42 profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram
Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for wind chimes is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 40 * Profit or Loss 32 20 24 PRICE ... Transcribed image text: 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for sports Watches is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 90 Profit or Loss 80 70 60 PRICE (Dollars per watch) 50 ...
4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 Profit or Loss o 70 ATC 60 2 50 40 ...
Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram
Does maximizing profit (producing where MR = MC) imply an actual economic profit? The answer depends on the relationship between price and average total cost. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a ... Transcribed image text: 6. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Consider a competitive market for shirts. The following graph shows the daily cost ...
Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. Suppose that the market for air fresheners is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost ... Profit Maximisation Theory: In the neo-classical theory of the firm, the main objective of a business firm is profit maximisation. The firm maximises its profits when it satisfies the two rules. MC = MR and the MC curve cuts the MR curve from below Maximum profits refer to pure profits which are a surplus above the average cost of production. Question: Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for polo shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily ... Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Consider a competitive market for shirts. The following graph shows the. labeled graph; makes sure you indicate where the optimal consumption now 3 ($5) or $15 and the price of good Y is now 3($10) or $30), the budget line Giffen goods are a type of goods whose demand curve is an upward sloping line.
Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for black sweaters is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. In the short run, at a market price of $15 per sweater, this firm will choose to 97%(30). Question: Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. 3. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for frying pans is a perfectly competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. 100 T 90 80 Profit or LoSS TC e 70 60 50 AVC 20 10 10152025 35404550 QUANTITY (Thousands of pans) In the short run, at a market price of ... In Figure 5.3, the MR curve is shown in blue. To find the profit maximizing point, set Q to the amount where the MR and MC curves intersect. These will be sold at price P m.Any other quantity will give a smaller profit (the red area on the graph). 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of ...2 answers · Top answer: As Figure 1 shows, an upward sloping marginal cost (MC) curve is the firm's supply curve. Therefore, ...
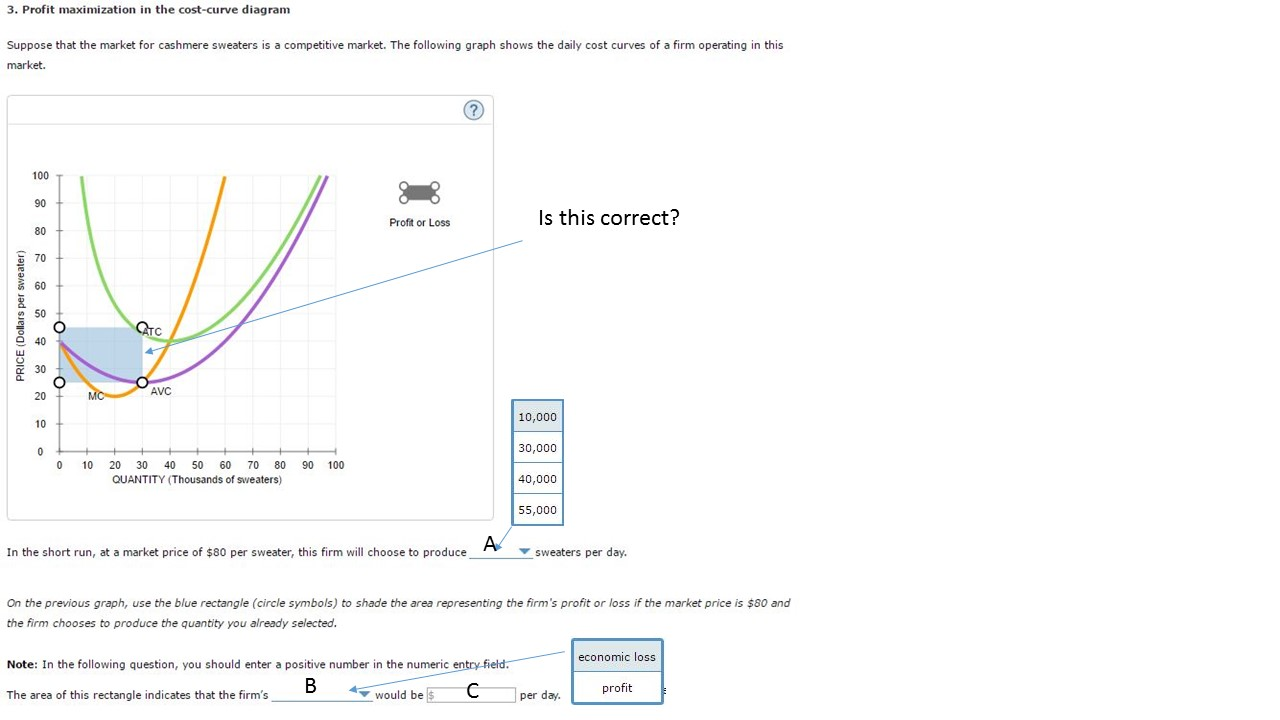
Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram | Chegg.com. 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for cashmere sweaters is a perfectly competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market 100 90 80 Profit or Loss 70 50 50 PRICE (Oolars per ATC 40 30 20 MC AVC 10 ... Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. Suppose that the market for dress shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost ... R(q)=100q, equivalent to saying that the firm sells at a market price of $100. The profit maximizing quantity is given by: q* 25. 100 4q 0 dq d (q) 100q 120 2q2 = = − = Π Example: Imagine that a firm has costs given by C(q)=420 + 3q + 4q2 and revenues given by R(q)=100q – q2. The profit maximizing quantity is given by: q* 9.7. 100 2q 3 8q ... Transcribed image text: 6. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Consider a competitive market for shirts. The following graph shows the daily cost ...
Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a ...
Does maximizing profit (producing where MR = MC) imply an actual economic profit? The answer depends on the relationship between price and average total cost.




0 Response to "42 profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram"
Post a Comment