI (B), EcoRI (E), HindIII (H), and XhoI (X). ligase. enzyme that joins the cut gene and the cut plasmid. DNA ligation. a phosphodiester bond is created between the 3 prime hydroxyl of one nucleotide and the 5 prime phosphate of the next nucleotide. if ligation works the way we want it to. only our gene will ligate with the cut plasmid. Drag the restriction enzyme names to the appropriate places on the plasmid diagram. This problem has been solved! See the answer ... 3. Explain why plasmid vectors are sometimes 5'-dephosphorylated before ligation. 4. If a plasmid vector is dephosphorylated, explain how a DNA fragment can be ligated into it, since it does not have the 5' phosphates that the ligase must recognize to form the phosphodiester bond. 5.
The diagram below shows a section of human DNA that contains an imaginary gene for video game proficiency (the vgp gene), shown in red. ... Below is a diagram of the PCR product ligated into the plasmid. Drag the restriction enzyme names to the appropriate places on the plasmid diagram. 16Kb- B 19Kb- X 4Kb- E 9Kb- H 01/03/2017 · The other cloning strategy though less extensively used is directional cloning where restriction endonuclease susceptible sites are intentionally included in PCR primers and after the digestion of PCR product, it is ligated into the desired vector digested with same endonucleases (Homann and Göringer, 1999). When the yeast gene is ligated into the plasmid, h erar2 s it w XbaI canlave(on n h eplasmi dan oncaf tr nof op ead ing f ramo t hyeasge ).T spoduc 2 bands, one is ~1250bp and the other is 5000bp. Colony 2's plasmid = VectorAlone (religated to itself) When there is no yeast gene ligated into the plasmid, Q.9. How is Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens modified to convert it into a cloning vector? A.9. The Ti plasmid is a tumour-inducing plasmid. The genes responsible for its pathogenic nature are either removed or altered so that it does not harm the plants and only delivers the gene of interest. Q.10.
Transcribed image text: Your group is a part of a research team that just received a grant from the National Institutes of Health to study cancer. As a first step, you decide to clone p53, a human gene that is mutant in many types of cancer cells Below is a diagram of the DNA product of a PCR amplification of the region of the human genome containing p The white region represents the coding ... Answer: They are related terms, but not identical. Carefully defined, Polymerase Chain Reaction is a technology for amplifying DNA sequences. Notice that using this definition PCR is not a test in and of itself; although you can use PCR to perform various kinds of tests. Historically when PCR ha... For example, let's say your plasmid backbone looks like the one found on the left side of the image below. It has a promoter (blue arrow) followed by the restriction sites EcoRI, XhoI, and HindIII. To place your gene in the proper orientation downstream of the promoter, you can add an EcoRI site just 5' of the start of the gene and a ... Transformation: After the PCR reaction, no ligation is required since the E. coli you transform your PCR products into will efficiently patch up the DNA. The resistance marker from the parental plasmid provides a mean for selecting for transformants which have taken up the mutagenized plasmid.
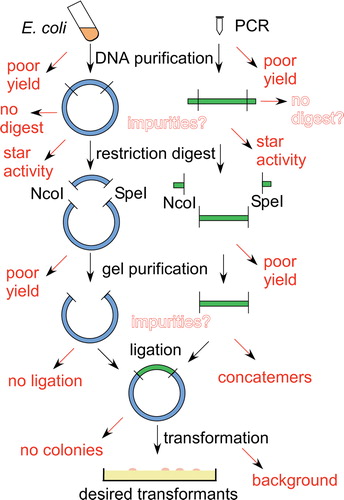
Isolate your PCR product from the rest of the PCR reaction using a kit, such as the QIAquick PCR Purification Kit. The PCR product is now ready for restriction digestion. Digest your DNA: Set up restriction digests for your PCR product and recipient plasmid. Because you lose some DNA during the gel purification step, it is important to digest ...
by CC Tao · 2020 — coli and cyclized by homologous recombination in vivo. Free from the limitation of restriction enzyme sites and omitting the ligation process, ...
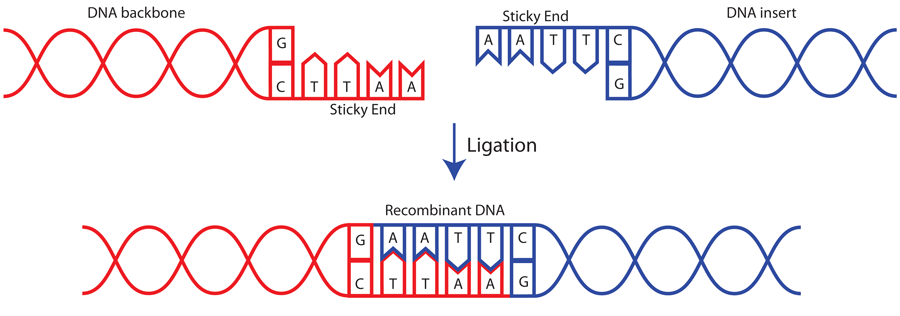
Restriction enzymes are DNA-cutting enzymes. Each enzyme recognizes one or a few target sequences and cuts DNA at or near those sequences. Many restriction enzymes make staggered cuts, producing ends with single-stranded DNA overhangs. However, some produce blunt ends. DNA ligase is a DNA-joining enzyme.
(a) PCR uses a DNA polymerase from a thermophilic bacterium. (b) PCR is particularly powerful because after each cycle of replication, there is a linear increase in the amount of DNA available. (c) For PCR, every round of replication is preceded by the denaturation of the double-stranded DNA molecules.
PCR cloning differs from traditional cloning in that the DNA fragment of interest, and even the vector, can be amplified by the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and ligated together, without the use of restriction enzymes. PCR cloning is a rapid method for cloning genes, and is often used for projects that require higher throughput than traditional cloning methods can accommodate.
PCR products are then directly ligated into the plasmid to create a library of genes that are methylated in that particular brain region. Ligations can be used to attach oligonucleotide linkers, which contain binding sites for PCR primers, to purify DNA fragments.
by MY Zhou · 2000 · Cited by 201 — ligation of Taq-amplified PCR products into the T-vector, ... Schematic diagram outlining the cloning procedures using universal T-vectors (see text for ...
04/11/2021 · The annotations from the inner to outer circles are indicated below the diagram. d Comparison of gene expression profiles in WP3NR/Dnd relative to WP3NR/DndΔE. The RNA-seq data represent three ...
29/10/2021 · The numbers of specific and shared peaks in each comparison are shown in the Venn diagram. ... subsequently ligated into pX330 ... PCR amplicons were subcloned into a …
The example below depicts the ligation of two sticky ends that were generated by EcoRI digestion: Usually, scientists select two different enzymes for adding an insert into a vector (one enzyme on the 5' end and a different enzyme on the 3' end). This ensures that the insert will be added in the correct orientation and prevents the vector from ...
Home » Unlabelled Pgem T Easy Vector Sequence / The 2kb Pcr Product Shown Below Was Ligated Into The Chegg Com - Convenient expression of cloned genes in vitro or in vivo. Senin, 19 Juli 2021.
PCR cloning differs from traditional cloning in that the DNA fragment of interest, and even the vector, can be amplified by the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and ligated together, without the use of restriction enzymes. PCR cloning is a rapid method for cloning genes, and is often used for projects that require higher throughput than traditional cloning methods can accommodate.
04/12/2008 · An aliquot of 2 μl above PCR products, the PCR products generated using QuickChange™ or generated as described in was transformed respectively into E. coli DH5α competent cells by heat shock. The transformed cells were spread on a Luria-Bertani (LB) plate containing antibiotics and incubated at 37°C over night.
This diagram below provides an example of what the oligos may look like, in this example the oligos are to be ligated NcoI and XbaI restriction sites. ... If the PCR product is to be ligated into a de-phosphorylated vector, heat-inactivating the PNK enzyme may be a good idea to prevent it from phosphorylating the backbone vector and leading to ...
Therefore, if a DNA fragment is ligated into the MCS, the lacZ gene will no longer function and will not produce the blue color. In the presence of X-gal, cells that contain a plasmid with a fragment inserted into the MCS will be white, whereas cells that contain a plasmid without a fragment inserted into the MCS will be blue.
In the diagram below, the chimeric plasmid carries resistance to ampicillin but the β-galactosidase gene has been disrupted. The bacteria are grown on a solid medium with ampicllin and X-gal. Cells resistant to ampicillin grow into colonies and white colonies (lac-) are …
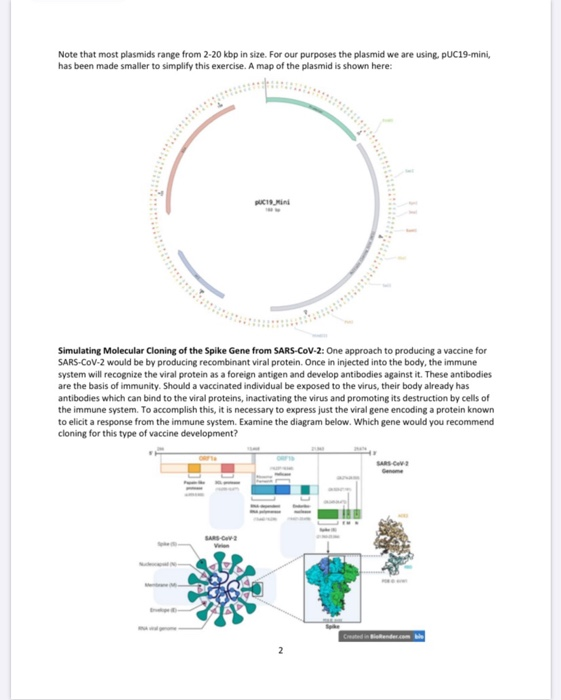
Let's start with a classic plasmid: pBR322 1. It is often used as a backbone for derivative vectors because it has all features needed for a successful cloning (Figure 1). As you see from the map center, the size of the linearized plasmid is 4361 base pairs. Before you start working with any plasmid, it is advisable to linearize it by cutting ...
Molecular cloning of PCR products: Restriction digestion guide. Cloning is a ubiquitous multi-step technique in molecular biology labs, and involves inserting a target gene (insert) into a circular, double-stranded, self-replicating plasmid vector backbone that is carrying an antibiotic resistance gene (most often ampicillin or kanamycin).
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
The aim at Oxford Genetics was to engineer a DNA plasmid system that could ... This diagram below provides an example of what the oligos may look like, in ...
Plasmid: Restriction enzyme N and H were used to create cuts so the PCR product and plasmid can be ligated. For the ...
The diagram below shows the concept behind the TA Cloning method. ... You will ligate the PCR product into pCR ... ng is the amount of PCR product of . y. base pairs to be ligated for a 1:1 (vector to insert) molar ratio. Notes on efficiency . In general, 0.5-1.0 .
The diagram below represents a section of the human genome. The coding sequence of a gene, YFG, is shown ... You would like to use PCR to amplify (make many copies of) the boxed section of the DNA sequence below: ... when you insert this DNA into a plasmid and transform it into the bacteria, you get no hormone production. Give two valid reasons ...
Suppose you find that the harE gene is in the plasmid, but now you want a restriction map of the recombinant plasmid. You take three individual samples of the plasmid and digest one sample with EcoRI, the second sample with HindIII, and the third sample with both EcoRI and HindIII. Then you run the digested DNA on a gel to see the fragments.
This is frequently done after performing either PCR - or restriction enzyme -based cloning to test individual clones before use of more expensive forms of plasmid verification, such as DNA sequencing. In the example above, digestion with enzyme RE1 will linearize the 6200bp plasmid into one single 6200bp fragment.
When PCR was in its infancy, researchers found that subcloning PCR products by simple blunt-ended ligation into blunt-ended plasmid cloning vectors was not easy. Part of the challenge is thermostable DNA polymerases, like Taq DNA polymerase, add a single nucleotide base extension to the 3´ end of blunt DNA in a template-independent fashion ...
To clone your gene of interest into pCR ® 2.1, you must first generate a PCR product. The PCR product is ligated into pCR ® 2.1 and transformed into competent cells. Since the PCR product can ligate into the vector in either orientation, individual recombinant plasmids need to be analyzed to confirm proper orientation.
(bp) in length for best results. Below is a typical workflow for cloning and sequencing a gene. The steps that the Ligation and Transformation module ... † Ligation of PCR product into pJet1.2 plasmid † Transform ligated plasmid into bacteria ... to the size of the PCR fragment ligated into the plasmid. Finally, the DNA








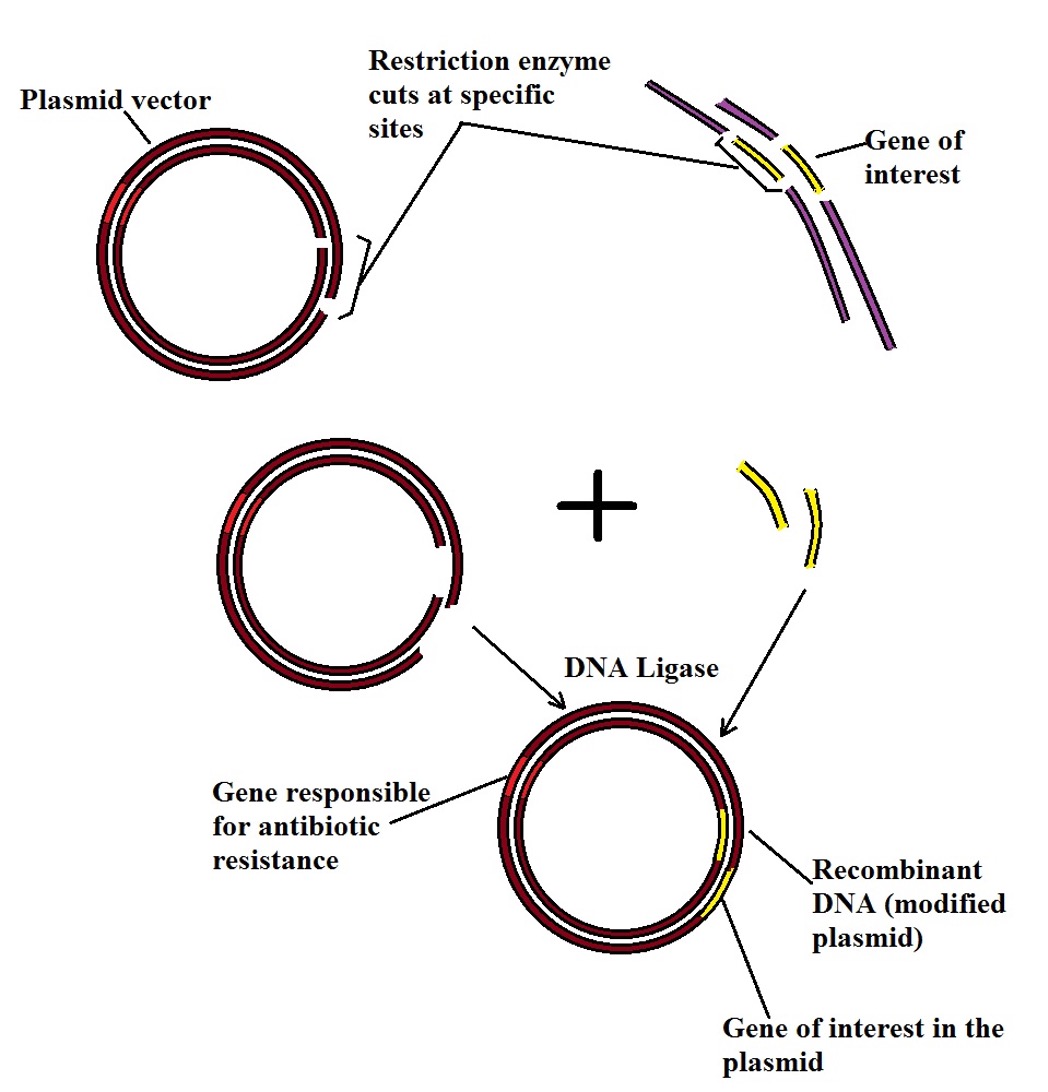









0 Response to "41 below is a diagram of the pcr product ligated into the plasmid."
Post a Comment