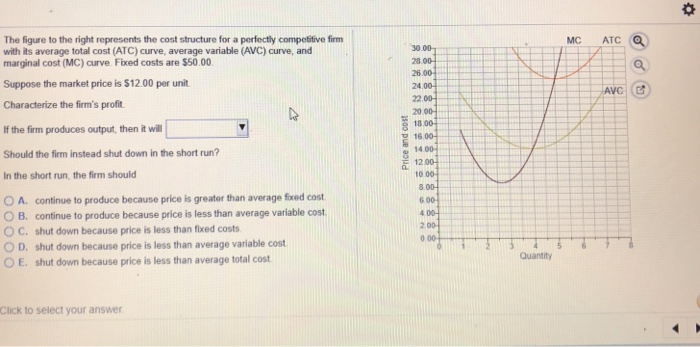
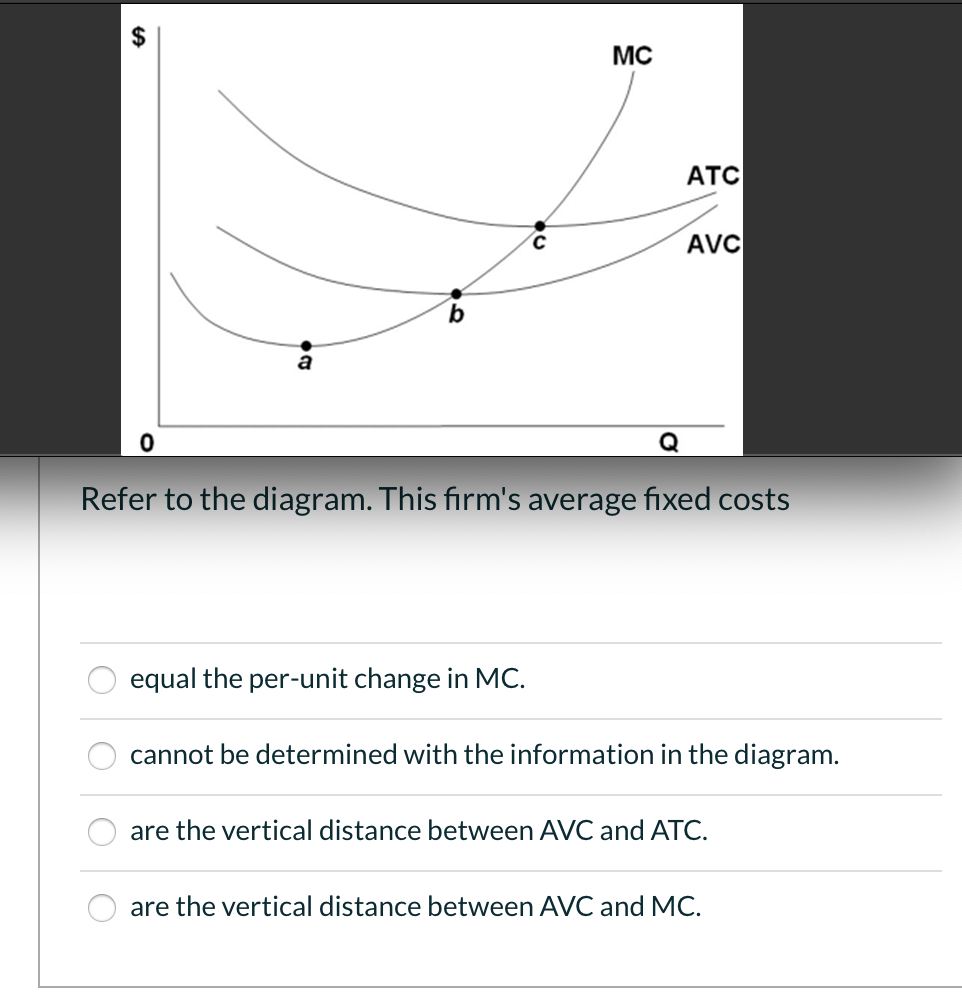
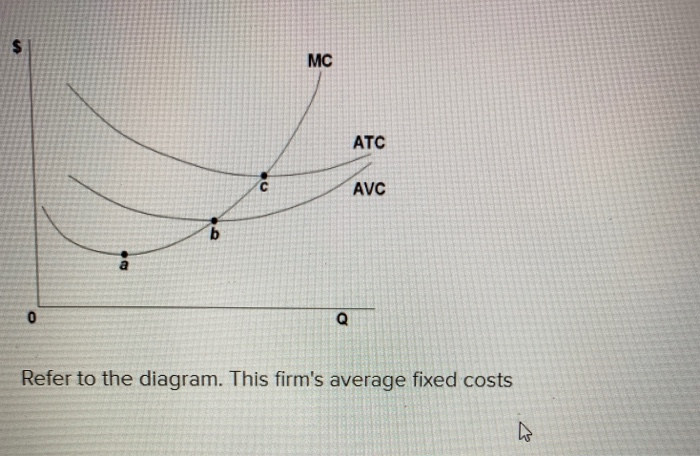
39 refer to the diagram. this firm's average fixed costs
Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: Select one: a. ... Assume that the amounts of all non-labor resources are fixed. Refer to the above data. Diminishing marginal returns become evident with the addition of the: ... and average variable costs of $150. The firm's total fixed costs are: Select one: a. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and average variable costs of $150. The firm's total fixed costs are: O A. $5,000. O B. $500. O C. $.50. O D. $50.
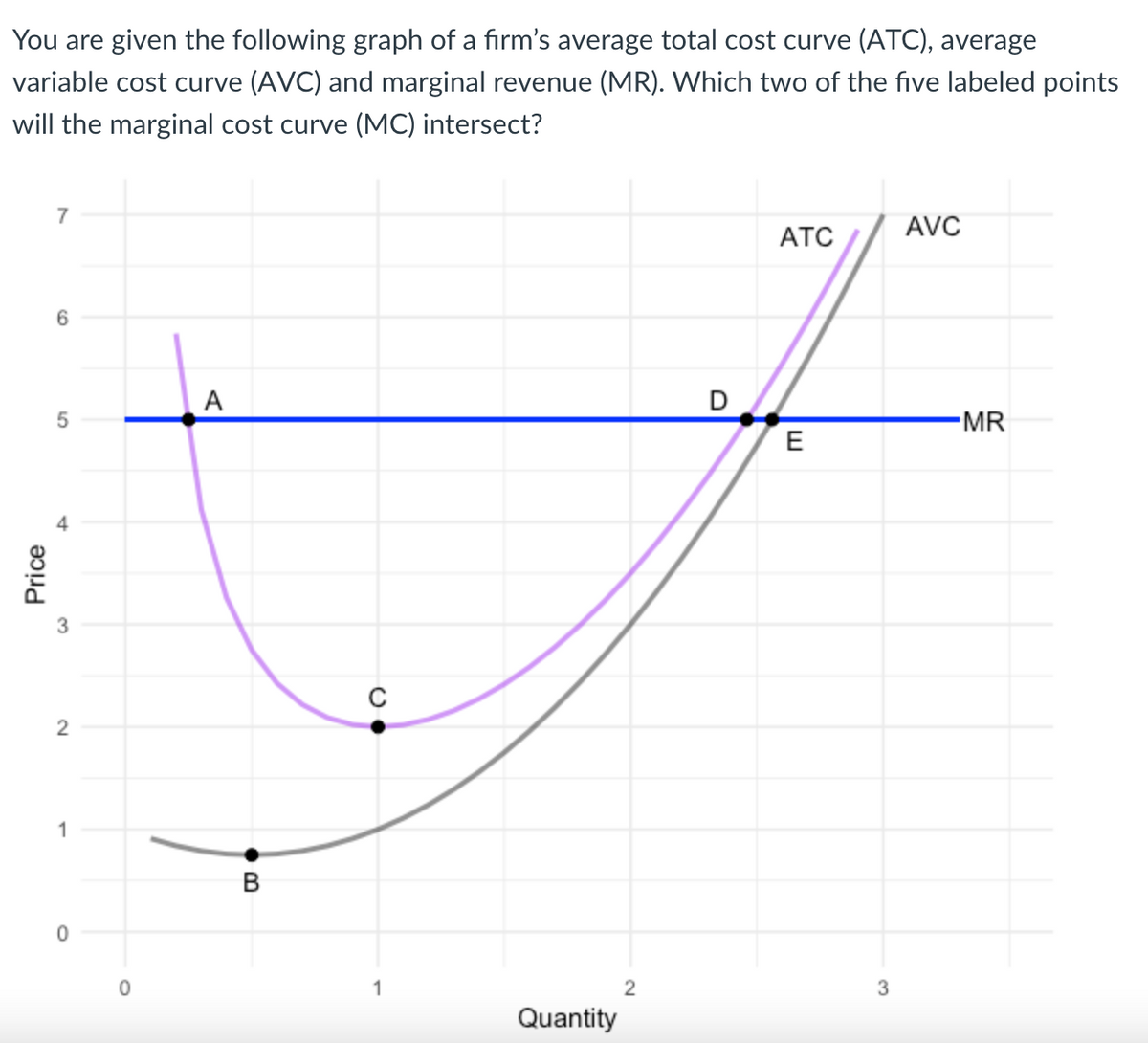
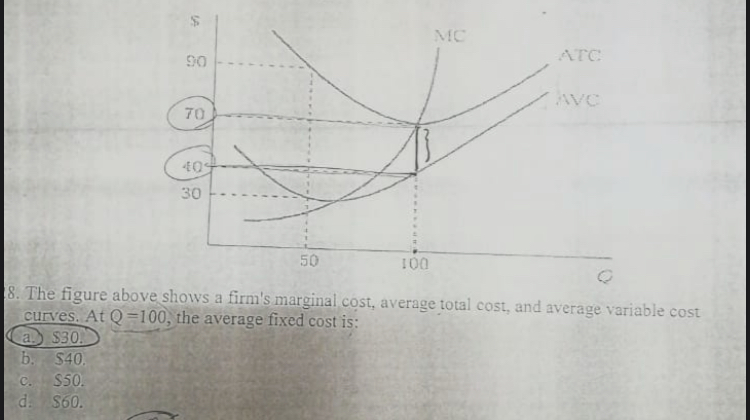
Economics questions and answers. ATC AVC Refer to the diagram. This firm's average fixed costs Multiple Choice - o cannot be determined with the information in the diagram. | I II o are the vertical distance between AVC and MC. o are the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. o equal the per-unit change in MC.

Refer to the diagram. this firm's average fixed costs
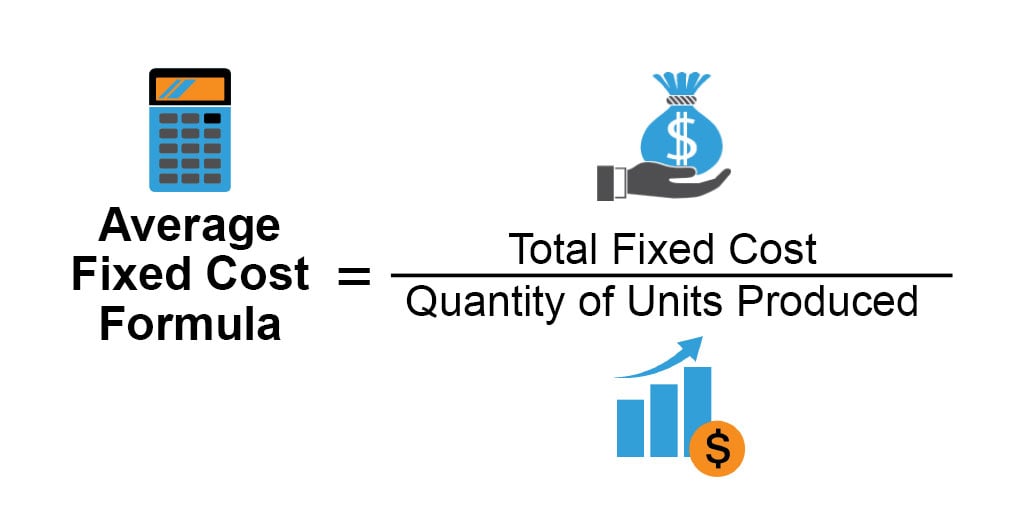
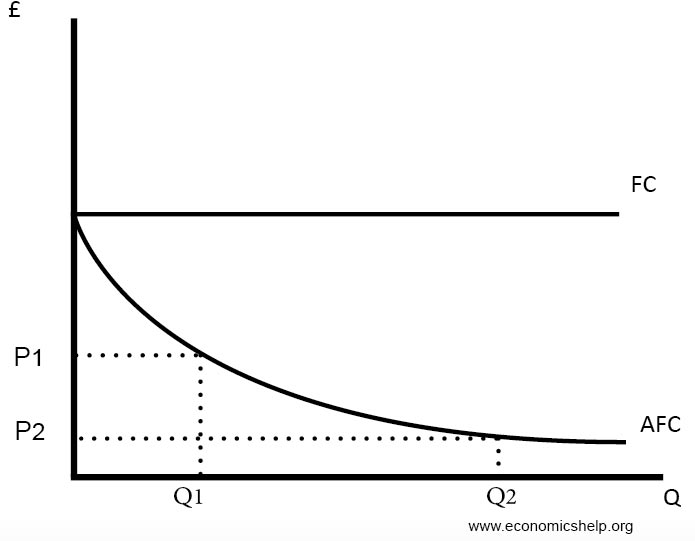
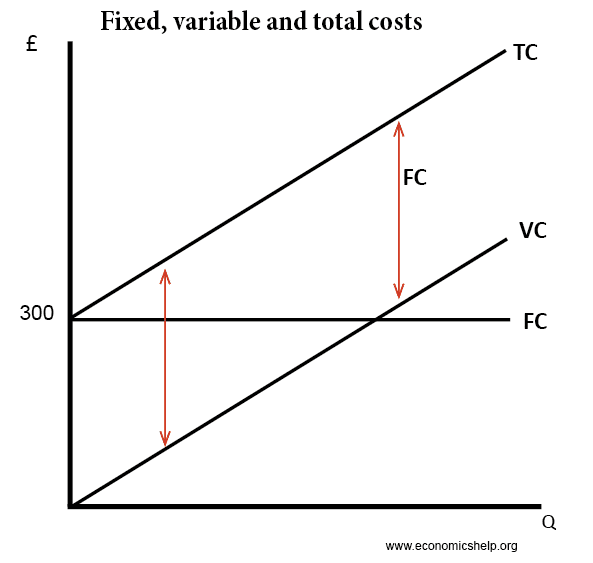
the average fixed cost at each level of output. Refer to the above information. Average fixed cost is: TFC-----Q. ... Refer to the above diagram. This firm's average fixed costs are: the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. Refer to the above diagram. If labor is the only variable input, the marginal product of labor is at a: ... The structure of costs in the short run. The cost of producing a firm's output depends on how much labor and physical capital the firm uses. A list of the costs involved in producing cars will look very different from the costs involved in producing computer software or haircuts or fast-food meals. Average variable cost is calculated by taking variable cost and dividing by the total output at each level of output. Average variable costs are typically U-shaped. If a firm's average variable cost of production is lower than the market price, then the firm would be earning profits if fixed costs are left out of the picture.
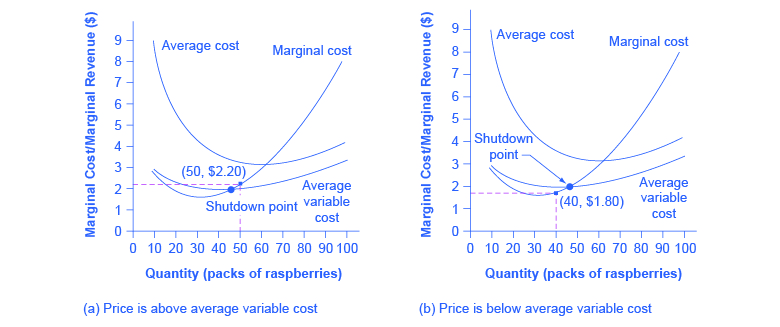
Refer to the diagram. this firm's average fixed costs. Average total cost curve is typically U-shaped i.e. it decreases, bottoms out and then rises. A firm's total cost is the sum of its variable costs and fixed costs. Variable costs are costs which vary with change in output level. Fixed costs, on the other hand, do not change with change in output. This firm's average fixed costs are: A) not shown. B) the vertical distance between AVC and MC. C) the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. D) equal to the per unit change in MC. 144. Refer to the above diagram. If labor is the only variable input, the marginal product of labor is at a: A) maximum at point a. B) minimum at point a. 41. Refer to the above diagram. At output C total variable cost is FGKJ. True False 42. Refer to the above diagram. At output C average fixed cost is GF. True False 43. Refer to the above diagram. At any price below R the firm will shut down in the short run. True False 44. Refer to the above diagram. Average total cost is total cost divided by the quantity of output. Since the total cost of producing 40 haircuts at "The Clip Joint" is $320, the average total cost for producing each of 40 haircuts is $320/40, or $8 per haircut. Average cost curves are typically U-shaped, as Figure 1 shows.
102. Refer to the above information. The marginal cost of the third unit of output is: A. $105.B. $25. C. $15. D. $20. 103. Refer to the above diagram. This firm's average fixed costs are: A. not shown.B. the vertical distance between AVC and MC. C. the vertical distance between AVC and ATC.D. equal to the per unit change in MC. 104. Refer to the above data. The average fixed cost of producing 3 units of output: A. is $8. B. is $7.40. C. is $5.50. ... why the firm's long-run average total cost curve is U-shaped. C. why the firm's short-run marginal cost curve cuts the short-run average variable cost curve at its minimum point. ... The above diagram shows the short-run ... This firm's average fixed costs A. cannot be determined with the information in the diagram. B. are the vertical distance between AVC and MC.C. are the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. D. equal the per-unit change in MC. 133. Refer to the diagram. If labor is the only variable input, the marginal product of labor is at a. Microeconomics: Chapter 9. Refer to the diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: is equal to <i>QE</i>. Refer to the data. Diminishing returns begin to occur with the hiring of the _________ unit of labor. Nice work!
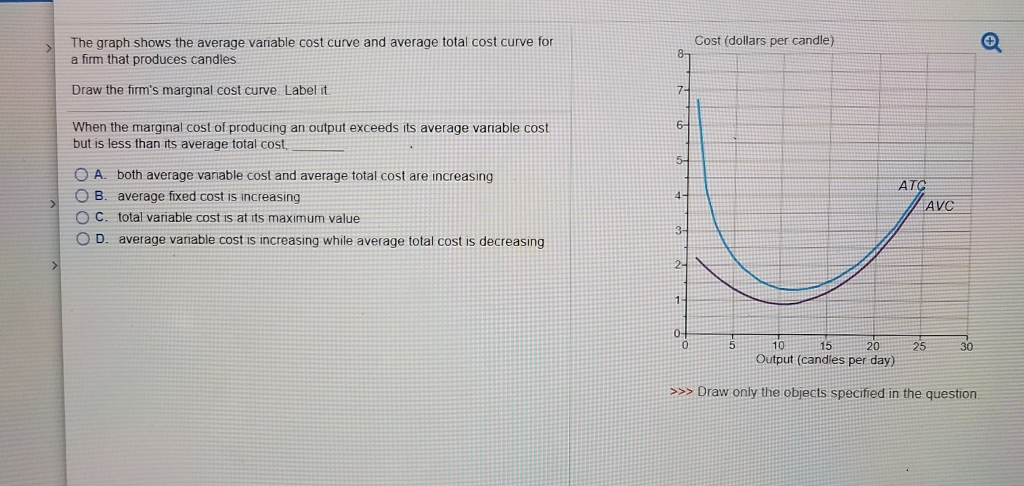
PRD‑1.A.6 (EK) Transcript. This video shows how to graph marginal cost, average variable cost, and average total cost. The relationship between these curves at important points is also explored. Short-run production costs. Fixed, variable, and marginal cost. Marginal cost, average variable cost, and average total cost. Graphs of MC, AVC and ATC. Refer to the long-run cost curve for a firm. If the firm produces output Q1 at an average total cost of ATC1, then the firm is ... Refer to the Diagram. This firm's average fixed costs. are the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. In 2018, the United states. imported more goods than it exported. 52. If marginal cost is rising in a competitive firm's short-run production process and its average variable cost is falling as output is increased, then . A. marginal cost is above average variable cost. B. marginal cost is below average fixed cost. C. marginal cost is below average variable cost. D. average fixed cost is constant. $35, what is the firm's average fixed cost at that level of output? A) $65 B) $50 C) $15 D) It is impossible to determine without additional information. 30. If a firm produces 20 units of output and incurs a total cost of $1,000 and a variable cost is $700, calculate the firm's average fixed cost of production if it expands output to 25 units.
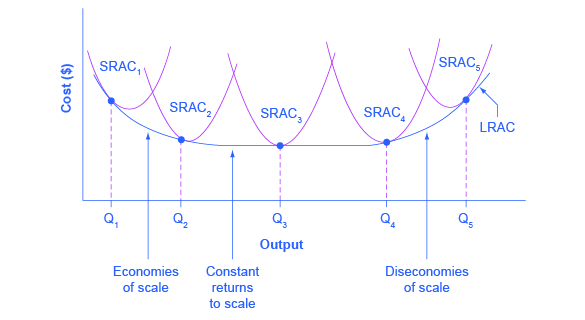
of rising average fixed costs. 2. A monopolistic firm has a sales schedule such that it can sell 10 prefabricated garages per week at $10,000 each, but if it restricts its output to 9 per week it can sell these at $11,000 each. ... Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm.
Refer to the above diagram This firms average fixed costs are A not shown B the from ECON 2 at Tarrant County College. Average Cost. The value of average cost is derived by dividing to tal cost with the number of units produced by a firm. The average cost includes average fixed cost as well as an average variable cost. Refer to the diagram of the market for product X. Curve St embodies all ...
161. Refer to the table and information. The fixed cost of the firm is $500. The firm's total variable cost is indicated in the table. The average variable cost of the firm when 5 units of output are produced is:
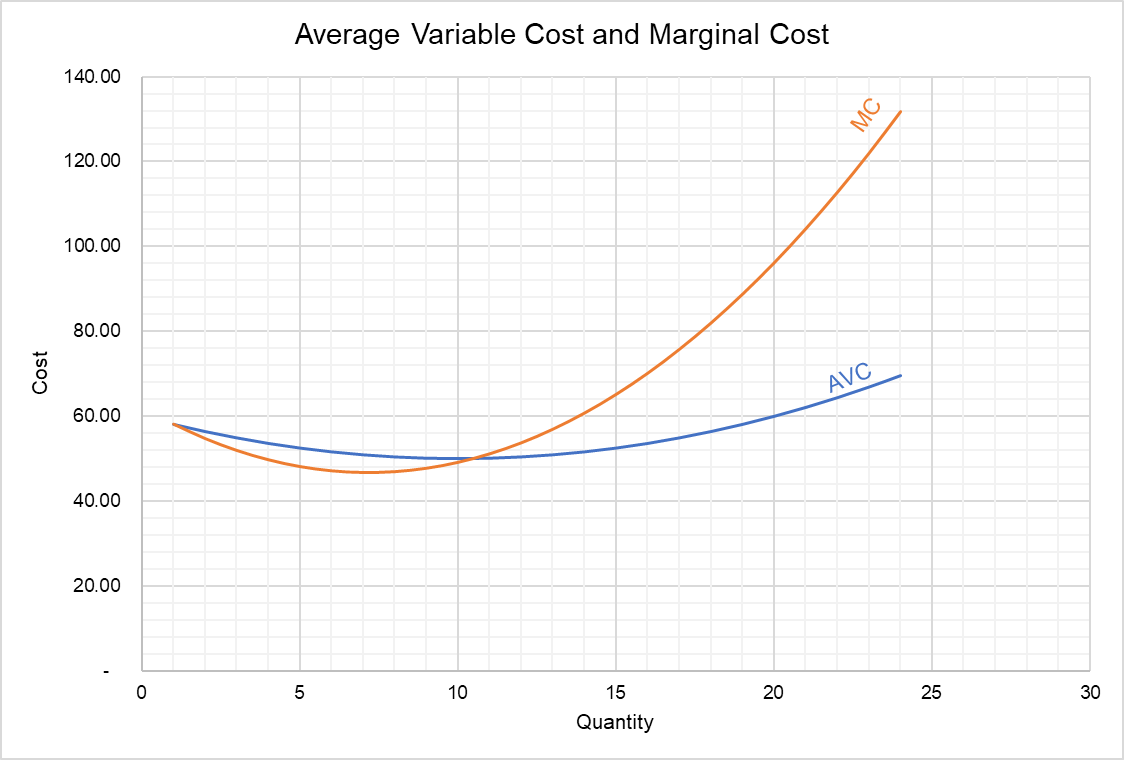
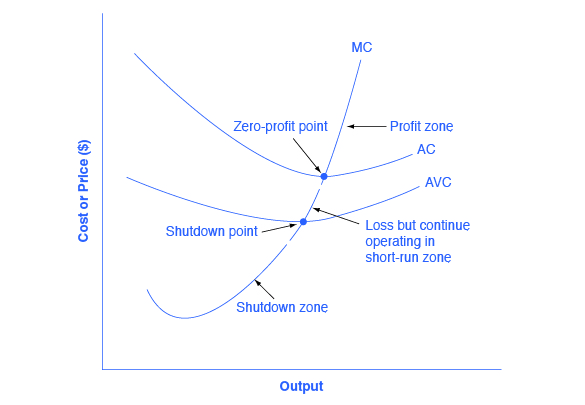
3. Average Total Cost (ATC) The average total cost is the sum of the average variable cost and the average fixed costs. That is, ATC = AFC + AVC. In other words, it is the total cost divided by the number of units produced. The diagram below shows the AFC, AVC, ATC, and Marginal Costs (MC) curves: It is important to note that the behaviour of ...
Refer to the above diagram. This firm's average fixed costs are: A) not shown. C) the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. B) the vertical distance between AVC and MC. D) equal to the per unit change in MC.
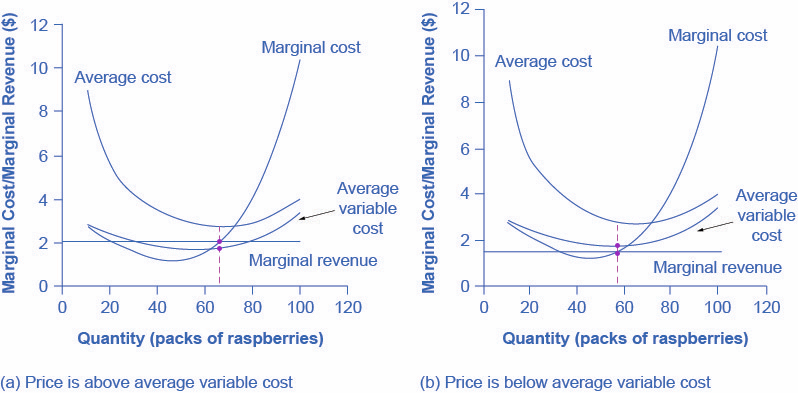
Consider the following short-run cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. FIGURE 9-1 26) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P1, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output B.
Refer to the diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue: is $400.
As output increases, a firm's average fixed costs will a. increase b. decrease c. increase then decrease d. decrease then increase. 11. Refer to the diagram above. Curve 1 represents. 12. Refer to the diagram above. Curve 3 represents (Curve 2) Total cost / Quantity = Fixed Cost / Quantity + Variable Cost / Quantity. Short Answer Questions 13.
This firm's average fixed costs are: - FOORQUIZ. Refer to the diagram. This firm's average fixed costs are: A. not shown. B. the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. C. the vertical distance between AVC and MC. D. equal to the per unit change in MC. ANSWER: B. the vertical distance between AVC and ATC.
B) It must rise to offset the increased cost. C) The firm will shut down. D) It must fall. 12) Refer to Table 12 -1. The firm will not produce in the short run if the output price falls below 12) A) $8. B) $4. C) $3.20. D) $2.80. 13) If, for a given output level, a perfectly competitive firm's price is less than its average variable cost, the ...
Total Cost Fixed Cost Variable Cost 100 540 40 500 150 740 40 700 Average Cost or Average Total Cost Average cost (AC), also known as average total cost (ATC), is the average cost per unit of output. To find it, divide the total cost (TC) by the quantity the firm is producing (Q).
Average variable cost is calculated by taking variable cost and dividing by the total output at each level of output. Average variable costs are typically U-shaped. If a firm's average variable cost of production is lower than the market price, then the firm would be earning profits if fixed costs are left out of the picture.
The structure of costs in the short run. The cost of producing a firm's output depends on how much labor and physical capital the firm uses. A list of the costs involved in producing cars will look very different from the costs involved in producing computer software or haircuts or fast-food meals.
the average fixed cost at each level of output. Refer to the above information. Average fixed cost is: TFC-----Q. ... Refer to the above diagram. This firm's average fixed costs are: the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. Refer to the above diagram. If labor is the only variable input, the marginal product of labor is at a: ...

A Why Is Total Variable Cost Curve Inverse S Shaped B What Is Average Fixed Cost Of A Firm B What Is Average Fixed Cost Of A Firm Why Is An

1 Of 34 Part Ii The Market System Choices Made By Households And Firms C 2012 Pearson Education 8 Short Run Costs And Output Decisions Chapter Outline Ppt Download

Draw The Cost Curves For A Typical Firm Explain How A Competitive Firm Chooses The Level Of Output That Maximizes Profit At That Level Of Output Show On Your Graph The Firm













0 Response to "39 refer to the diagram. this firm's average fixed costs"
Post a Comment