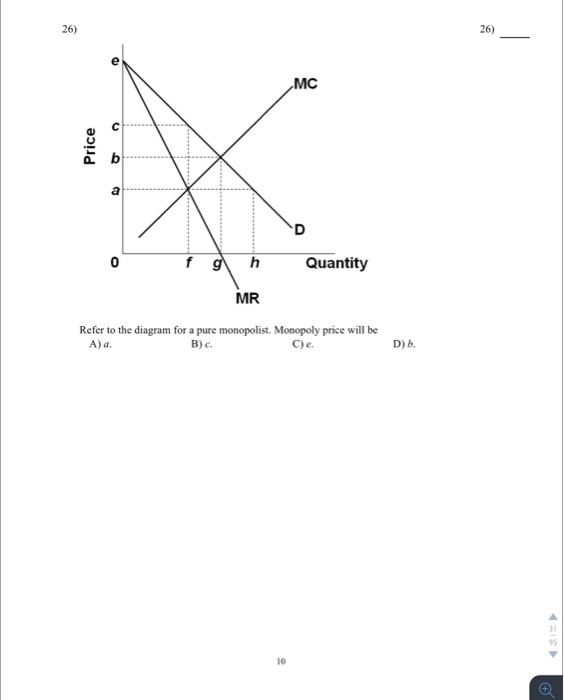
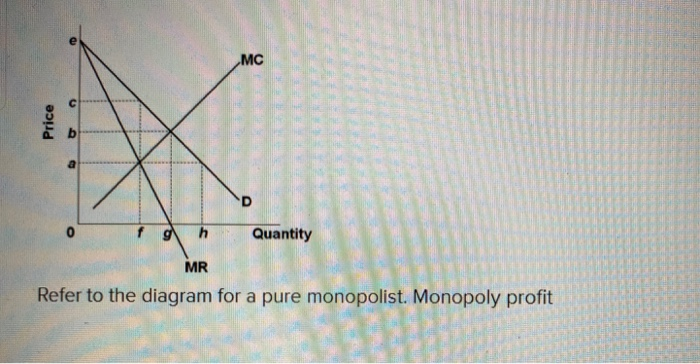
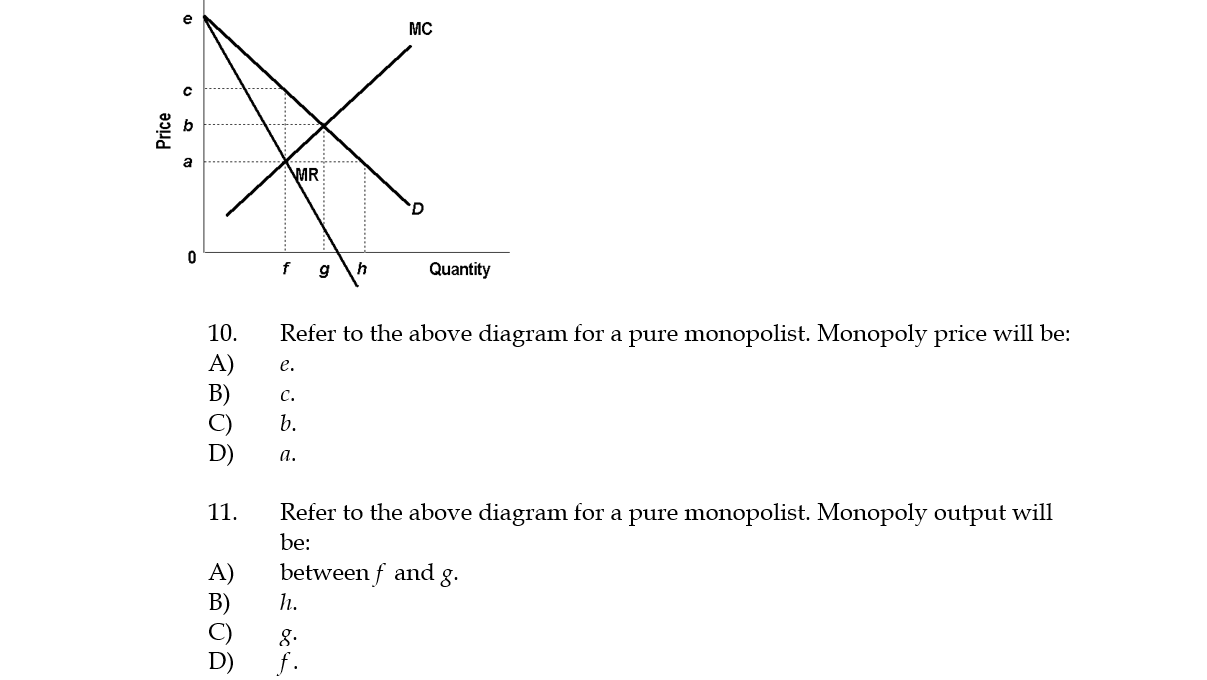
41 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be
Refer To The Diagram For A Pure Monopolist Monopoly Output ... Refer To The Diagram For A Pure Monopolist Monopoly Output ... Pure Monopoly; ... Solved: 8. Price-discriminating Monopolist Aa Aa Daesun, A ... Business Game: Monopolist App for iPhone - Free Download ... 9. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: A) an economic profit of ABHJ. B) an economic profit of ACGJ. C) a loss of GH per unit. D) a loss of JH per unit. 10. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be: A) e. B) c. C) b. D) a. 11.
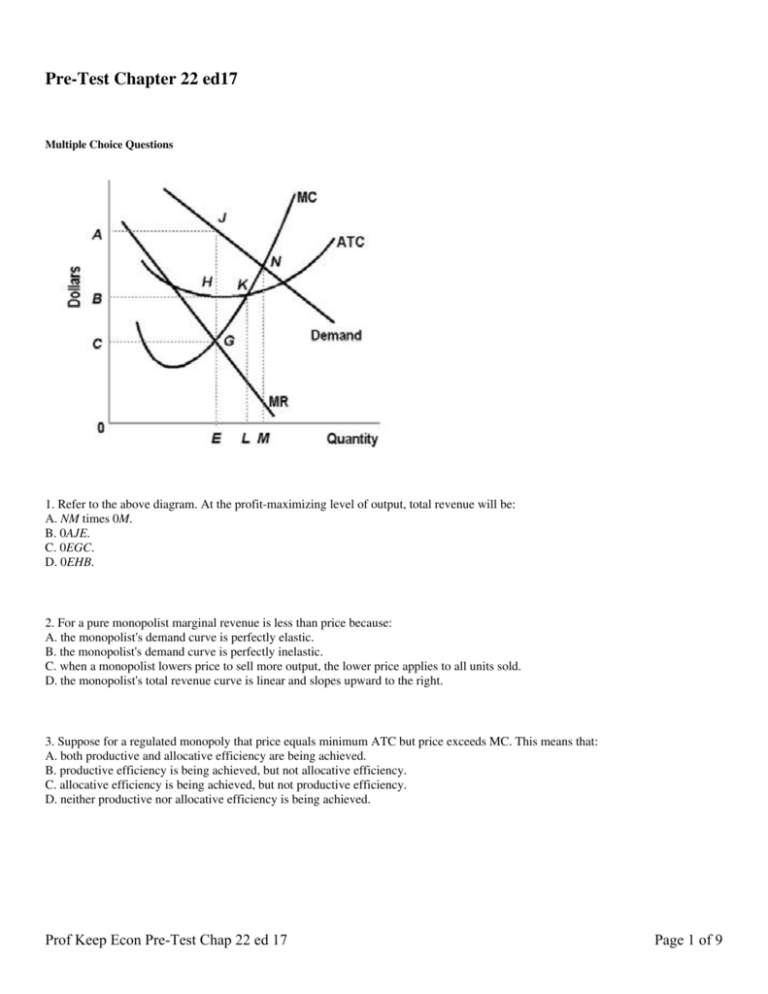
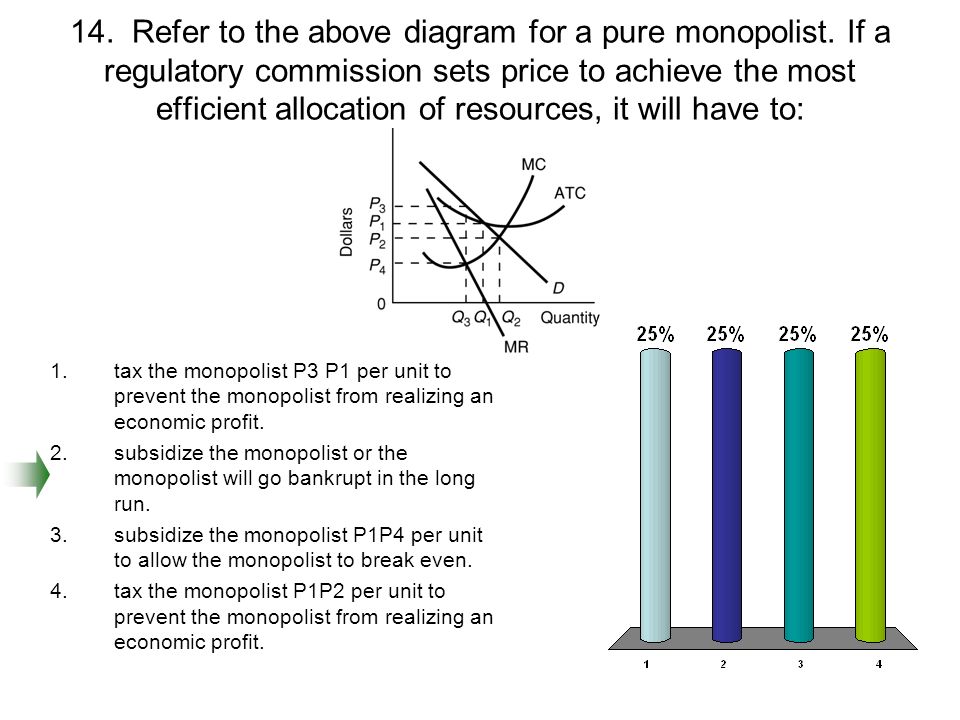
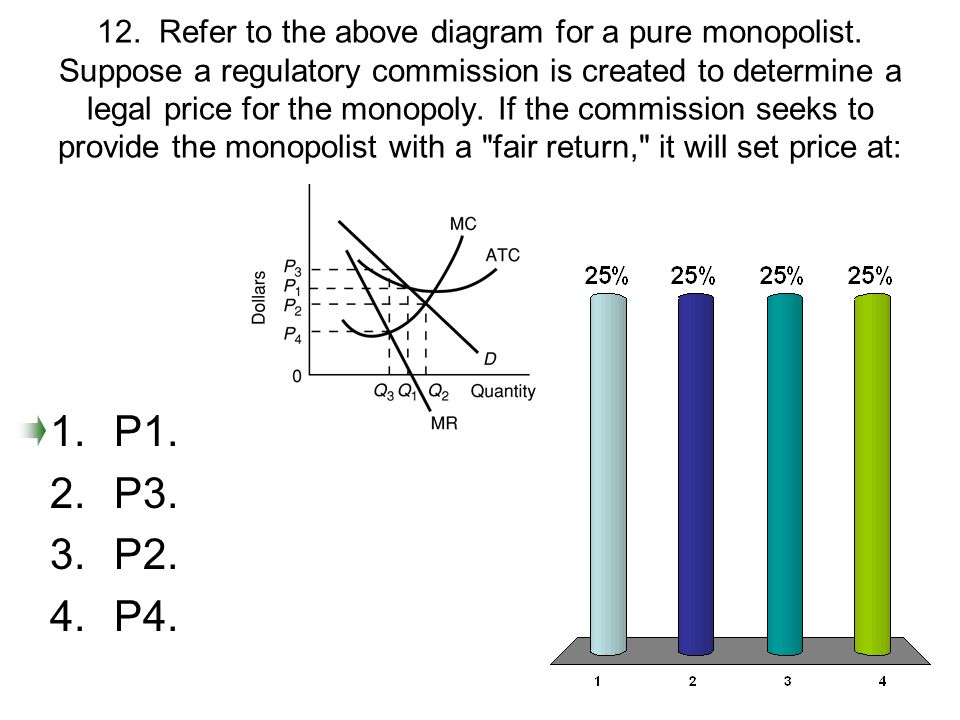
155. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. If a regulatory commission sets the price to achieve the socially optimal allocation of resources, it will have to A. tax the monopolist P 3 P 1 per unit to prevent the monopolist from realizing an economic profit. B. subsidize the monopolist or the monopolist will go bankrupt in the long run. C. subsidize the monopolist P 1 P 4 per unit to ...
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be
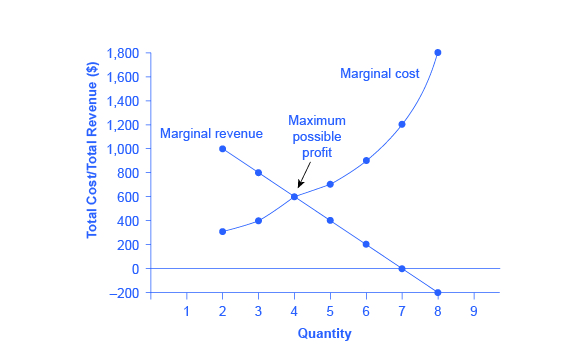
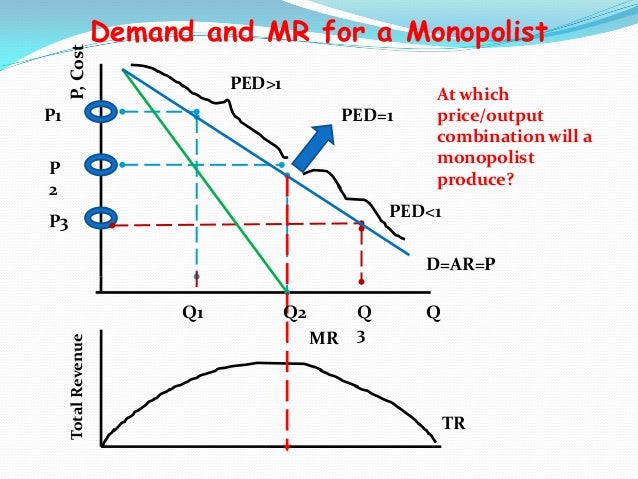
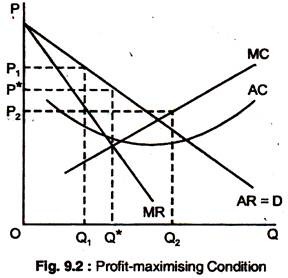
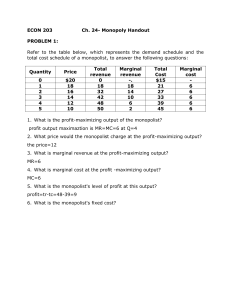
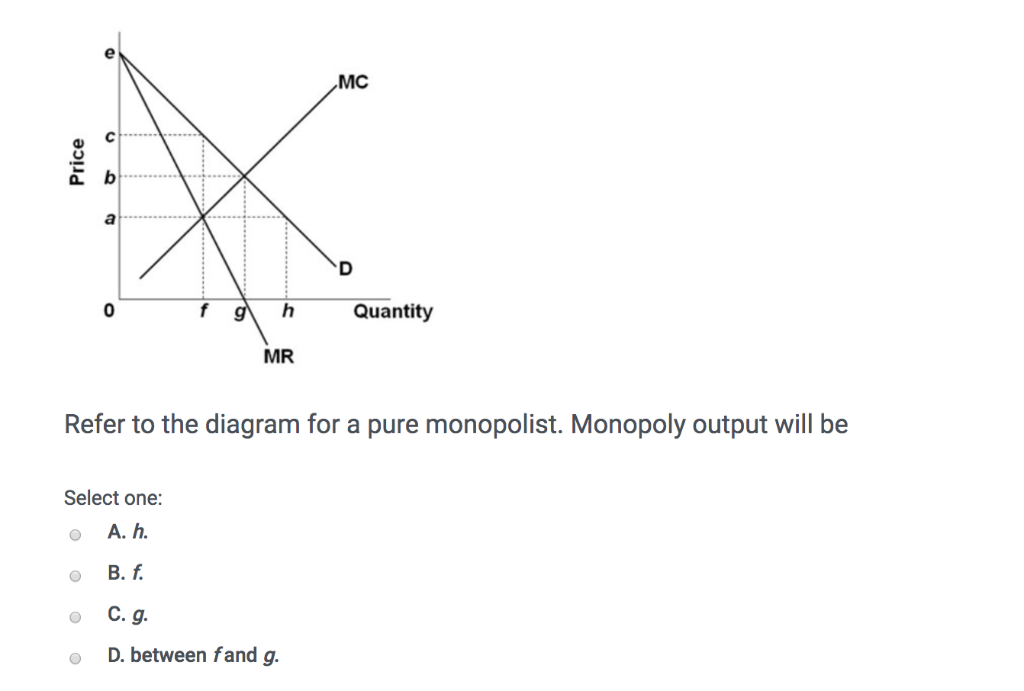
In Step 1, the monopoly chooses the profit-maximizing level of output Q 1, by choosing the quantity where MR = MC. In Step 2, the monopoly decides how much to charge for output level Q 1 by drawing a line straight up from Q 1 to point R on its perceived demand curve. Thus, the monopoly will charge a price (P 1 ). 61. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be: A. between f and g. B. h. C. g. D. f. 62. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: A. cannot be determined from the information given. B. will be ae per unit sold. C. will be bc per unit sold. D. will be ac per unit sold. 63. (Supposed to be a graph) Refer to the diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission set a maximum price of P1, the monopolist would produce output a.) Q2 and realize a normal profit. b.) Q4 and realize a normal profit. c.) Q3 and realize an economic profit. d.) Q4 and realize a loss.
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be. 160. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: profit of $480. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Short-run equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by: diagram c only. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit cannot be determined from the information given. If the industry depicted in the graph is purely monopolistic, the profit-maximizing price and quantity will be P 3 and Q 3. If the industry depicted in the graph comprises only one seller, the profit-maximizing price and quantity will be ... Refer to the above diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission set a maximum price of P 1, the monopolist would produce output: A. Q 2 and realize a normal profit. B. ... Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be: A. e. B. c. C. b. D. a. 62. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: A. cannot be determined from the information given. B. will be ae per unit sold. C. will be bc per unit sold. D. will be ac per unit sold.
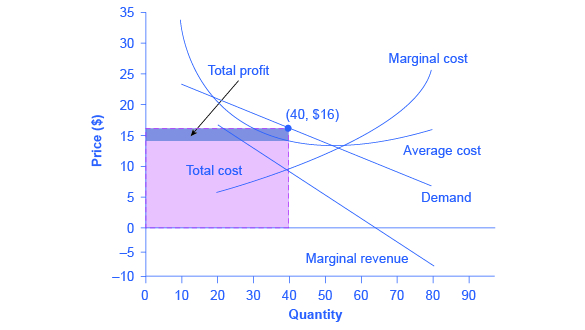
Refer to the above data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's total profit will be:$82. A pure monopolist is producing an output such that ATC = $4, P = $5, MC = $2, and MR = $3. This firm is realizing:an economic profit that could be increased by producing more output. D)Successful price discrimination will generally result in a lower level of output than would be the case under a single-price monopoly 20) If a regulatory commission imposes upon a nondiscriminating natural monopoly a price that is equal to marginal cost and below average total cost at the resulting output, then Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at: Price D f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be A) a. B). Ce. D) b. Price o f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A . B) g. Ch. D) between fand g. 28) When a pure monopolist is producing its profit-maximizing output, price will A) equal MR. 60.
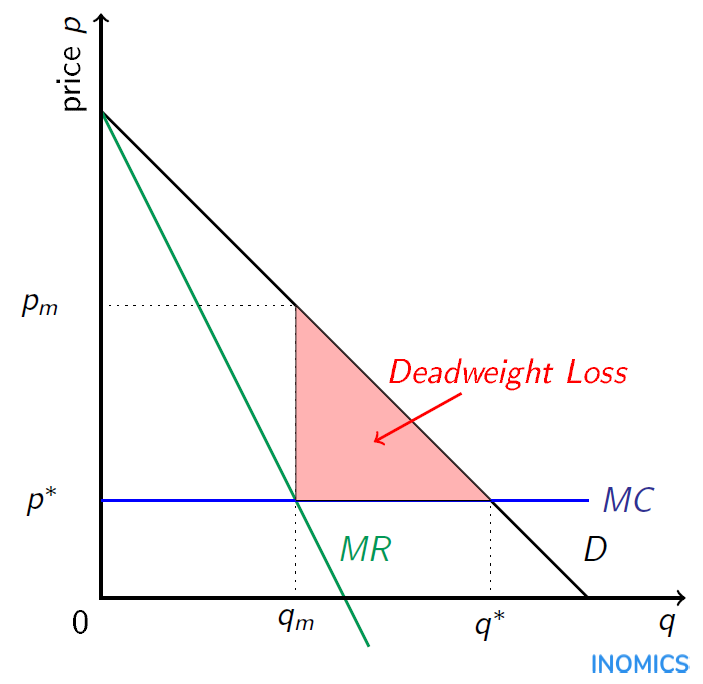
Board: AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB. A pure monopolist in an industry is a single seller. It is rare for a firm to have a pure monopoly - except when the industry is state-owned and has a legally protected monopoly. Monopoly Price Output and Profit - revision video. Monopoly profit analysis. Monopoly Graph. A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where MR = MC. This will be at output Qm and Price Pm. Compared to a competitive market, the monopolist increases price and reduces output. Red area = Supernormal Profit (AR-AC) * Q. Blue area = Deadweight welfare loss (combined loss of producer and consumer surplus ... Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Will be ae per unit sold. If this firm is able to price discriminate between children and adults its economic profit will be. P2 mc q1c q2. Monopoly output will be. Suppose that a pure monopolist can sell 4 units of output at 2 per unit and 5 units at 175 per unit. Monopoly price will be:c. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will:f . Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit:cannot be determined from the information given. In the short run a pure monopolist's profit:may be positive, zero, or negative. Purely competitive firms and pure monopolists are ...
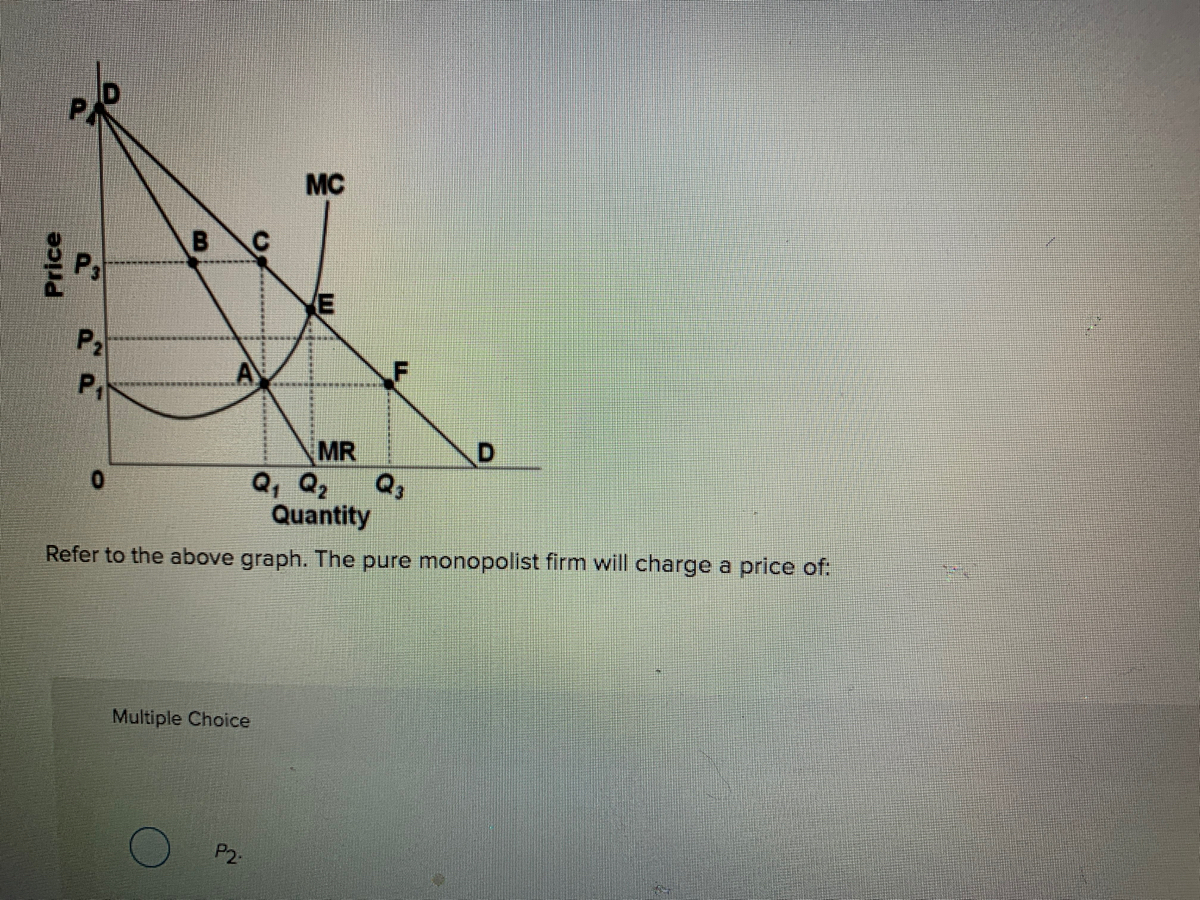
Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3.. B. price P3 and producing output Q3.. C. price P2 and producing output Q2.. D. price P1 and producing output Q1.. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist.

The Graph Shows The Marginal Cost Curve Average Total Cost Curve And Demand Curve Of A Natural Monopoly Draw A Point To Indicate The Output And Price Under An Average Cost Pricing
Question 6 0 out of 1 points Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If a regulatory commission seeks to achieve the most efficient allocation of resources to this line of production, it will set a price of: Selected Answer: [None Given] Correct Answer: P 2.
131. Comparing a pure monopoly and a purely competitive firm with identical costs, we would find in long-run equilibrium that the pure monopolist's A) price, output, and average total cost would all be higher. B) price and average total cost would be higher, but output would be lower. C) price, output, and average total cost would all be lower.

Suppose A Pure Monopolist Is Faced With The Cost Data Shown In The Table On The Left And The Demand Schedule Shown On The Right A Calculate The Missing Total Revenue And Marginal Revenue
Price D f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be A) a. B). Ce. D) b. Price o f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A . B) g. Ch. D) between fand g. 28) When a pure monopolist is producing its profit-maximizing output, price will A) equal MR.
Monopoly output will be. P2 mc q1c q2. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Subsidize the monopolist or the monopolist will go bankrupt in the long run. 1 refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Cannot be determined from the information given. In the short run a pure monopolists profitmay be positive zero or negative.
Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: Answer cannot be determined from the information given. will be ae per unit sold. will be bc per unit sold. will be ac per unit sold. 2.667 points Question 2 A profit-maximizing monopolist will set its price: Answer as far above ATC as possible. along the elastic portion of.
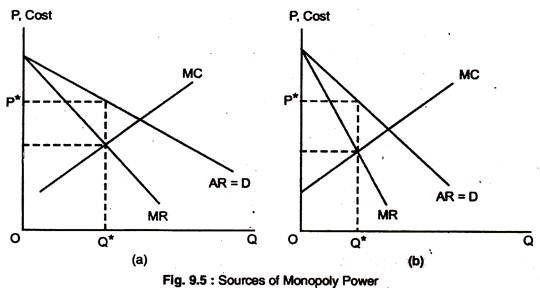
For example, a small town may have only one gas station that sets prices a little lower than the monopoly price (i.e., it does not act as a pure monopolist) in order to keep profits low enough to deter others from entering the market. Alternatively, a firm may build a facility larger than needed as a threat that it will increase production if ...
Refer to the diagram below for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A) a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3. B) price P3 and producing output Q3. C) price P2 and producing output Q2. D) price P1 and producing output Q1.
less elastic than that of a pure monopolist, but more elastic than that of a purely competitive seller. ... Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. 5. R-1 F25030. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically ...
Comparing a pure monopoly and a purely competitive firm with identical costs, we would find in long-run equilibrium that the pure monopolist's: A. price, output, and average total cost would all be higher.

Refer To The Graph Above For A Pure Monopoly If The Government Regulated The Monopoly And Made It Charge The Socially Optimal Price This Price Would Be A Higher Than The Profit Maximizing
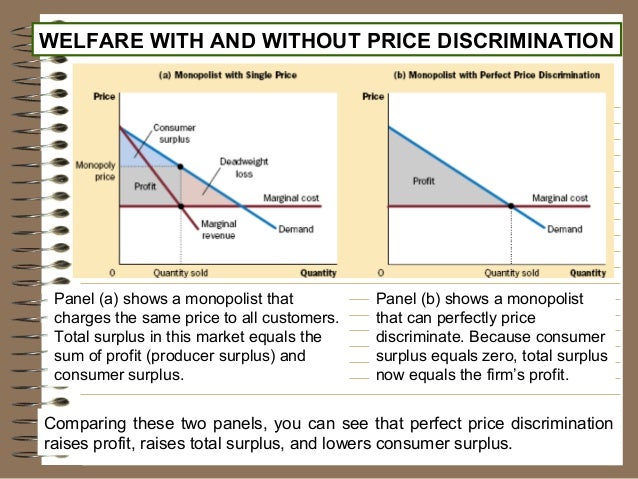
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be. f. A single-price monopoly is economically inefficient because, at the profit-maximizing output, society values additional units of the monopolized product more highly than it does the alternative products those resources could otherwise produce.
64. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output Q average variable cost is QJ. True False 65. Refer to the above diagrams. Both firms are selling their products in purely competitive markets. True False 66. Refer to the above diagrams. The demand for Firm A's product is perfectly elastic. True False 67. Refer to the ...
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be. c. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be. f. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit. cannot be determined from the information given. In the short run, a monopolist's economic profits.
(Supposed to be a graph) Refer to the diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission set a maximum price of P1, the monopolist would produce output a.) Q2 and realize a normal profit. b.) Q4 and realize a normal profit. c.) Q3 and realize an economic profit. d.) Q4 and realize a loss.
61. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be: A. between f and g. B. h. C. g. D. f. 62. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: A. cannot be determined from the information given. B. will be ae per unit sold. C. will be bc per unit sold. D. will be ac per unit sold. 63.
In Step 1, the monopoly chooses the profit-maximizing level of output Q 1, by choosing the quantity where MR = MC. In Step 2, the monopoly decides how much to charge for output level Q 1 by drawing a line straight up from Q 1 to point R on its perceived demand curve. Thus, the monopoly will charge a price (P 1 ).

Use The Graph To Answer These Questions For An Unregulated Pure Monopolist A What Is The Price And Quantity That Will Be Charged By The Monopoly B What Area Represents The Efficiency









0 Response to "41 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be"
Post a Comment