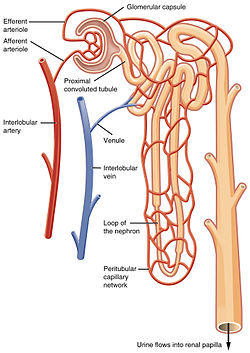
36 renal blood flow diagram
Renal blood flow is massive (400ml/100g/min), and most of this is for the purpose of filtration rather than renal metabolism. The kidneys autoregulate their own blood flow within a wide range of MAP values (60 to 160 mmHg) by two main mechanisms. Myogenic autoregulation is an intrinsic property...
diagram below. Sunburn Sunburn is a complex reaction involving increased blood flow through the skin, inflammation, pain and in severe cases blistering. This is illustrated by the fact that generally there is far more blood flowing in the skin than is necessary to maintain its metabolism.
Osmosis Renal Blood Flow Regulation high-yield notes offers clear overviews with striking illustrations, tables, and diagrams. and renal blood flow. The kidneys achieve consistency between 80-200mmHg by adjusting their own arteriole resistance. Figure 60.2 The region where the distal...
Renal blood flow diagram
BLOOD VESSELS. The renal circulation is diagrammed in Figure 37-3. The afferent arterioles are short, straight branches of the interlobular arteries. From the renal plasma flow, the renal blood flow can be calculated by dividing by 1 minus the hematocrit: Hematocrit (Hct): 45%.
Renal function, in nephrology, is an indication of the kidney's condition and its role in renal physiology. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) describes the flow rate of filtered fluid through the kidney. Creatinine clearance rate (CCr or CrCl) is the volume of blood plasma that is cleared of creatinine per unit time...
renal blood flow. 1. Diagnostika i lechenie arterialnoi gipertenzii. Rossiyskie rekomendatsii (IV peresmotr) [Diagnosis and management of arterial hypertension.
Renal blood flow diagram.
After determining effective renal plasma flow and hematocrit, renal blood flow can be calculated. Normal - 1000-1300 mL/min. Evaluation of these parameters is important for objective evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of patients with various renal diseases.
In the physiology of the kidney, renal blood flow (RBF) is the volume of blood delivered to the kidneys per unit time. In humans, the kidneys together receive roughly 25% of cardiac output, amounting to 1.2 - 1.3 L/min in a 70-kg adult male. It passes about 94% to the cortex.
Renal failure is caused by impaired processes of renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, renal tubular reabsorption and secretion. Blood flow to different organs of the body is not equal. The most vitally important organs of the body receive the greatest supply of blood.
Download scientific diagram | Renal blood flow and renin release ... of renal blood flow and pressure-depen- dent renin release as observed in a resting conscious dog is depicted in Fig. ... coincides very accurately with the lower limit of renal blood flow autoregulation (60-70 mmHg).
Renal blood circulation. Intrarenal blood pressures. Factors that affect renal flow. Glomerular pressure. Formation and composition of urine. The renal blood flow is greater when a person is lying down than when standing; it is higher in fever; and it is reduced by prolonged vigorous exertion, pain...
Basic blood flow indices (blood pressure, blood flow velocity, vascular resistance) in arterial, microcirculatory and venous parts of the vascular 2. How much will the kidney blood flow change if the diameter of the renal artery diminishes 2-fold? 3. In what way deep inspiration and expiration do...
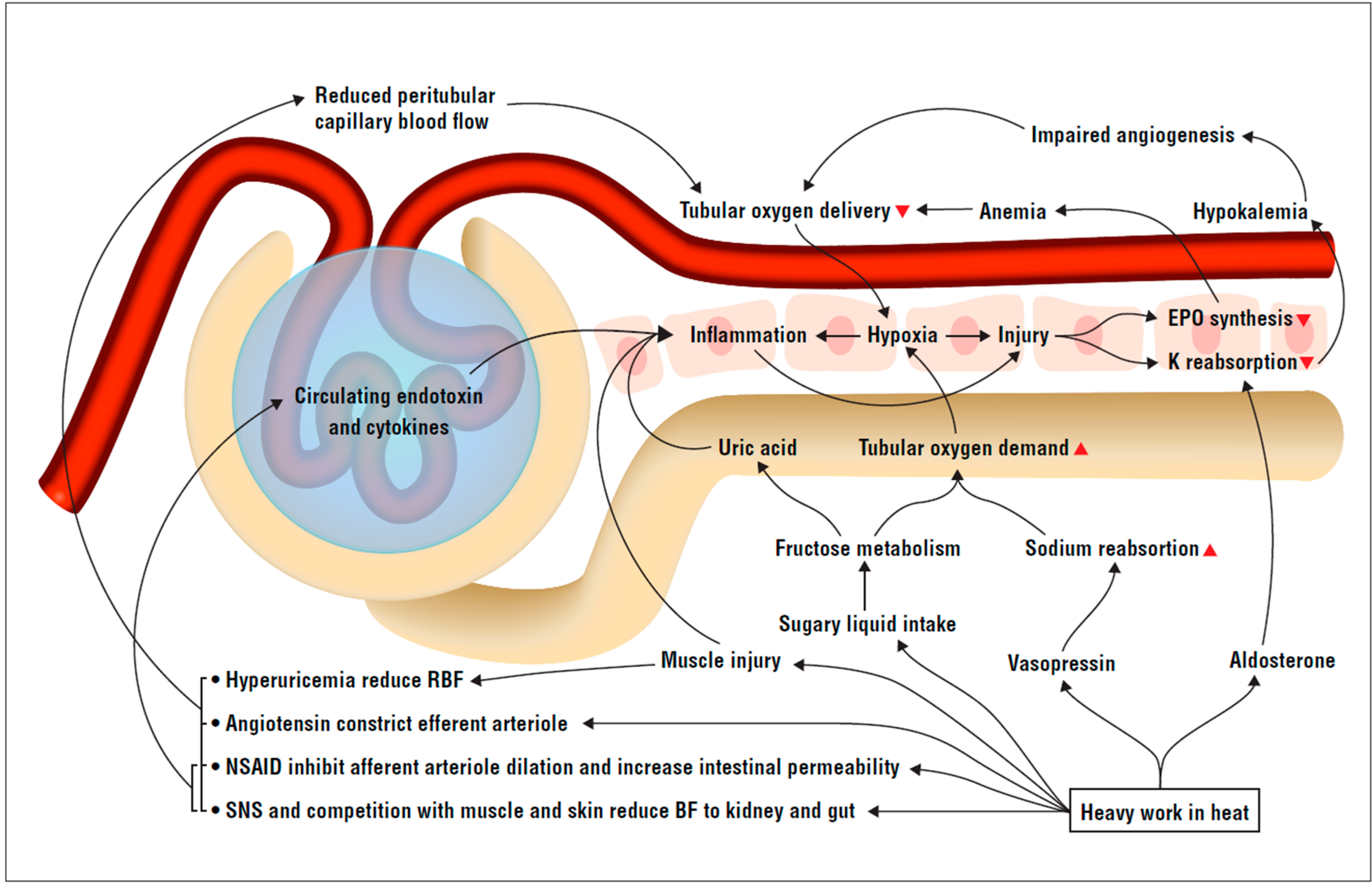
The renal system regulates glomerular filtration and renal blood flow through the tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism. A more pronounced decrease in renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate can be seen due to the increased severity of the stenosis.
Renal Blood Flow (RBF). -Equal to about 25% of cardiac output (~1.25 L/min). -Major RESISTANCES of the renal vasculature occur in the afferent arterioles Plot of mean arterial blood pressure vs. renal blood flow rate illustrates a critical feature of renal function. -Note that over a range of mean arterial...
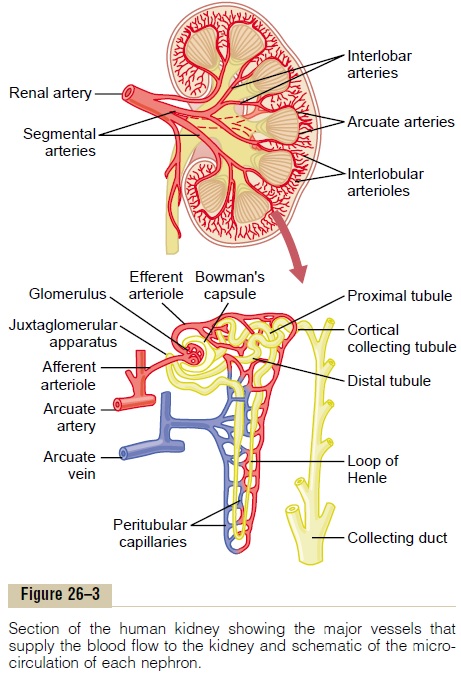
Primarily it is regulated by the rate of renal blood flow . This article will describe the system, discuss how the system is regulated and outline some [caption id="attachment_16112" align="aligncenter" width="799"] Fig 1 - The juxtaglomerular apparatus demonstrated as a diagram, accompanied by an...
Renal blood flow gradually decreases as the diastolic BP increases and arteriolar sclerosis begins. GFR remains normal until late in the disease, and, as a result, the filtration fraction is increased. Coronary, cerebral, and muscle blood flow are maintained unless concomitant severe atherosclerosis...
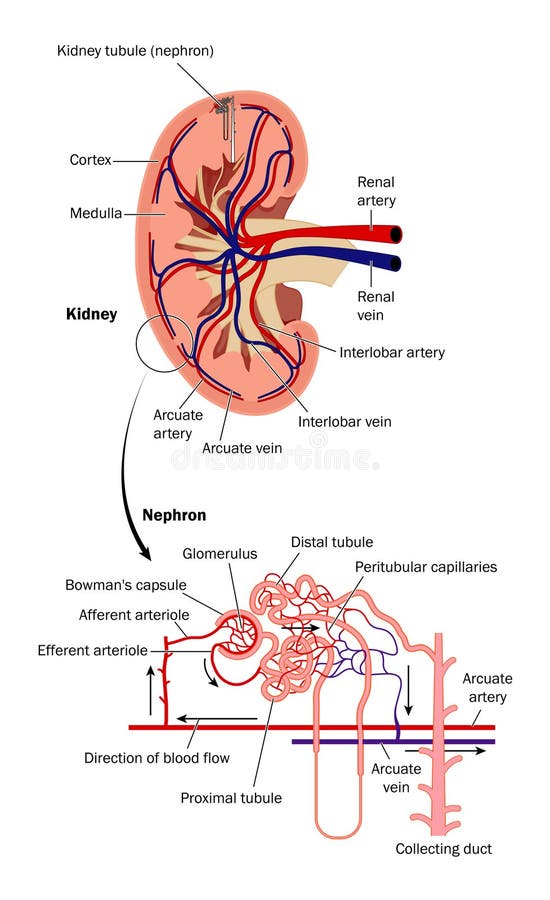
Renal function. Diagram showing the basic physiologic mechanisms of the kidney. Renal function, in nephrology, is an indication of the state of the kidney and its role in renal physiology. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) describes the flow rate of filtered fluid through the kidney.
flow-probe-measured renal blood flow; ∆ PSV, percent- change of Doppler-derived resistive index; Asterisk, statistically age change of peak systolic velocity; ∆ EDV, percentage change significant correlation of end diastolic velocity; ∆ RAD, percentage change of renal 1508 198.3 ± 77.5 ml/min, p...
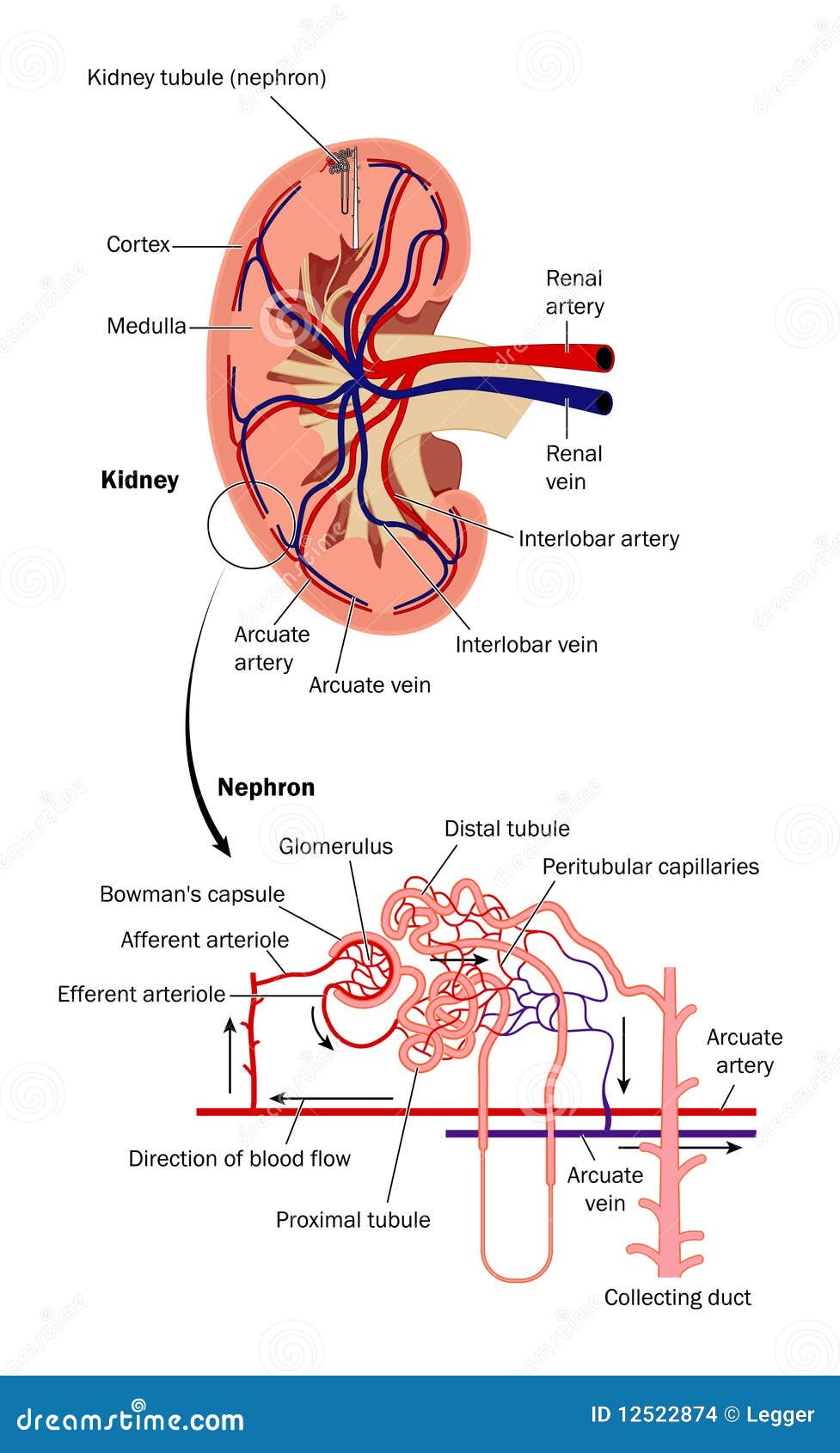
Illustration about Diagram of blood flow through the kidney showing detail of kidney tubule (nephron). Illustration of glomerulus, distal, capsule - 12522874. Renal blood flow. Royalty-Free Stock Photo. Download preview.
In normal circumstances, ACE inhibitors do not decrease renal blood flow. In the setting of bilateral renal stenosis, there is low perfusion to the kidney. Because of this, the protective physiological mechanism used by the kidneys is to constrict the efferent arteriole to increase hydrostatic pressure in...
Wilcox CS:Regulation of renal blood flow by plasma chloride. J Clin Invest 1983; 71: 726-735 Wilcox CS Peart WS:Release of renin and angiotensin II into plasma and lymph during hyperchloremia.Am J Physiol 1987; 253: F734-F741.
A randomized, controlled, double-blind crossover study on the effects of 2-l infusions of 0.9% saline and Plasma-Lyte 148 on renal blood flow velocity and renal cortical tissue Lactate- or bicarbonate-buffered solutions in continuous extracorporeal renal replacement therapies / HP Kierdorf, C Leue, S...
In general, renal blood flow is auto-regulated in parallel with GFR, but GFR is more effi-ciently autoregulated under certain conditions. Although renal blood flow and GFR are relatively stable under most conditions, there are circumstances in which these variables change significantly.
Renal blood flow—or, more correctly, the effective renal plasma flow (ERPF)—may be estimated by measuring the disappearance of a tracer (e.g., Hippuran) from the blood following a single intravenous injection if the tracer used is cleared only by the kidneys.
It is vital that the flow of blood through the kidney be at a suitable rate to allow for filtration. Reduction of sympathetic stimulation results in vasodilation and increased blood flow through the kidneys during resting conditions.
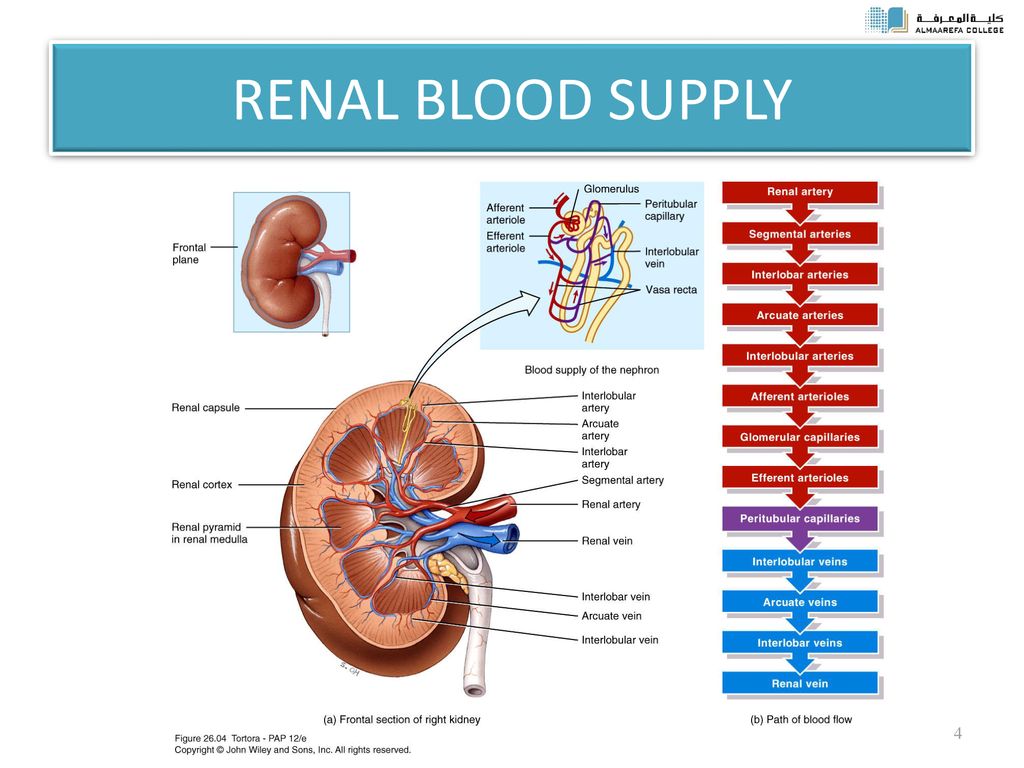
Blood enters the renal vascular system through the renal artery. This artery branches into the segmental arteries then the interlobar arteries, arcuate arteries, cortical radiate arteries then the afferent arterioles, glomerular capillaries where ...
Coronary blood flow can be limited by arterial thrombi or spasm. Congenital abnormalities of the left coronary artery may cause myocardial ischemia and The urine should be examined for evidence of diabetes mellitus and renal disease, since both these conditions may accelerate atherosclerosis.



















![PDF] A Newtonian Model on the Two Phase Renal Blood Flow in ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/80f376923e9c2f88df269c467a657b89fd9f52bb/1-Figure1-1.png)




0 Response to "36 renal blood flow diagram"
Post a Comment