42 force diagram roller coaster loop
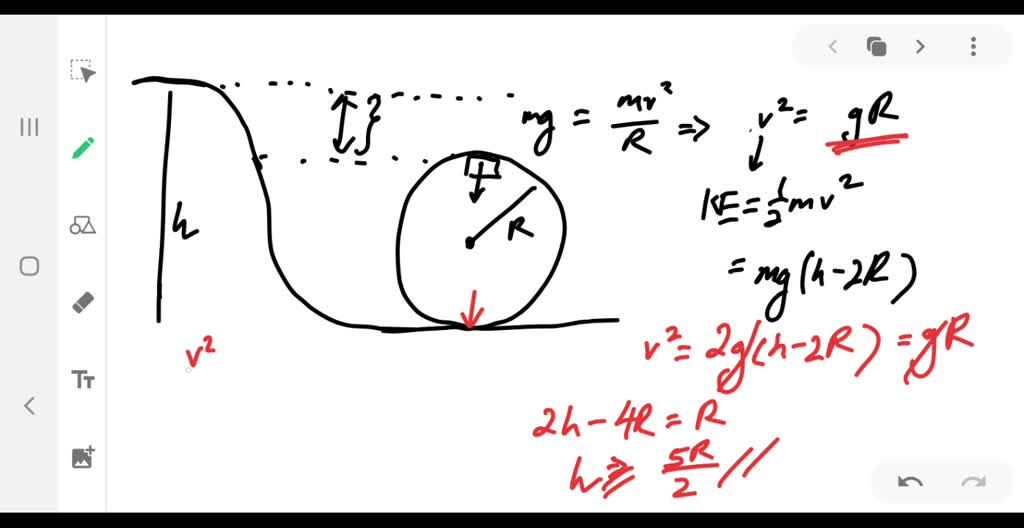
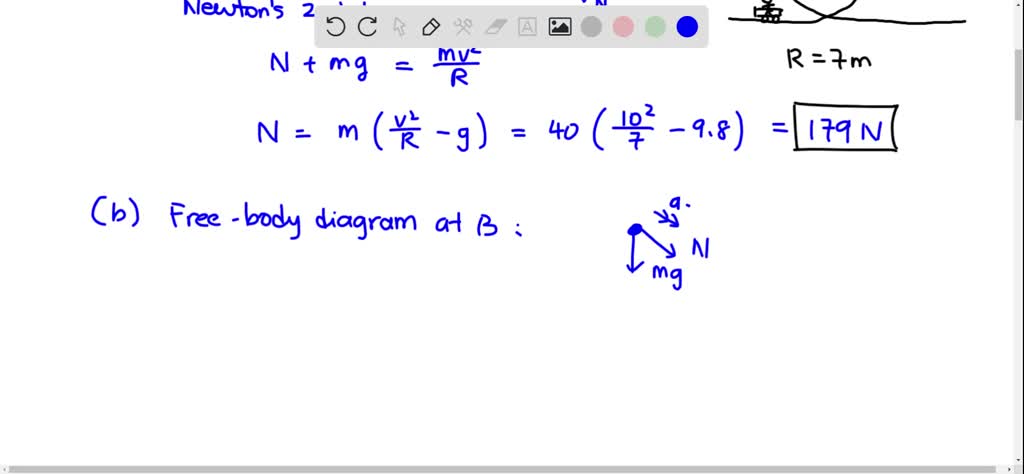
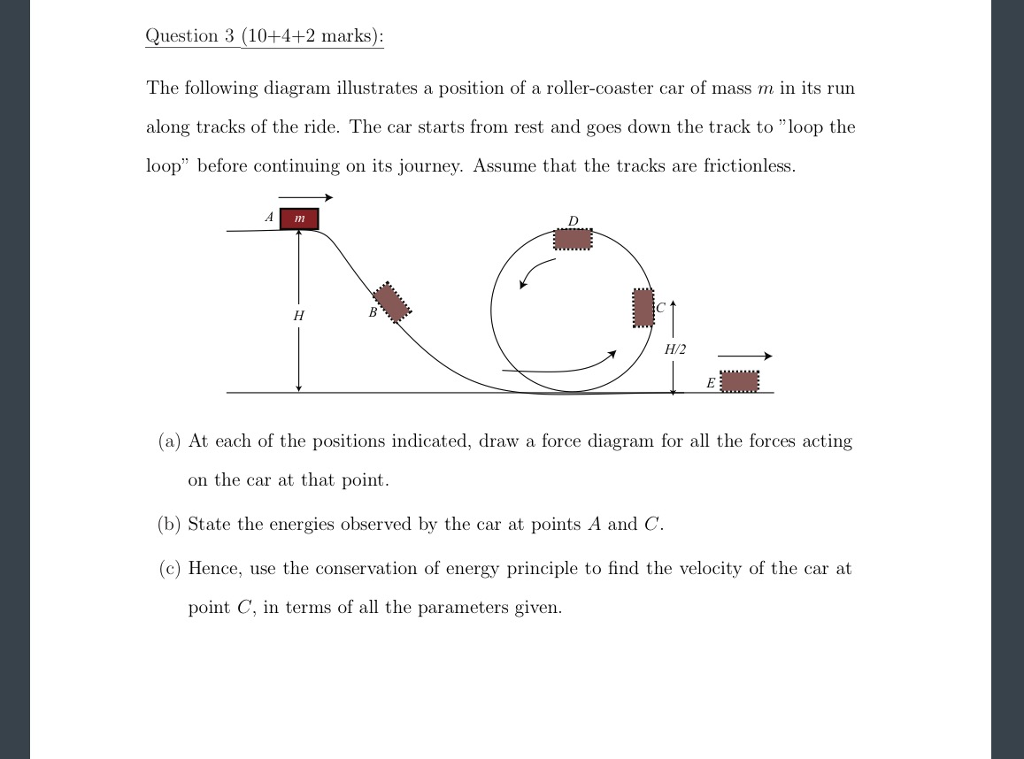
Solving for Centripetal Force using a Free Body Diagram A 70 kg student is riding a roller coaster and is at the top of the vertical loop. The loop has a radius of 16 m, and the car's velocity at the top is 12 m/s. The above discussion and force analysis applies to the circular-like motion of a roller coaster car in a clothoid loop. The second ... Roller Coaster Loop Problem. A roller-coaster car initially at position a position on the track a height h above the ground begins a downward run on a long, steeply sloping track and then goes into a circular loop of radius R whose bottom is a distance d above the ground. Ignore friction.
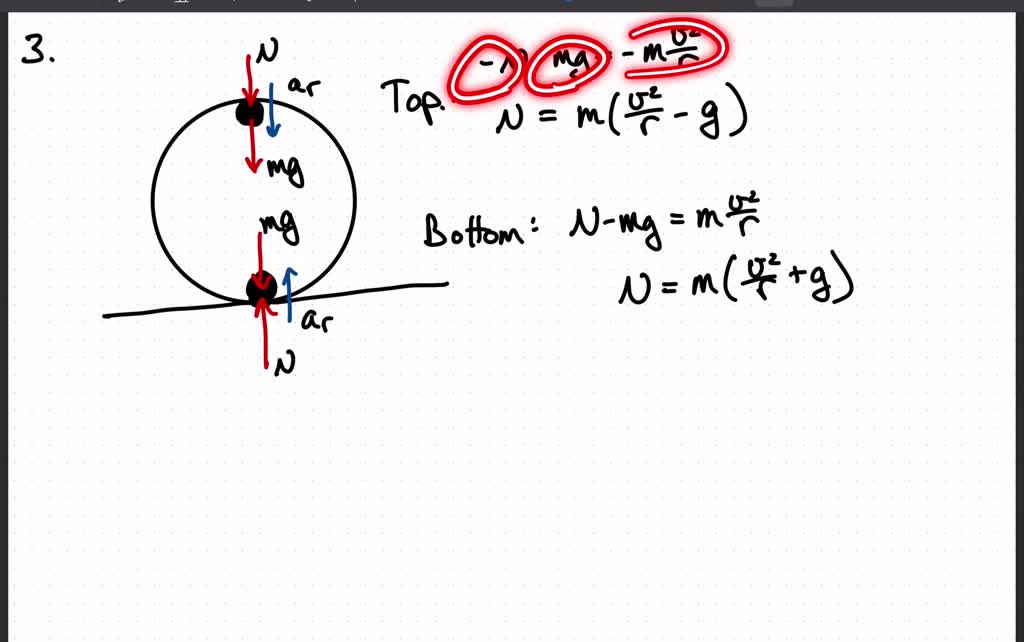
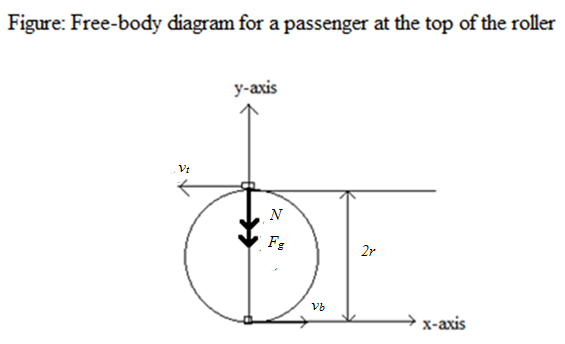
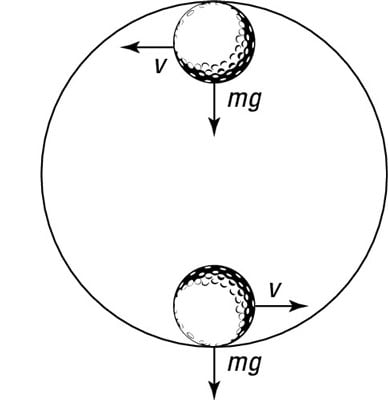
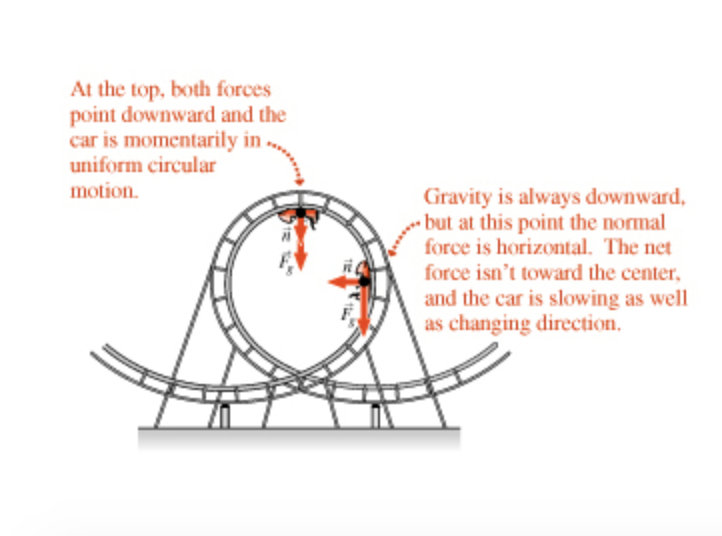
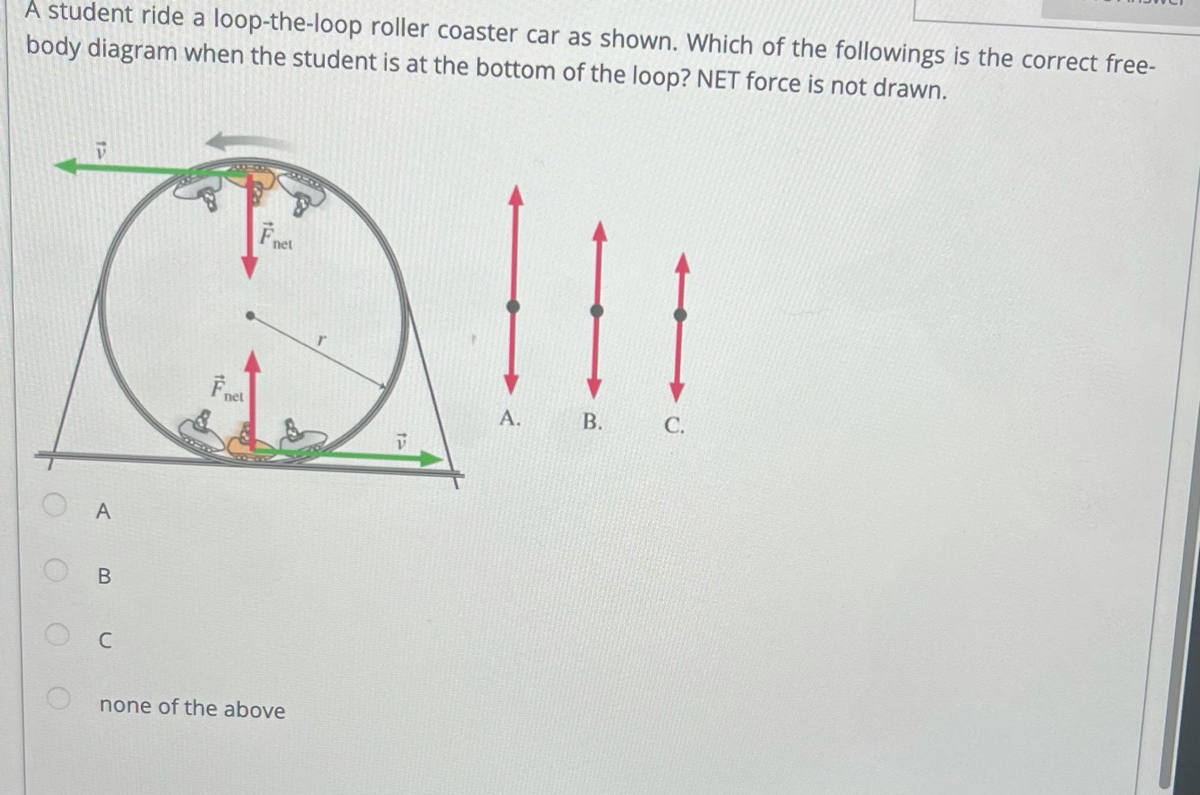
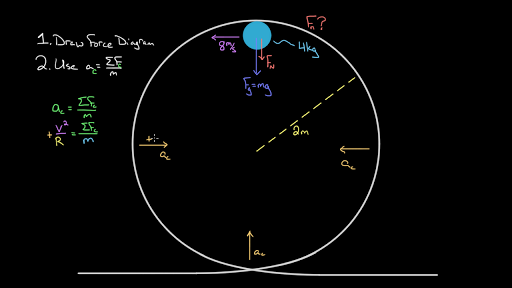
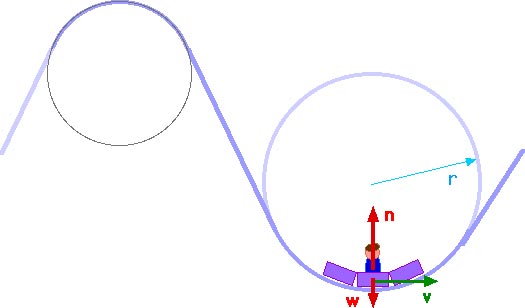
The figure shows the roller-coaster free-body diagram at the bottom of the loop. ! Since the net force is toward the center (upward at this point), n > F G .! This is why you “feel heavy” at the bottom of the valley on a roller coaster. ! The normal force at the bottom is larger than mg. Slide874$ CHAPTER8_LECTURE8.1$ 12
Force diagram roller coaster loop
The acceleration experienced by riders on roller coasters can be quite high, as much as 3-6 g (which is 3-6 times the force of gravity). In summary, the physics of roller coasters (in general) is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy (high speed), and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration ... Negative G-Force Tolerance. The human body exhibits alarming symptoms at just -2gz and on a coaster a level higher than -1gz would be considered dangerous. At -1gz, humans exhibit a sense of pressure in their head. At -2gz, there will be a severe headache, nose bleeds and swelling of the eyelids. Keywords: Acceleration, force, roller coaster, loop, clothoid ... The grid has been kept in the diagram to facilitate comparison with the similar, ...
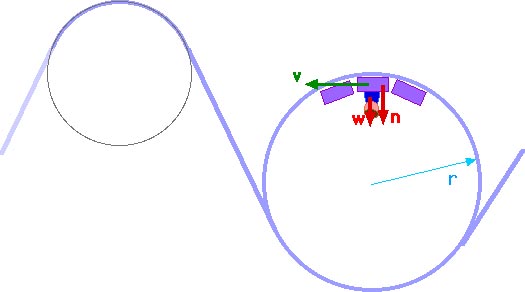
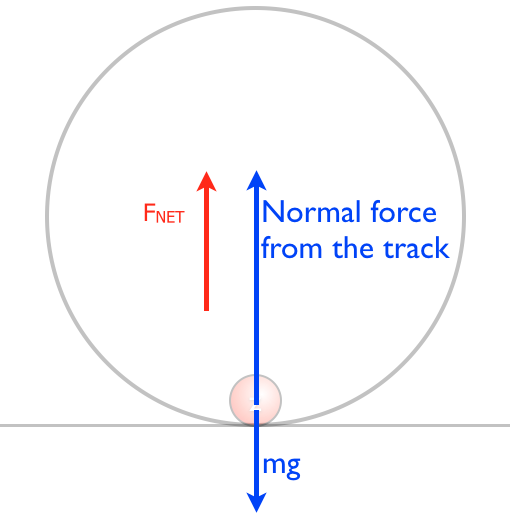
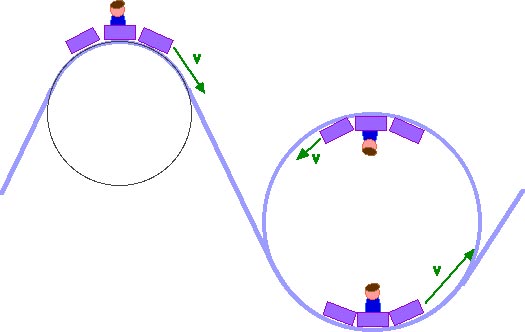
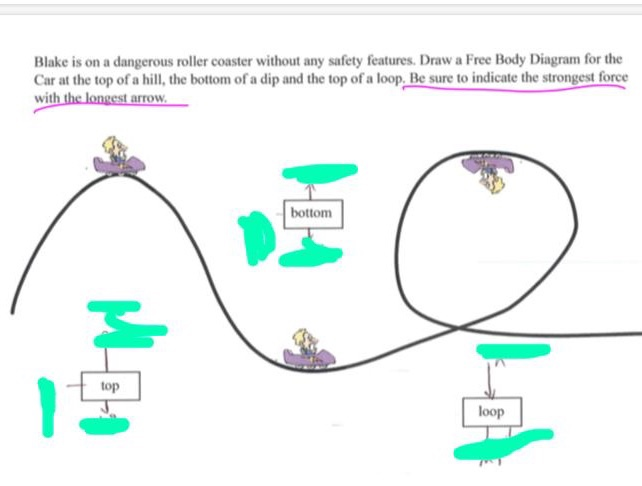
Force diagram roller coaster loop. If you have ever been on a roller coaster ride and traveled through a loop, then you have likely experienced this small normal force at the top of the loop ... The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the bottom of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed upwards and Force of Gravity is pointed downwards. This gives us a net force equation of Fnet = Fn - Fg. The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the left of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed rightwards and ... Analyzing the force diagrams of both positions we arrive at: Notice that at the bottom of the loop the forces act in opposite directions and at the top of the loop, the forces act in the same direction. This will affect how net force is calculated. At the bottom: Fnet = Fnorm – Fgrav. At the top: Fnet = Fnorm + Fgrav. Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Draw the free body diagrams for a coaster at the boom and top of a loop and write the equaons for the net force. mg F net F N F net =ma = ma c The net force in the loop must be centripetal force F net = F N +(– mg) ...
We might ask how fast the coaster can go until the rider just (barely) looses contact with the seat. That means the normal force between seat and rider is zero. That occurs for. n = mg - m v 2 / r = 0. m v 2 / r = mg. v 2 / r = g. v 2 = g r. We have described this with a diagram showing a guest on the top of a hill of a roller coaster. The Physics of Roller Coaster Loops. ... then the net force must be used with the free body diagram to determine the normal force. This two-step process is shown below for the top and the bottom of the loop. Bottom of Loop F net = m * a F net = (864 kg) * (26.3 m/s 2, up) F net = 22 723 N, up ... Keywords: Acceleration, force, roller coaster, loop, clothoid ... The grid has been kept in the diagram to facilitate comparison with the similar, ... Negative G-Force Tolerance. The human body exhibits alarming symptoms at just -2gz and on a coaster a level higher than -1gz would be considered dangerous. At -1gz, humans exhibit a sense of pressure in their head. At -2gz, there will be a severe headache, nose bleeds and swelling of the eyelids.
The acceleration experienced by riders on roller coasters can be quite high, as much as 3-6 g (which is 3-6 times the force of gravity). In summary, the physics of roller coasters (in general) is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy (high speed), and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration ...

Solved You Ride A Roller Coaster With A Loop The Loop Compare As Best You Can The Normal Force That The Seat Exerts On You To The Force That Earth Exerts On You When You
Solved Roller Coaster Car At The Nzm 3 Consider An Upowered When Instant It Passes The Peak Of A Vertical Loop That Is The Car Is Upside Down See Figure N2 9 Do Not Ignore Car

Roller Coaster Simulator Javascript Simulation Applet Html5 Open Educational Resources Open Source Physics Singapore
Solved In A Roller Coaster Loop A Passenger M 60 Kg Arrives At Point A Upside Down With A Speed Of 7 M S The Radius Of The Loop Is 12m A Find

Expressing Starting Position Of A Roller Coaster On A Track So That It Can Then Go Through A Loop De Loop By Unknowns Physics Stack Exchange














0 Response to "42 force diagram roller coaster loop"
Post a Comment