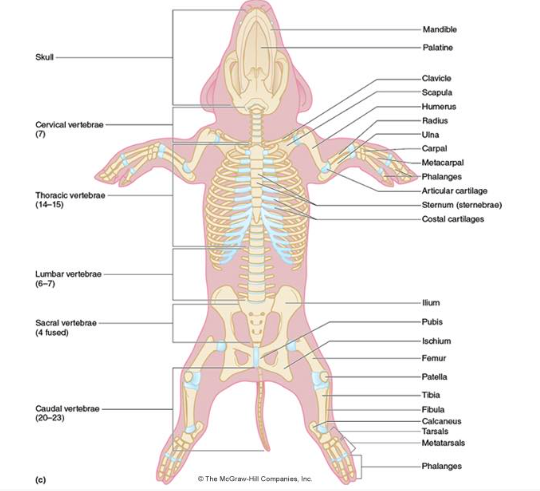
39 fetal pig muscle diagram
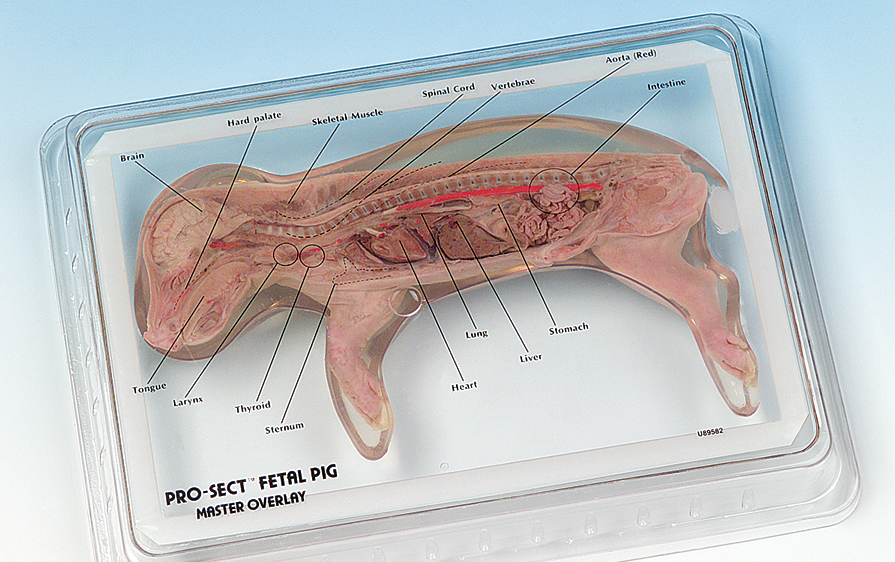
Fetal Pig Dissection 5 Diaphragm Fibrous pericardium Thymus FIGURE F1.1bThymus gland in the fetal pig. 5. The female gonads are called ovaries and are very small,oval organs located posterior to the kidneys. 6. The male gonads,the testes, are located outside of the abdominopelvic cavity in the scrotum. Because these pigs are fetal,the scrotum ... This is an online quiz called Fetal Pig Anatomy. There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Your Skills & Rank. Total Points. 0. Get started! Today's Rank--0. Today 's Points. One of us! Game Points. 15. You need to get 100% to score the 15 points available.
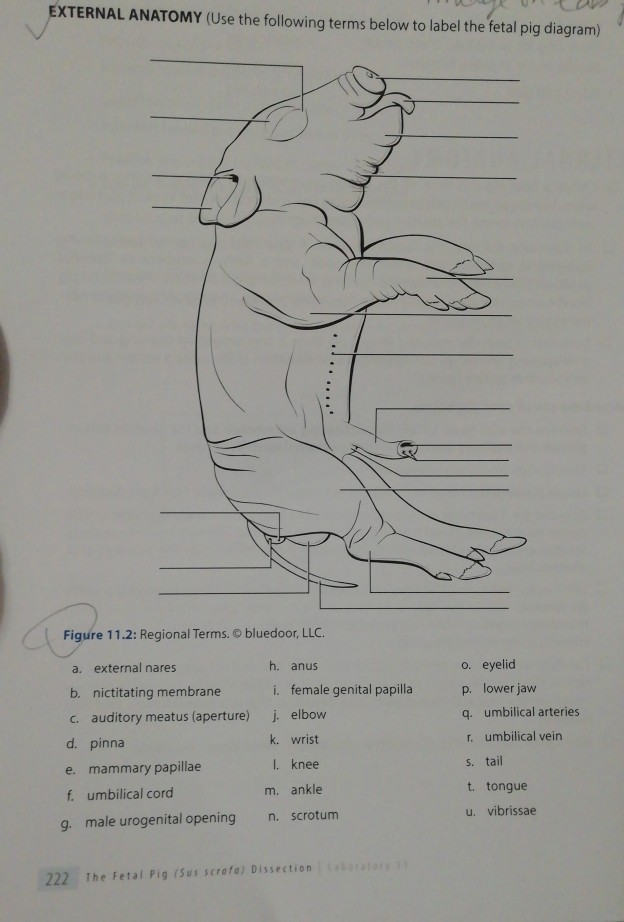
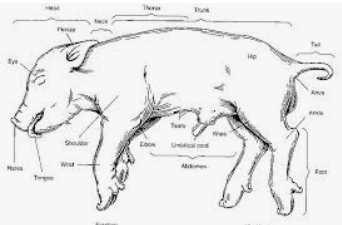
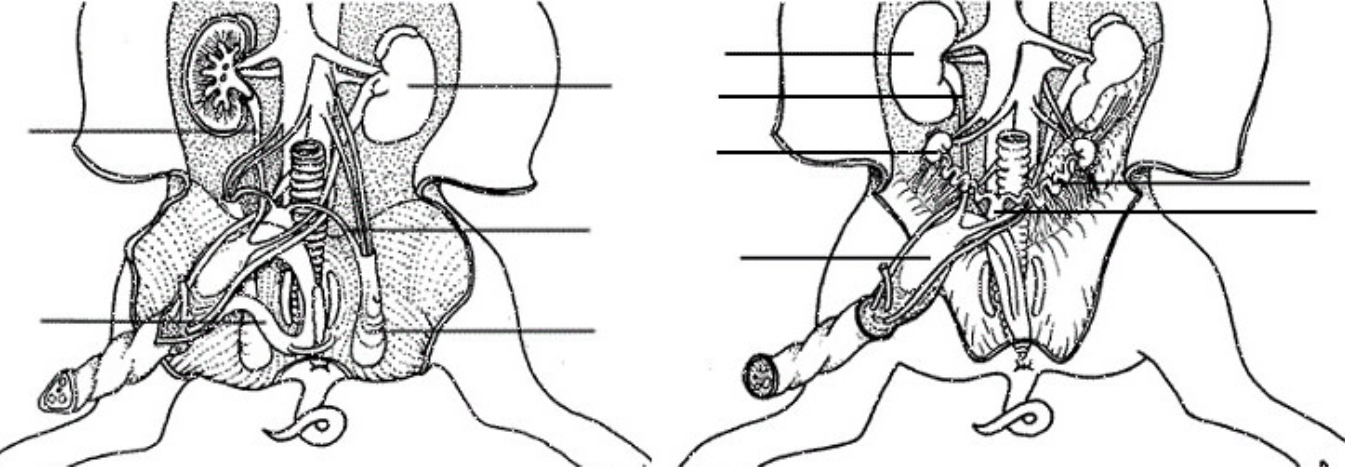
In the male fetal pig diagram, you can see that male fetal pigs have a urogenital opening located behind the umbilical cord. The swelling behind the hind legs of the fetal pig is the scrotum. If the fetal pig is a female, there will be a fleshy protrusion ventral near the anus called the genital papilla. The female’s internal reproductive ...

Fetal pig muscle diagram
Fetal Pig Anatomy. In this lab you'll dissect a fetal pig to get a look at the anatomy of a mammal. In addition, you should study the two pre-dissected specimens available in lab. Objectives. Recognize the structures labeled on the pictures on this page or listed in bold in the text. Specimens. Fetal pig that you can dissect with your group Jul 29, 2021 · This muscle extends the foot and originates at the distal end of the femur and inserts by the tendon the deltoid is a superficial muscle that cover most of the scapula region. 14+ Fetal Pig Dissection Diagram. A fetal pig is a great choice for dissection because the size of the organs make them easy to find and identify. Fetal pigs are readily available, since farmers find it profitable to breed female pigs which they plan to sell. Thus, pig fetuses are byproducts of the slaughter houses. The period of gestation is 112 to 115 days, and there are, on the average, about seven to eight offspring in a litter. At birth the pigs vary from 12 to 14 inches in length. The
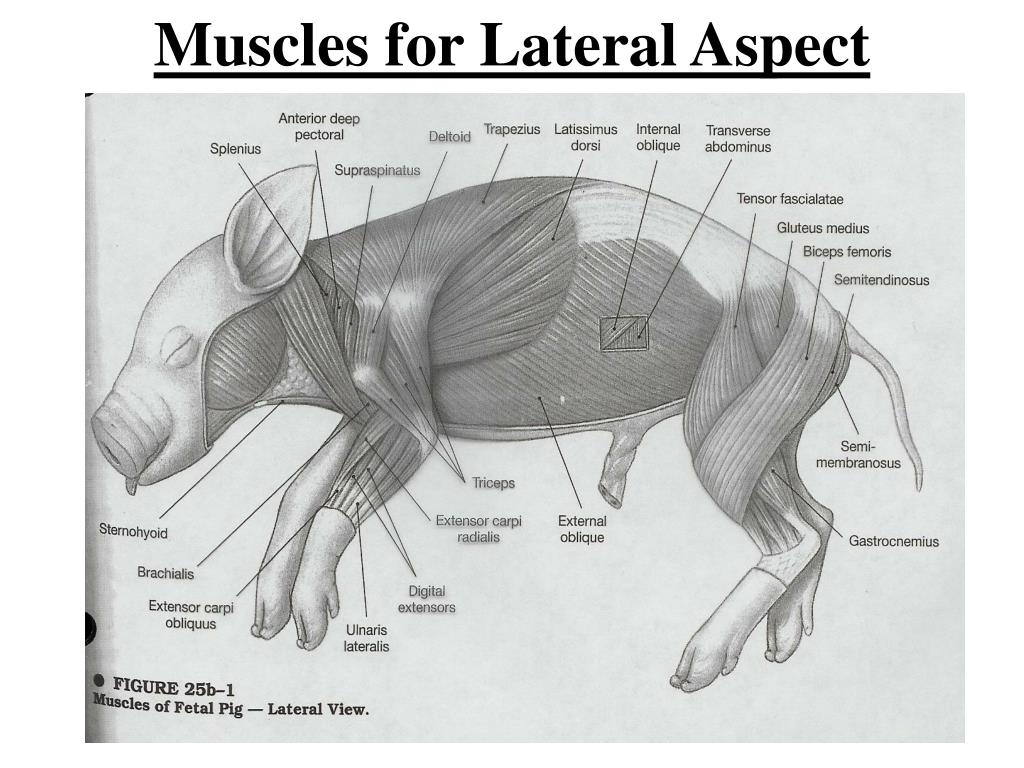
Fetal pig muscle diagram. The pig in the first photograph below is laying on its dorsal side. Ventral is the belly side. It is opposite the dorsal side. The pig in the first photograph below has its ventral side up. External Structures. Obtain a fetal pig and identify the structures listed in the first photograph. Use the photographs below to identify its sex. Fetal Pig Dissection Objectives 1. Compare and contrast the anatomy of human and pig organ systems. 2. Identify the muscles of the pig back, shoulder, neck, chest, abdomen, forelimb and hindlimb. 3. Identify the major nerves of the brachial and sacral plexuses. 4. Dissect and examine the spinal cord. 5. Locate and identify the major glands of the Humans and Pigs may be closer than you think! Both are mammals We share common body systems The anatomy of the pig is close to that of humans The fetal pigs will tell us more about our own bodies and give us a way Objective: - Locate and describe the external features of a fetal pig, identify some of the major skeletal muscles and muscle groups of a mammal. Muscles are critical for movement, posture, balance, circulation, digestion, and breathing. There are 3 types of muscles cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscles. Skeletal muscles cover the entire body ...
names for the pig. The period of gestation for the pig is 112-115 days. The age of the fetus can be estimated by measuring the body length from the tip of the snout to the attachment of the tail. Compare this length to the data given on relative sizes of a fetal pig at different times during gestation or the time of development inside the uterus. The different regions of the stomach are labeled in the video and in the diagram below for your convenience. - The part closest to the esophagus is the cardiac region. - The fundus is the anterior portion of the stomach near the diaphragm. - The pyloric region connects to the duodenum at the pyloric sphincter. - The body lies between the fundus and the pylorus. Fetal Pig Dissection Humans and fetal pigs share very similar anatomy as they are both mammals. Fetal pigs are also a popular choice for dissections as they are a bi-product of the pork industry, therefore as long as people Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening is located near the umbilical cord. If your pig is female, you should also note that urogenital papilla is
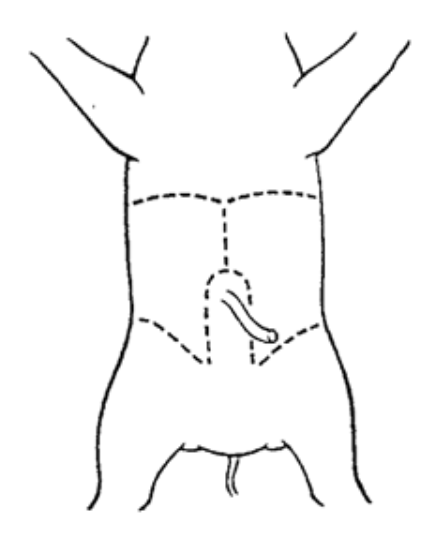
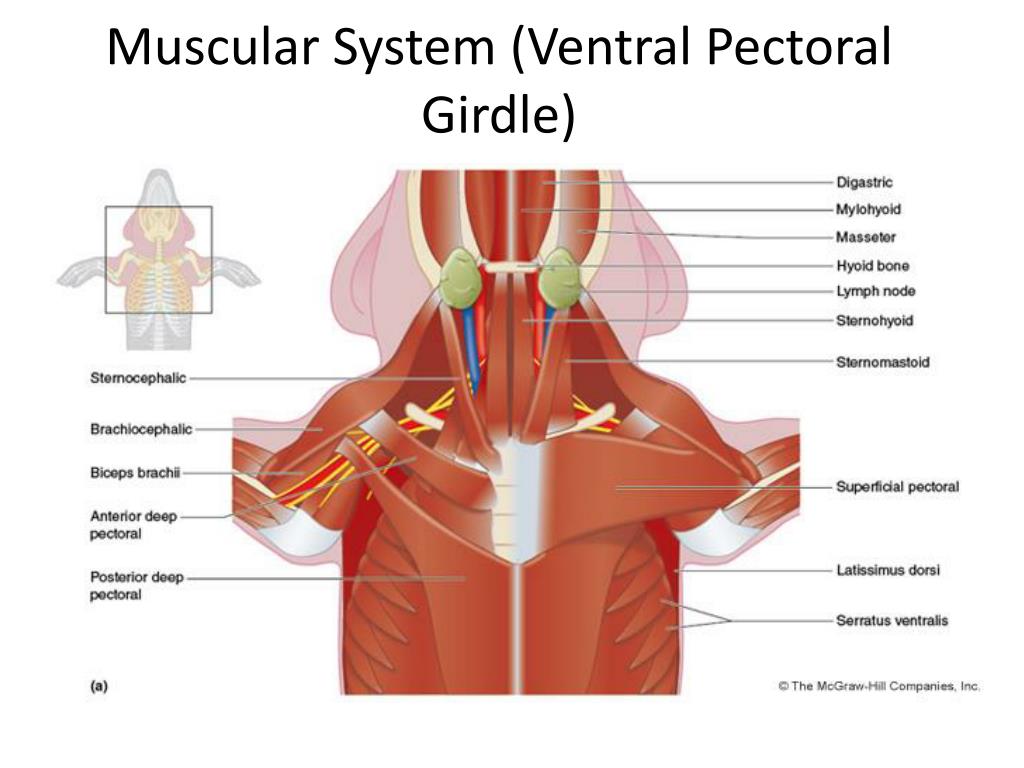
Place your fetal pig in the dissecting pan ventral side up. Use string to "hog-tie" your pig so that the legs are spread eagle and not in your way. Use scissors to cut through the skin and muscles according to the diagram. Do not remove the umbilical cord. In the first section, you will only examine the abdominal cavity (the area below the ... Nov 12, 2019 · A fetal pig is a great choice for dissection because the size of the organs make them easy to find and identify. Tinyhouse prepper live simple live free recommended for you. Made with explain everything. This muscle originates at the aponeuroses covering the infraspinous muscle its insertion is at the deltoid ridge of the humerus. The fetal pig (Sus scrofa) belongs to the class "Mammalia", the same class to which man belongs. The gestation period of the pig is about 115 days and the fetal pigs are approximately 30 cm in length at the end of this period. Mammals are vertebrates having hair on their body and mammary glands to nourish their young. 6. Brachiocephalous muscle 7. Sternomastoid muscle 8. Sternohyoid muscle 9. Omohyoid muscle 10. Sternothyroid muscle 11. Trapezius muscle 12. Triceps brachii muscle 13. Deltoid 14. Lattissmus dorsi muscle 15. Digastric muscle 16. Mylohoid 17. Pectoralis Lower limb 18. Biceps femoris muscle 19. Tensor fasciae latae 20. Gluteus medius muscle 21 ...
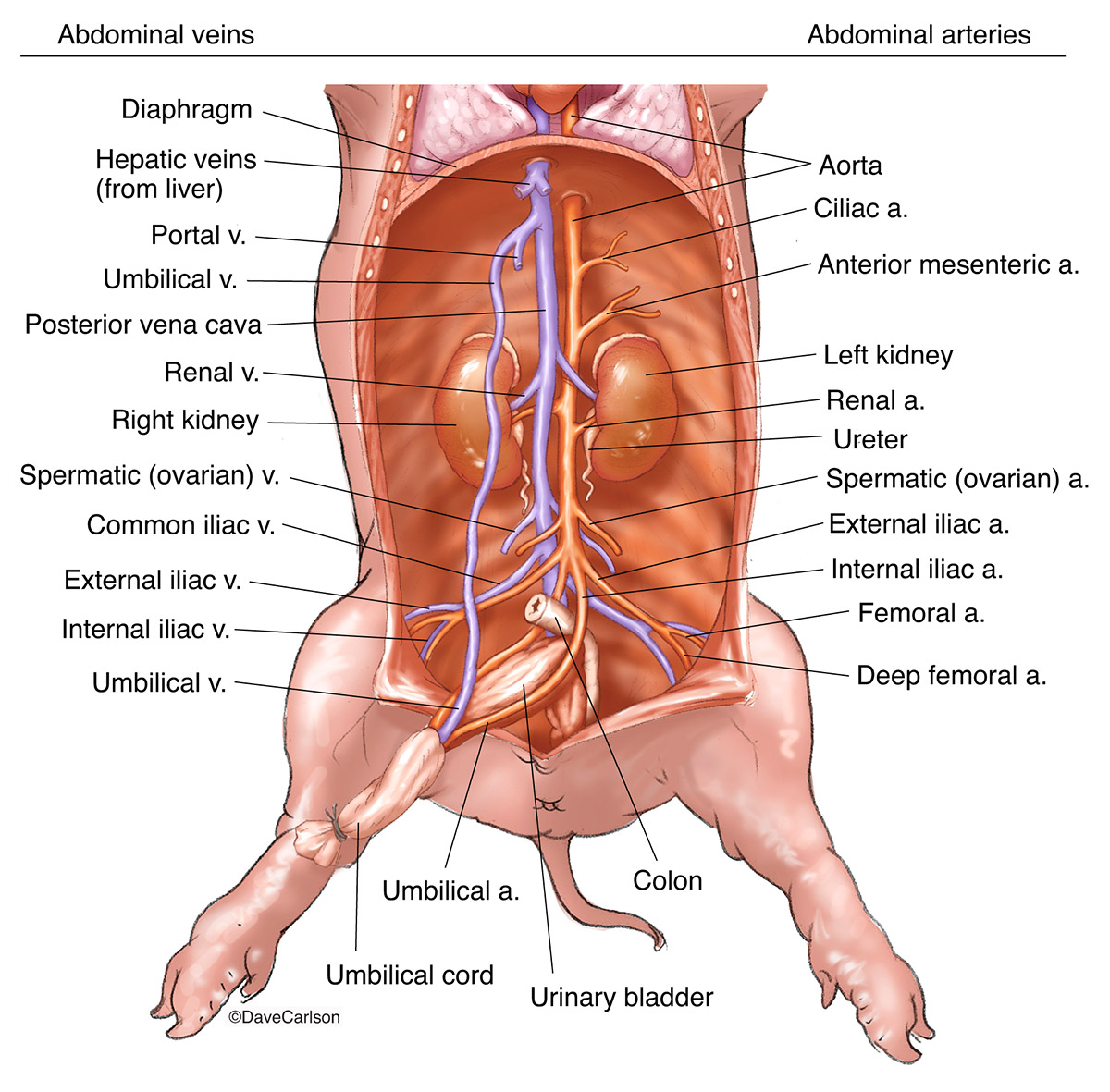
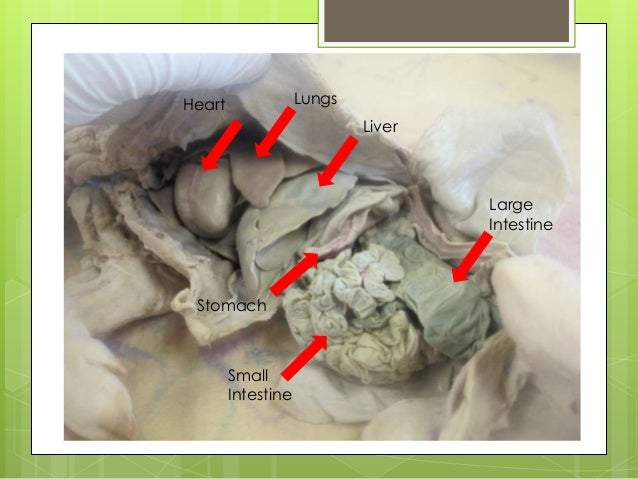
Pigs like other mammals have a four-chambered heart. The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs (pulmonary circulation), and the left side pumps blood out to the rest of the body (systemic circulation). Each side of the heart has two chambers, the upper chambers are called atria and the lower chambers are called the ventricles.
Arm and shoulder muscles. Latissimus Dorsi. Major retractor muscle of the arm. Deltoid. Helps to protract the upper arm. Deep Pectoral. Adducts the limb and pulls the limb caudally. Triceps Brachii. Extends the elbow and flexes the shoulder. Biceps Brachii. Flexor of the forearm
Place your fetal pig in the dissecting pan ventral side up. Use string to tie the legs behind the back of the pan. Use scissors to cut through the skin and muscles according to the diagram. Do not remove the umbilical cord. After completing the cuts, locate the umbilical vein that leads from the umbilical cord to the liver. You will need to cut ...
Fetal Pig Diagrams. While pictures are useful for learning the anatomy of the fetal pig, be careful with only memorizing drawings. Real pigs are not as cleanly pictured and the parts not perfectly aligned. Be sure to study the real pig photographs also.
fetal pig outer arm muscles. 13 terms. tori_rainboth PLUS. Other sets by this creator. Fetal pig digestive. 13 terms. tori_rainboth PLUS. Fetal pig male reproductive ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Labs Dr. J. Lim Objective: In this exercise you will examine the organization of the many body systems studied this semester in the context of a single specimen, the fetal pig. Be sure to identify the major organs as you explore the extent of each system.
Description: The latissimus dorsi is a large muscle wrapped around the sides of the thoratic region and chest, its purpose it to extend the upper forelimb at the shoulder point. The trapezius, is the muscle anterior to the latissimus dorsi, its purpose it to elevate the shoulder.The deltoid is a muscle that covers the shoulder region, its purpose it to raise or pull the upper forelimb anteriorly.
a tube through which the air passes to get to the lungs, windpipe. lungs. responsible with gas exchange. diaphragm. The muscle that aides in the breathing process. Separates the thoracic cavity from the gastrointestinal cavity. esophagus. tube connecting mouth to the stomach. small intestine.
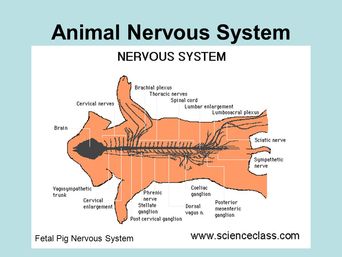
2. Identify the major anatomical features of the vertebrate body in a dissected specimen. 3. Understand the relationship between structure and function in the vertebrate body and relate concepts covered in lecture to st ructures found in your pig. 4. Understand mammalian fetal circulation from a mechanical, physiological, and evolutionary ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Resources. To study the pig in more detail, go to this Virtual Pig Dissection. It covers all the body systems and includes quizzes to test your knowledge! Label the Anatomy of a Fetal Pig. Print out these PDFs and fill in the labels to test your knowledge of fetal pig anatomy. Internal anatomy: label the middle section
Muscles. In almost every case, fetal pigs have the same muscles as humans, with some small variations in the size and location of some muscles related to the fact that pigs are quadrupedal and humans are bipedal. For example, the major chest and abdominal muscles found in humans are present in the pig.
Fetal Pig Dissection and Lab Guide External Anatomy of the Fetal Pig. 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening is located near the umbilical cord. If your pig is female, you should also note that urogenital papilla is present near the genital ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Background: Mammals are vertebrates having hair on their body and mammary glands to nourish their young. The majority are placental mammals in which the developing young, or fetus, grows inside the female's uterus while attached to a membrane called the placenta.The placenta is the source of food and oxygen for the fetus, and it also serves to get rid of fetal wastes.
Fetal pigs are readily available, since farmers find it profitable to breed female pigs which they plan to sell. Thus, pig fetuses are byproducts of the slaughter houses. The period of gestation is 112 to 115 days, and there are, on the average, about seven to eight offspring in a litter. At birth the pigs vary from 12 to 14 inches in length. The
Jul 29, 2021 · This muscle extends the foot and originates at the distal end of the femur and inserts by the tendon the deltoid is a superficial muscle that cover most of the scapula region. 14+ Fetal Pig Dissection Diagram. A fetal pig is a great choice for dissection because the size of the organs make them easy to find and identify.
Fetal Pig Anatomy. In this lab you'll dissect a fetal pig to get a look at the anatomy of a mammal. In addition, you should study the two pre-dissected specimens available in lab. Objectives. Recognize the structures labeled on the pictures on this page or listed in bold in the text. Specimens. Fetal pig that you can dissect with your group










0 Response to "39 fetal pig muscle diagram"
Post a Comment