38 boron molecular orbital diagram
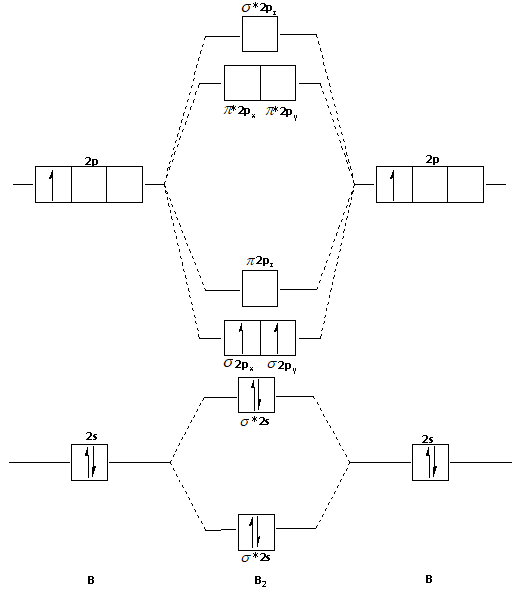
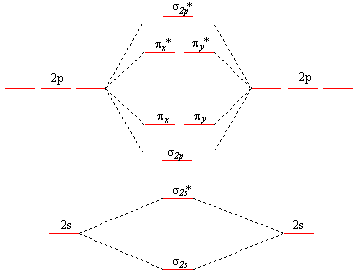
B2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. Magnetic properties: Since each 2px and 2py MO contains unpaired electron, therefore B2 molecule is paramagnetic. The compound does not exist but that doesn't mean its MO diagram And From the MOT concept Be2 doesn't exists as its Border is 0 and in.CAcT Home Molecular ... Boron molecular orbital diagram have the following form: The nuance is that the level pi lies below the level sigma2. For building molecular orbital diagram I use modiagram package. \\documentcla...
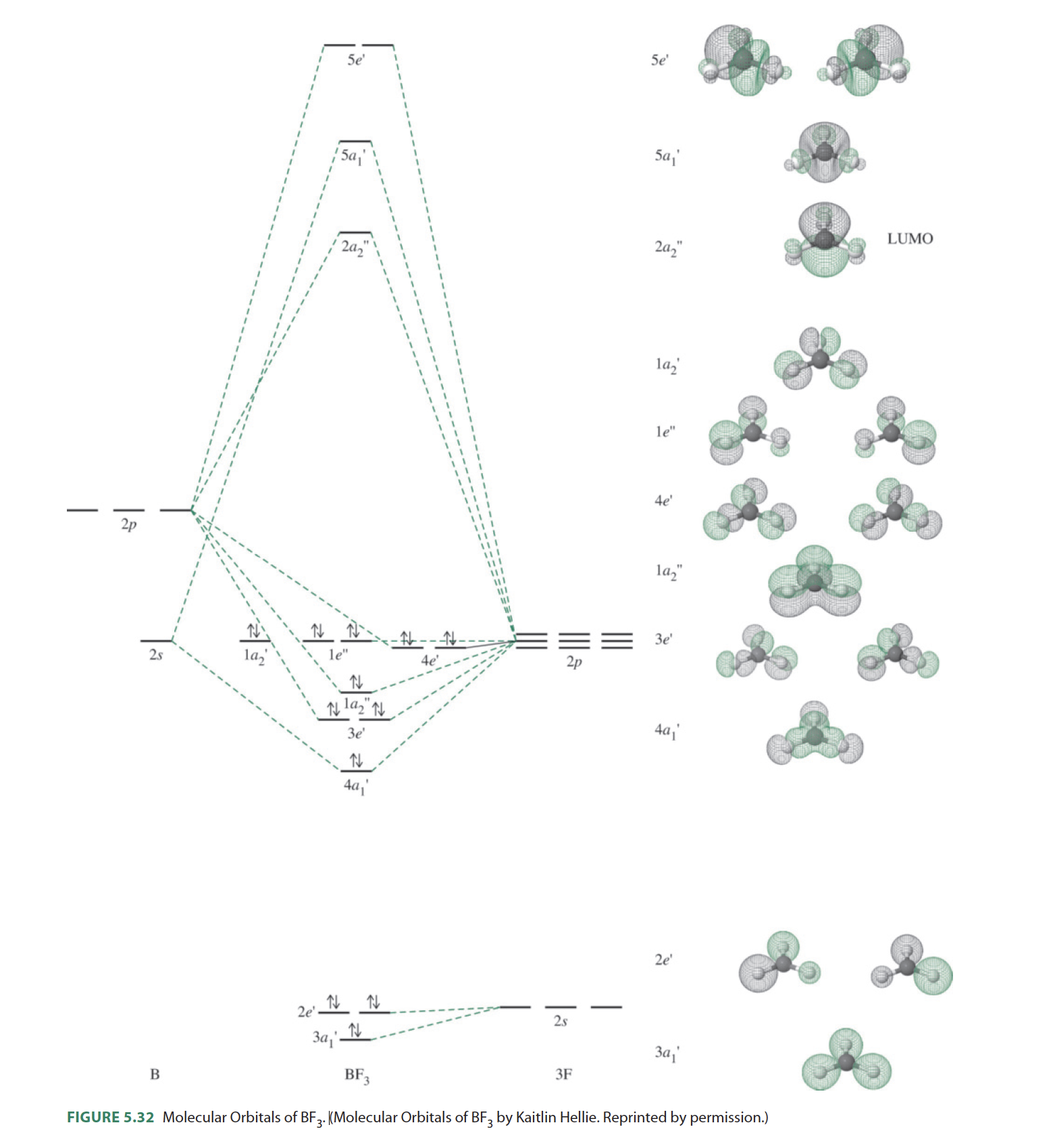
The three hybridized sp 2 orbitals are usually arranged in a triangular shape. BF 3 molecule is formed by bonding between three sp 2 orbitals of B and p of 3 F atoms. All the bonds in BF 3 are sigma bonds. BF 3 Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles. Normally, boron forms monomeric covalent halides which have a planar triangular geometry.

Boron molecular orbital diagram
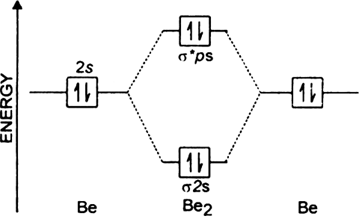
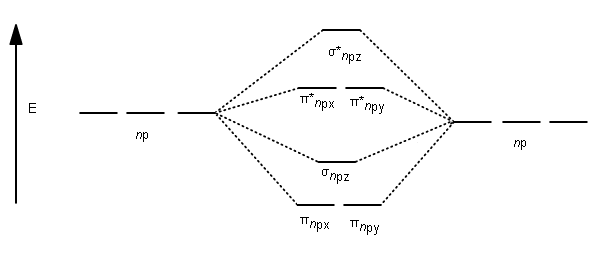
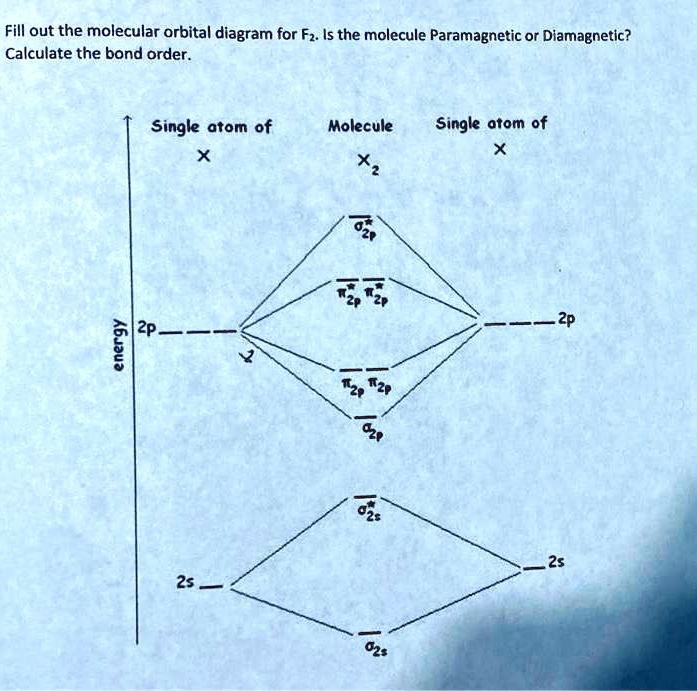
Molecular Orbital Diagrams and Bond Order Constants Periodic Table Part A The blank molecular orbital diagram shown here (Figure 1) applies to the valence of diatomic lithium, beryllium, boron carbon, or nitrogen. Bonding orbitals are marked with σ or π and antibonding orbitals with σ* or π*. hybridization and molecular orbital mo theory molecular shapes based on valence electrons lewis dot structures and electron repulsions •molecular orbital theory mo - a molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals electrons are then distributed into mos a molecule is a collection of nuclei with the orbitals ... A molecular orbital diagram, Beryllium has an electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2, so there are again two electrons in the valence level. However, the 2s can mix with the 2p orbitals in diberyllium, whereas there are no p orbitals in the valence level of hydrogen or helium. The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I ...
Boron molecular orbital diagram. From this I built A1 bonding and antibonding orbitals, A'2 bonding and antibonding orbitals, 1 A'2 and 2 E''2 non bonding orbitals. I'm now stuck because I have 4 E' on the F side and only 2 E' on the B side. I found the following diagram for BF 3 online but it doesn't generate the E' anti bonding and also doesn't generate enough molecular ... Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in Molecular geometry and molecular shape will be the same for the molecules with 0 lone pair; which is the case of BCl3. Molecular Orbital Diagram of BCl3. Molecular orbital diagrams give us an idea about the mixing of orbitals in molecules. Let's look into the MO diagram of boron trichloride. In this video we will draw the molecular orbital diagrams for diatomic nitrogen, carbon and boron. We will also calculate their bond order and determine if t...
Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. a blank molecular orbital diagram (part a 1 figure) has been provided to you. rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. to rank items as equivalent, overlap them. f2, f2+, f2- Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ... Molecular Orbitals for Diborane, B 2 H 6. Jmol models of calculated wavefunctions. To view a model, click in a molecular orbital circle in the energy level correlation diagram shown Mouse Control of Models. Left mouse drag to rotate; Shift Left drag up or down to resize; Shift Right drag or Shift Left drag horizontally to z-rotate; Right click ... Dec 22, 2020 · 1 answerDraw and explain the M.O. diagram of Boron molecule. · 1. Electronic configuration of B = 1s2 2s2 2p · 2. Electronic configuration of B, =σ1s2 σ* ...
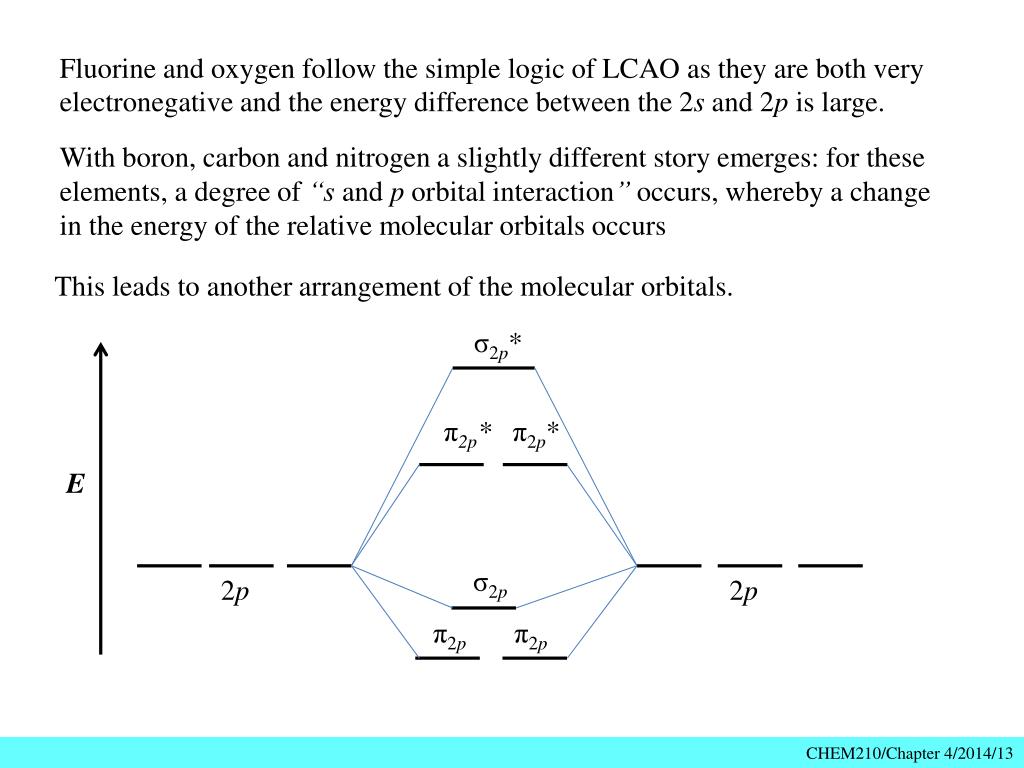
Problem 37. The ions and molecules N O +, C N −, C O, and N 2 and N 2. form an isoelectronic series. The changing nuclear charges will also change the molecular energy levels of the orbitals formed from the 2 p atomic orbitals ( 1 π, 3 σ, and 1 π ∗) Use molecular modeling software for the following: a. molecular orbital diagram as a non-bonding molecular orbital. 7. There are a total of 6 electrons to add to the molecular orbital diagram, 3 from boron and 1 from each hydrogen atom. sp Hybrid Orbitals in BeH2 1. The Lewis structure shows that the beryllium in BeH Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer. The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. Fig. No. 5 Order of Energy Levels for Boron, Carbon, Nitrogen etc. This kind of energy reversal is due to mixing of 2s and 2p orbitals where the energy difference is very close, that is, for B, C, and N atoms. According to the symmetry interactions, the two ...
Molecules with Similar Molecular Orbital Diagrams Molecules and ions formed from 2 boron atoms or from 2 carbon atoms have molecular orbitals diagrams of the same sort as N 2. Diatomic molecules made up of two different atoms also have molecular orbital diagrams very similar to that of N 2.When the electronegativity of one atom is lower than the other, the more electronegative atom's orbitals ...
Before we can draw a correlation diagram for B2, we must first find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals.
7.3: How to Build Molecular Orbitals. The molecular orbital (MO) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. The applications of the MO theory extend beyond the limitations of the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model and the Valence Bond theory.
Reading off the character table, we see that the group orbitals match the metal s orbital (A1g), the metal p orbitals (T1u), and the dz2and dx2-y2 metal d orbitals (Eg). We expect bonding/antibonding combinations. The remaining three metal d orbitals are T2gandσ-nonbonding. 5. Find symmetry matches with central atom.
Jan 27, 2015 — Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to ...1 answer · Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram of Boron Molecule Video Lecture from Chapter Nature of Chemical Bond of Subject Chemistry Class 11 for HSC, IIT JEE, CBSE & NEET.Wa...
The molecular orbitals having the same sign combine and give bonding molecular orbitals. We have to draw the molecular orbital diagram for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2} ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.Electron Configuration for Boron (B)Electron Configuration for Boron (B)
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
An orbital diagram is similar to electron configuration, except that instead of indicating the atoms by total numbers, each orbital is shown with up and down. 1s2, 2s2, 2p1 Boron 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d1. Scandium. Answer to Draw an orbital diagram for boron. Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Draw an orbital diagram for ...
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral borax, and the ultra-hard crystal boron carbide.
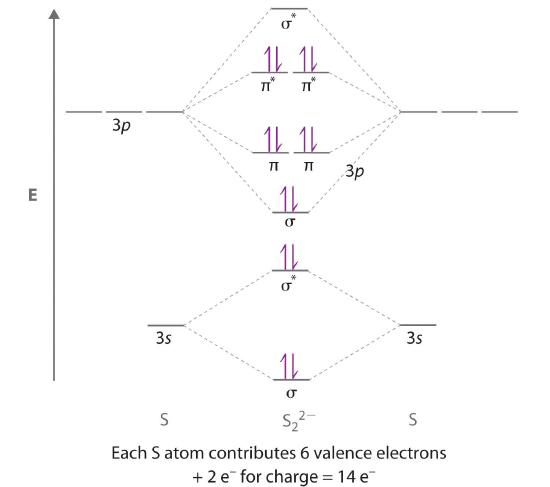
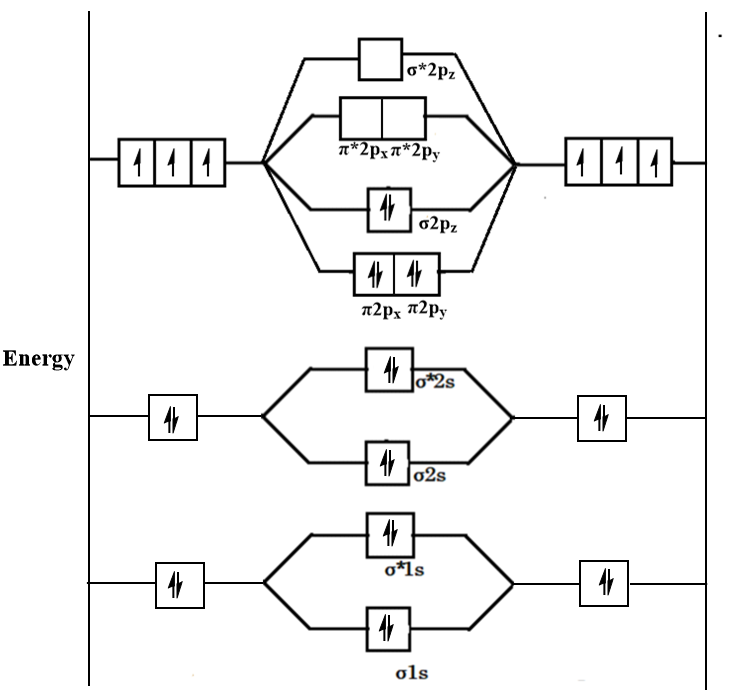
B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom = 3. In the formation of B 2 molecule, three valence electrons of each boron atom i.e. 6 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies. MO electronic configuration:
We have to draw the molecular orbital diagram for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2} ... B2 molecule is for med by the overlap of atomic orbital s of both boron atoms. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom = 3. In the for mation of B2... Rating: 4,4 · 740 votes · Free · Android · Educational. Molecular orbital diagram for b2.
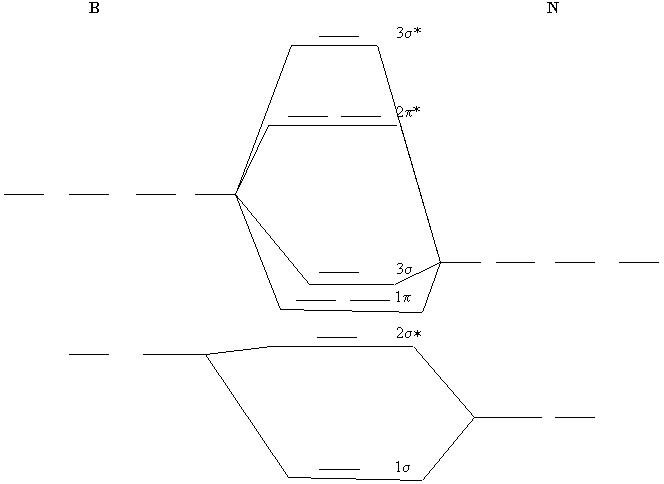
This is the general MO diagram you need to fill with the valence electrons of BN. Boron has 3 valence electrons, and nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, this makes 8 electrons. You have to start filling the orbitals from those with lowest energy to those with higher energy. So, 2 electrons on σ 2 s, two electrons on σ 2 s ∗, two electrons on ...
This is the general MO diagram you need to fill with the valence electrons of BN Boron has 3 valence electrons, and nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, this makes 8 electrons. You have to start filling the orbitals from those with lowest energy to those with higher energy. So, 2 electrons on σ2s , two electrons on σ∗2s, two electrons on σ2p .
A molecular orbital diagram, Beryllium has an electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2, so there are again two electrons in the valence level. However, the 2s can mix with the 2p orbitals in diberyllium, whereas there are no p orbitals in the valence level of hydrogen or helium. The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I ...
hybridization and molecular orbital mo theory molecular shapes based on valence electrons lewis dot structures and electron repulsions •molecular orbital theory mo - a molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals electrons are then distributed into mos a molecule is a collection of nuclei with the orbitals ...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams and Bond Order Constants Periodic Table Part A The blank molecular orbital diagram shown here (Figure 1) applies to the valence of diatomic lithium, beryllium, boron carbon, or nitrogen. Bonding orbitals are marked with σ or π and antibonding orbitals with σ* or π*.
















0 Response to "38 boron molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment