40 two step reaction diagram
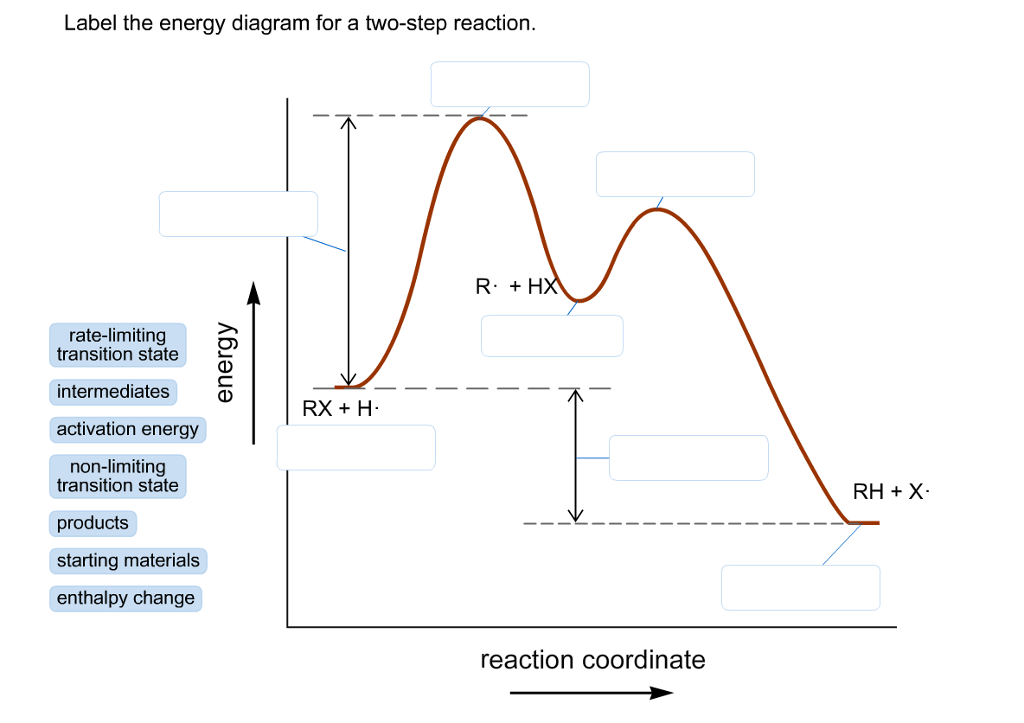
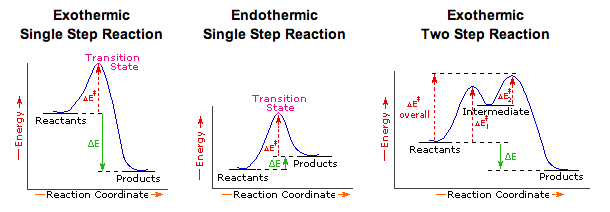
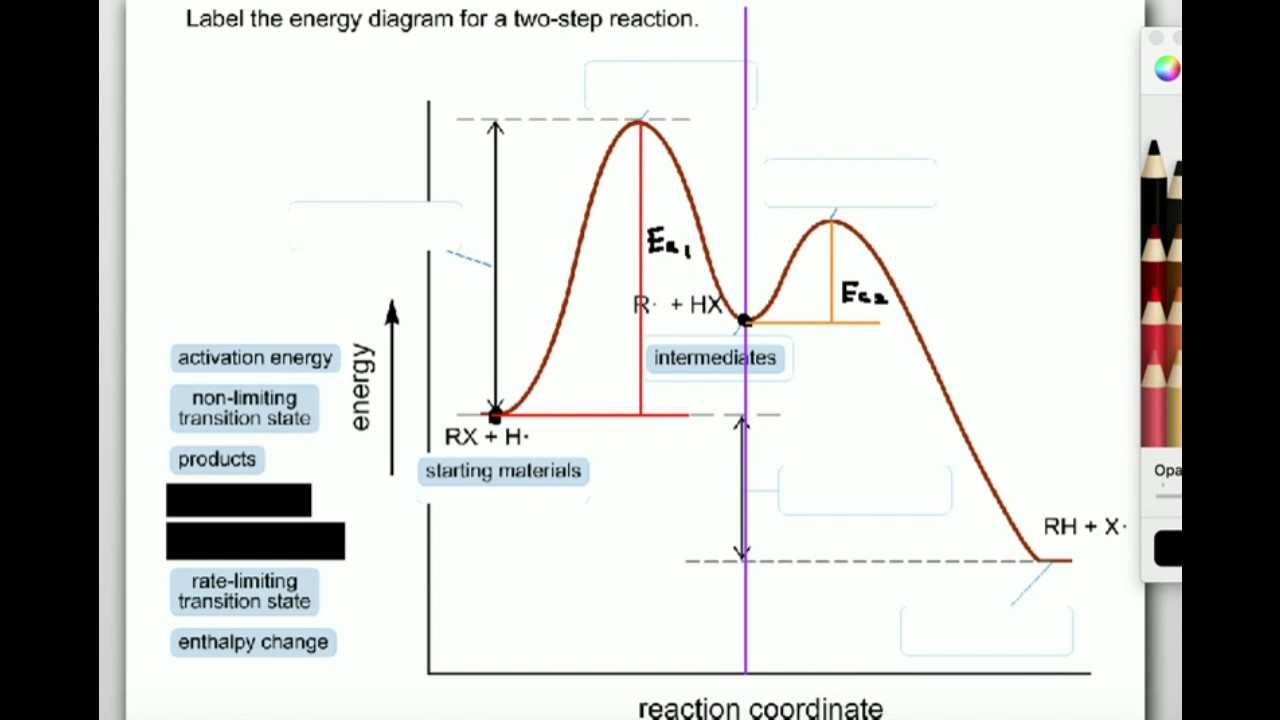
Oct 06, 2018 · This chemistry video tutorial focuses on potential energy diagrams for endothermic and exothermic reactions. Label the energy diagram for a two step reaction. Heroin C21h23no5 Pubchem The activation energy for each step is labeled e a1 and e a2. Label the energy diagram for a two step reaction. Endothermic because energy is needed to break the a b bond. Step 1: 2X (g)→X2 (g) Step 2: X2 (g)+Y (g)→X2Y (g) The diagram above shows the progress of the chemical reaction for the synthesis of ammonia from its elements. The adsorption of the N2 molecules on the surface of Ru weakens the triple bond between the two N atoms.
Draw a reaction energy diagram for a two-step reaction that has an endothermic first step and an exothermic second step. Label the reactants, transition states, reaction intermediate, activation energies, and enthalpy differences. Step-by-step solution. 100% (4 ratings) for this solution.

Two step reaction diagram
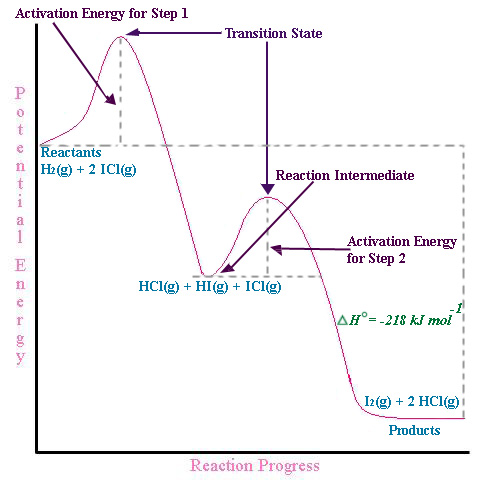
The reaction involves two steps, step 1 is the slowest step and step 2 is the fastest step. Both steps are exothermic. Indicate on the diagram the overall enthalpy change of the reaction, the reaction for the transition states and intermediate states. The reaction is a reaction between hydrogen gas and brown vapor of iodine monochloride. II III 8888 III Reaction cannot happen Which step is the rate determining step in the mechanism of a reaction possessing the below reaction energy diagram? AG Reaction Coordinate 1st 2nd 3rd ооооо 4th 5th Which of the following reaction coordinate diagrams. Using Molecularity to Describe a Rate Law. The molecularity of an elementary reaction is the number of molecules that collide during that step in the mechanism. If there is only a single reactant molecule in an elementary reaction, that step is designated as unimolecular; if there are two reactant molecules, it is bimolecular; and if there are three reactant molecules (a relatively rare ...
Two step reaction diagram. The catalyzed reaction is the one with lesser activation energy, in this case represented by diagram b. Check Your Learning Reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. Both reactions involve a two-step mechanism with a rate-determining first step. Watch Complete videos @ www.LearningChemistryOnline.com Organic Chemistry 1 In this video, I go over how to properly label and explain a reaction mechanism diagram which is also referred to as an energy diagram or energy graph. I'll ... Sketch an energy diagram for a two-step reaction in which both steps are exergonic and in which the second step has a higher-energy transition state than the first. Label the parts of the diagram corresponding to reactant, product, intermediate, overall $\Delta G^{\dagger},$ and overall $\Delta G^{\circ}.$
One-step vs. Two-step RT-qPCR. RT-qPCR can be performed in a one-step or a two-step assay (Figure 1, Table 1). One-step assays combine reverse transcription and PCR in a single tube and buffer, using a reverse transcriptase along with a DNA polymerase. One-step RT-qPCR only utilizes sequence-specific primers. ChemistryQ&A LibrarySketch an energy diagram for a two-step reaction in which both steps are exergonic and in which the second step has a higher-energy transition state than the first. Label the parts of the diagram corresponding to reactant, product, intermediate, overall AG†, and overall AG°. Sketch an energy diagram for a two-step reaction in which both steps are exergonic and in which the second step has a higher-energy transition state than the first. This chemistry video tutorial focuses on potential energy diagrams for endothermic and exothermic reactions. It also shows the effect of a catalyst on the f... The diagram below shows the reaction progress of the two-step mechanism proposed. Notice how the reaction intermediate and the transition states do not last very long, but the intermediate can be isolated due to its fully formed bonds. Diagram of a Two-Step Reaction Mechanism Example with a Fast Reversible First Step then a Slow Step
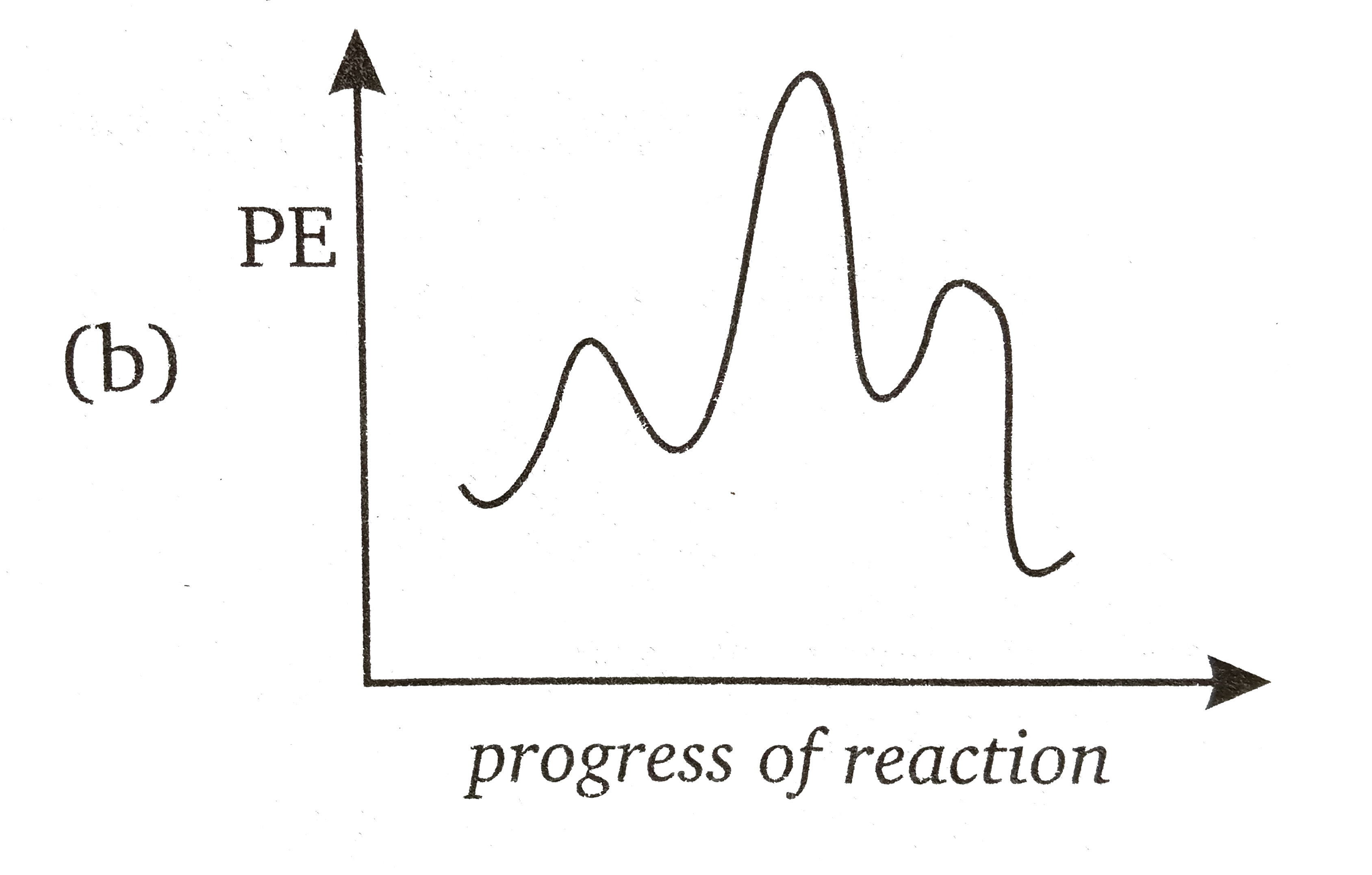
The reaction coordinate diagram for the ozone photolysis reaction is a little different from those above because this is an endothermic reaction. Together, the products O 2 and atomic O, have a higher energy than the reactant O 3 and energy must be added to the system for this reaction. Using Reaction Diagrams to Compare Catalyzed Reactions The two reaction diagrams here represent the same reaction: one without a catalyst and one with a catalyst. Identify which diagram suggests the presence of a catalyst, and determine the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction: Solution Two reactions are represented above. The potential-energy diagram for reaction I is shown below. The potential energy of the reactants in reaction Il is also indicated on the diagram. Reaction Il is endothermic, and the activation energy of reaction I is greater than that of reaction O Reaction Pathway Label the energy diagram for a two-step reaction. Q. A reaction coordinate diagram is shown below for the reaction of A to form E. Answer the following questions.i) Identify the transition state (s)?ii) W... Q. Which reaction coordinate diagram represents a reaction in which the activation energy, Ea, is 50 kj.mol-1 and the ΔHrxn is -15 kj. mol-1?
Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction, A → B → C, where the relative energy of these compounds is C < A < B, and the conversion of B → C is rate-determining. check_circle Expert Answer. Want to see the step-by-step answer? See Answer. Check out a sample Q&A here.
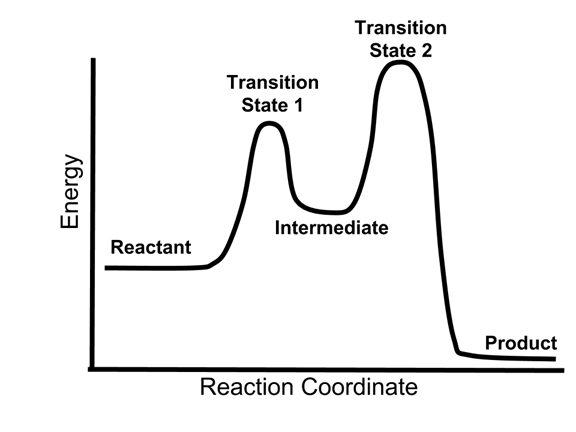
• An energy diagram for a two-step reaction with one intermediate. Energy Diagrams. 9 • Organic chemists use a technique called electron pushing, alternatively called arrow pushing, to depict the flow of electrons during a chemical reaction.
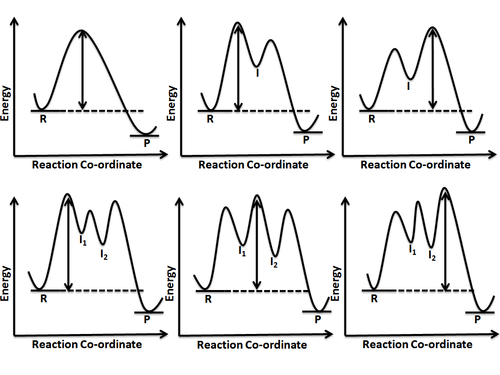
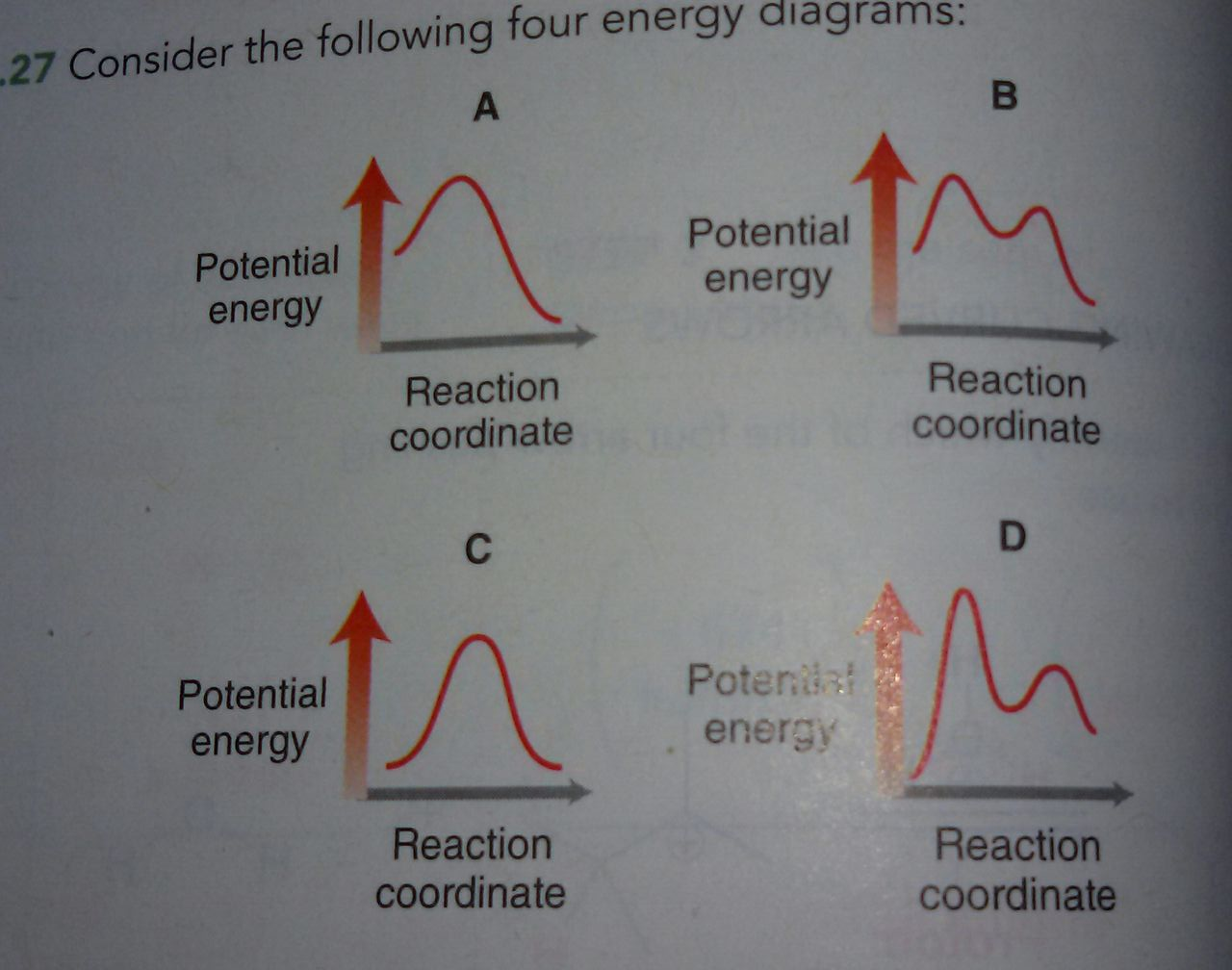
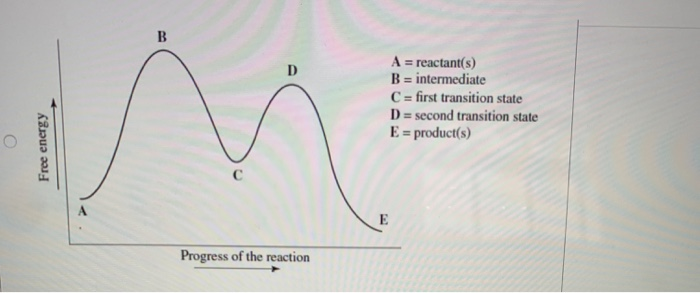
Transcribed image text: Choose the correct reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step reaction in which the first step is endergonic, the second step is exergonic, and the overall reaction is endergonic. Pay attention to the reactants, products, intermediates, and transition states A reactants) B = first transition state C = intermediate D = second transition state E =product(s) Free energy ...
In order to sketch this energy diagram we must make two notations. The first is that we are asked to have a two step process where both steps are exergonic, i.e. lower in energy than the previous starting point. The second notation we must make is that the transition state of the second step is higher in energy that the transition state of the first.
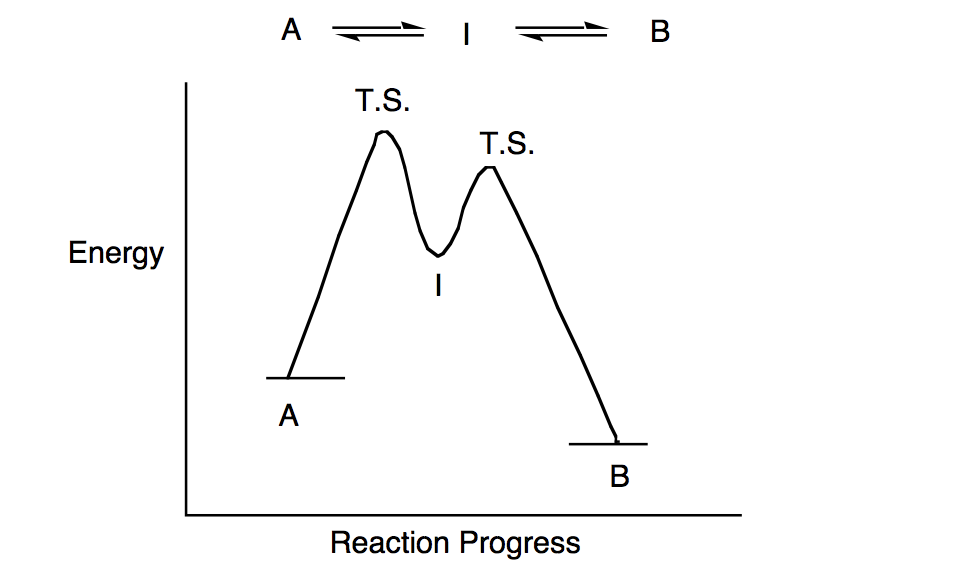
The energy diagram of a two-step reaction is shown below. In the above reaction, a reactant goes through one elementary step with a lower activation energy (transition state 1) to form the intermediate. The intermediate then goes through a second step (transition state 2) with the highest energy barrier to form the product.
Draw a reaction coordinate for the following catalyzed two-step exothermic reaction with the second step being the rate determining step:A -- B
Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction that is exothermic overall, and consists of a fast but endothermic first step, and a slow but exothermic second step. Indicate DG rxn, as well as DG 1 * and DG 2 * for the first and second activation energies, respectively. Label the positions corresponding to the transition states with an asterisk.
Solving Two Step Equations MY HOMEWORK Monday: algebra tile worksheet Tuesday: Tape Diagram Worksheet Wednesday: Solving Equations algebraically Worksheet Thursday: Homework practice worksheet Friday: Quiz No homework 7.EE.4a I CAN solve word problems leading to equations of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific
5.6: Reaction Energy Diagrams and Transition States. use a Reaction Energy Diagram to discuss transition states, Ea, intermediates & rate determining step. You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy ...

Draw A Labeled Reaction Energy Diagram For A Two Step Reaction With An Early First Transition State And A Late Second Transition State State Whether The Transition States Resemble The Starting Material Intermediate Or
Energy Diagram: The diagram which indicates the number of steps in which the reaction gets completed and the energy required for each step can be shown by plotting graph of rate of reaction versus ...
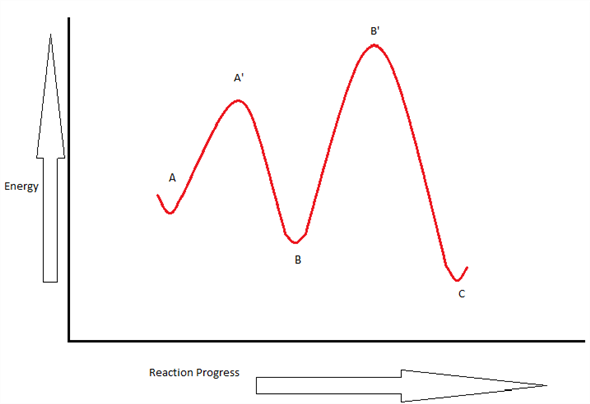
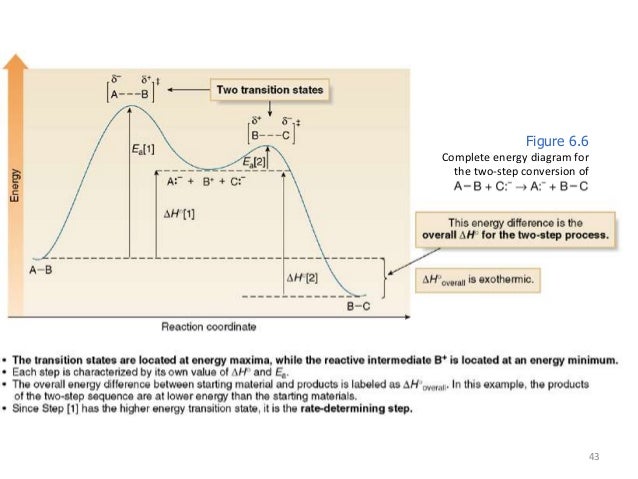
A Two-Step Reaction Mechanism. The transition states are located at energy maxima. The reactive intermediate B+ is located at an energy minimum. Each step has its own delta H and activation energy. The overall energy difference between the starting materials and products is delta H overall. Step 1 has the higher transition energy state, thus it is the rate-determining step.
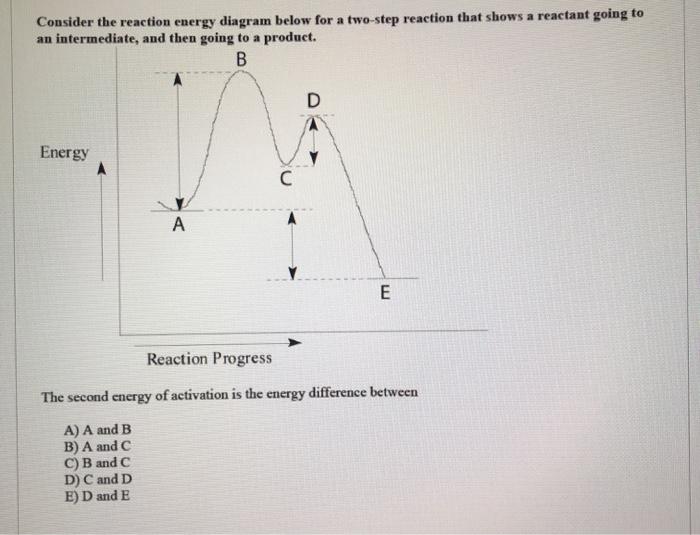
The reaction energy diagram below represents a two step reaction mechanism. Reaction coordinate – would be To determine the activation energy of the second step in the reaction, the energy of species subtracted from the energy of species Enter the letter that represents the appropriate chemical species. QUESTION 1 Which energy difference in ...
Feb 03, 2020 · Each elementary step has its own activated complex labeled ac 1 and ac 2. Show more 1 label the energy diagram shown below for a two step reaction. Reaction Coordinate Wikipedia The activation energy for each step is labeled e a1 and e a2. Label the energy diagram for a two step reaction. It also shows the effect of a catalyst on the forward and reverse activation energy.
As simple illustrations of stepwise mechanisms, we will consider two distinct scenarios for reactions which occur in two steps. First Step Rate-Determining. Mechanism: Reaction Path Diagram: The term "rate-determining step" or "rds" has a specific meaning. An rds is a step of a reaction the rate of which is equal to the rate of the ...
Draw a reaction coordinate for the following catalyzed two-step exothermic reaction with the first step being the rate determining step:A -- B
Solved The Diagram Below Shows A Reaction Profile For A Two Step Reaction What Does The Letter C Represent Course Hero
Using Molecularity to Describe a Rate Law. The molecularity of an elementary reaction is the number of molecules that collide during that step in the mechanism. If there is only a single reactant molecule in an elementary reaction, that step is designated as unimolecular; if there are two reactant molecules, it is bimolecular; and if there are three reactant molecules (a relatively rare ...
II III 8888 III Reaction cannot happen Which step is the rate determining step in the mechanism of a reaction possessing the below reaction energy diagram? AG Reaction Coordinate 1st 2nd 3rd ооооо 4th 5th Which of the following reaction coordinate diagrams.
The reaction involves two steps, step 1 is the slowest step and step 2 is the fastest step. Both steps are exothermic. Indicate on the diagram the overall enthalpy change of the reaction, the reaction for the transition states and intermediate states. The reaction is a reaction between hydrogen gas and brown vapor of iodine monochloride.

Welcome To Modern Organic Chemistry Chapter 4 The Study Of Chemical Reactions Organic Chemistry 5 Th Edition L G Wade Jr Ppt Download

Draw An Energy Diagram For A Two Step Reaction Where The First Step Is Exothermic And The Reaction Overall Is Endothermic The First Step Is Rate Limiting Label Reactants Products And Intermediates



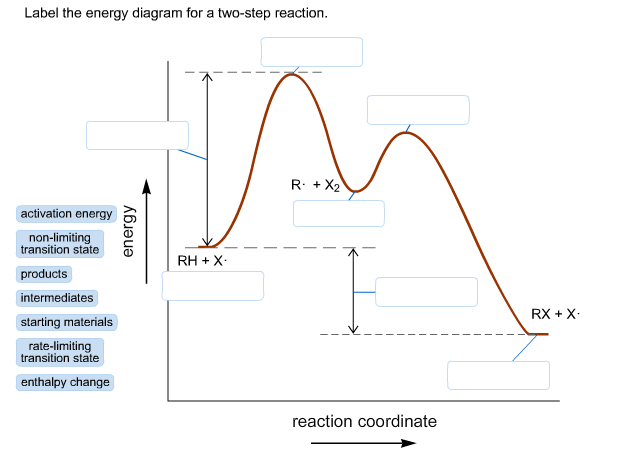
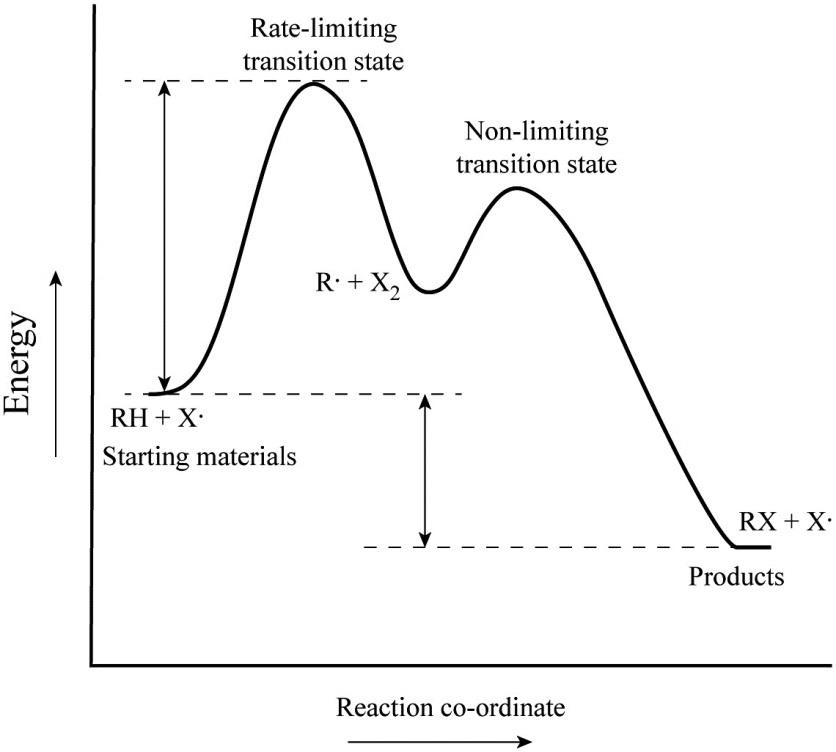
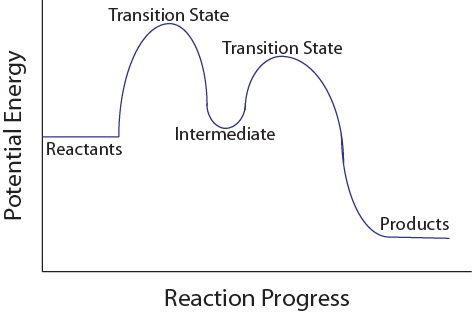
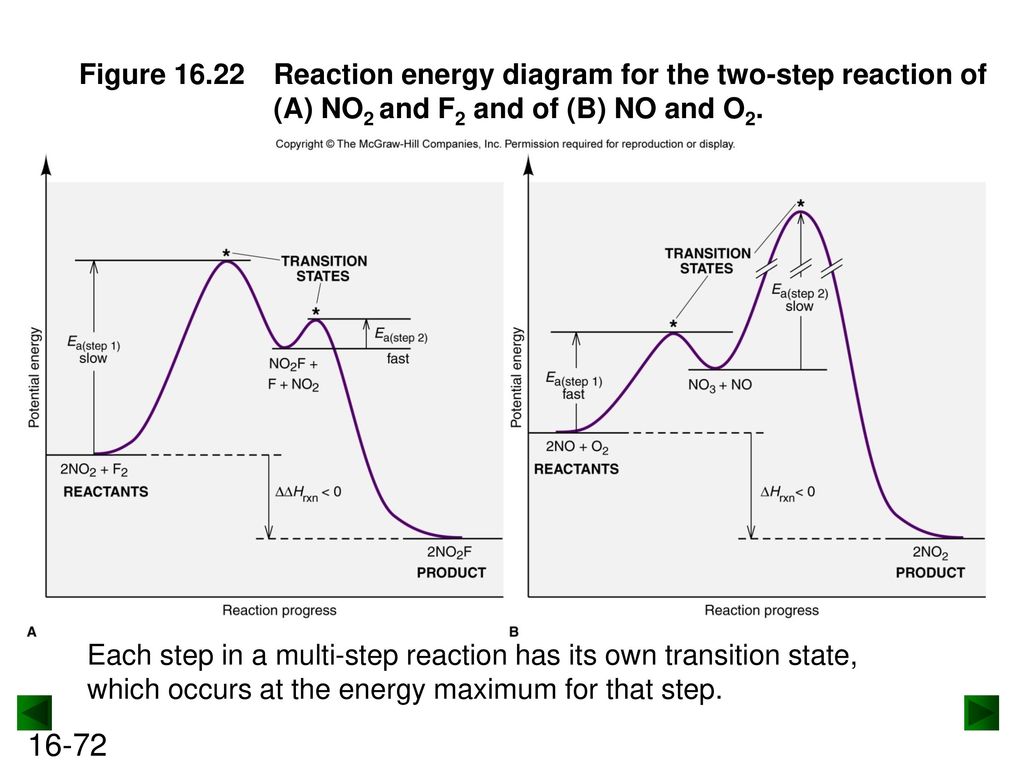









0 Response to "40 two step reaction diagram"
Post a Comment