39 plunging syncline block diagram
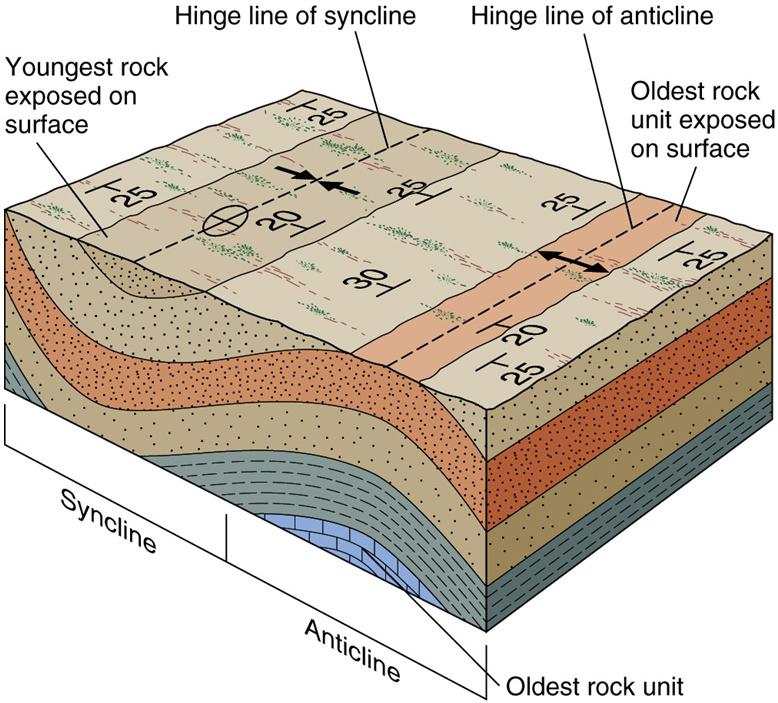
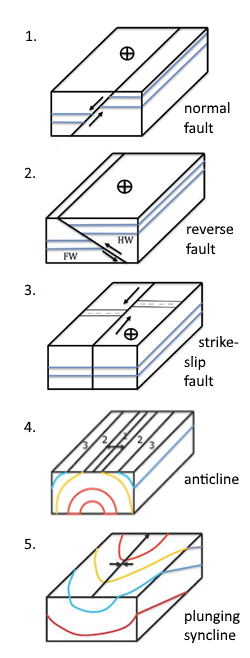
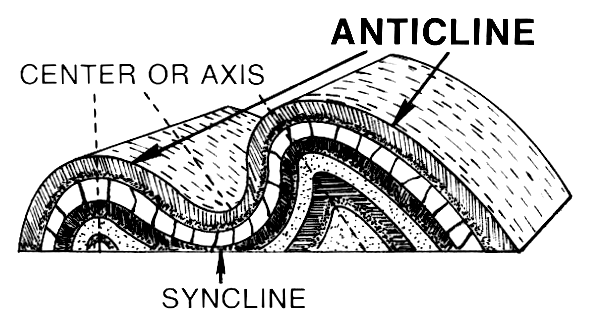
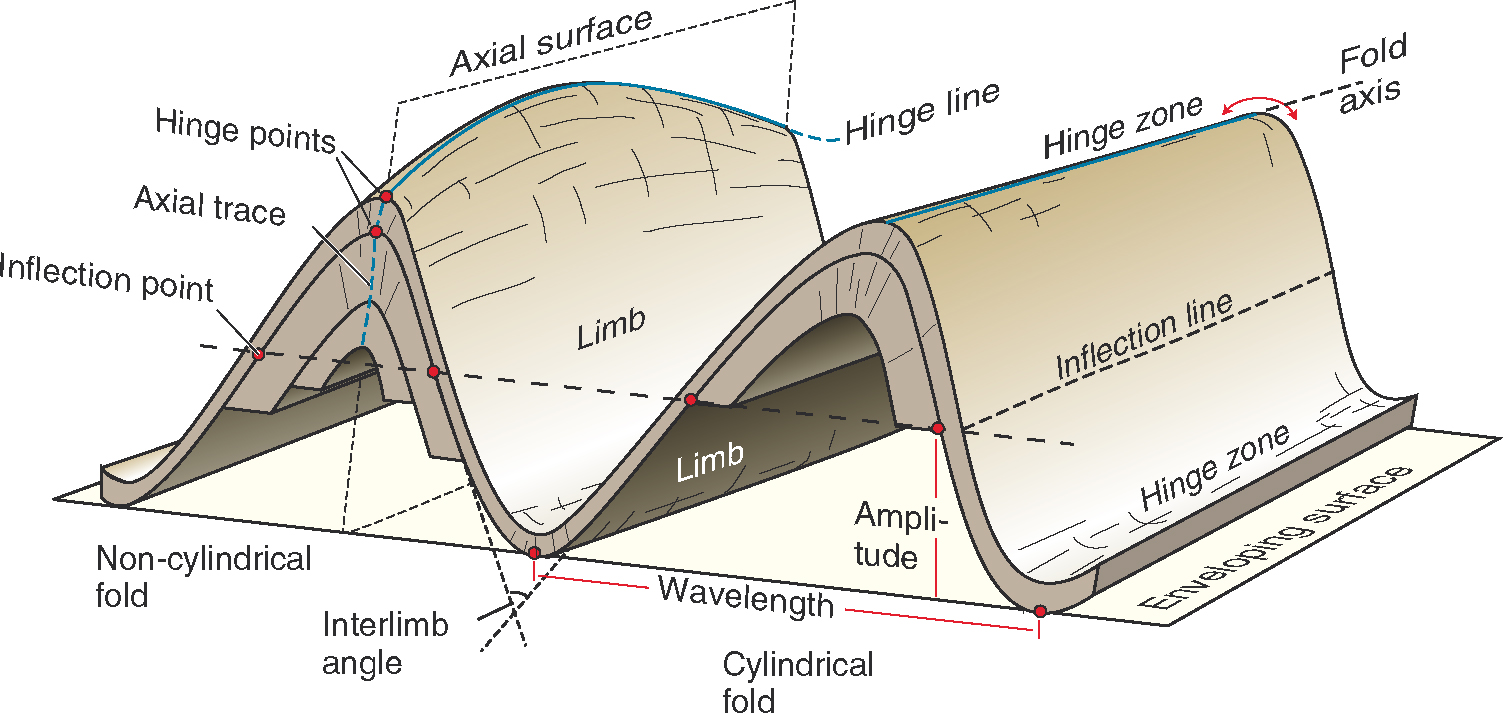
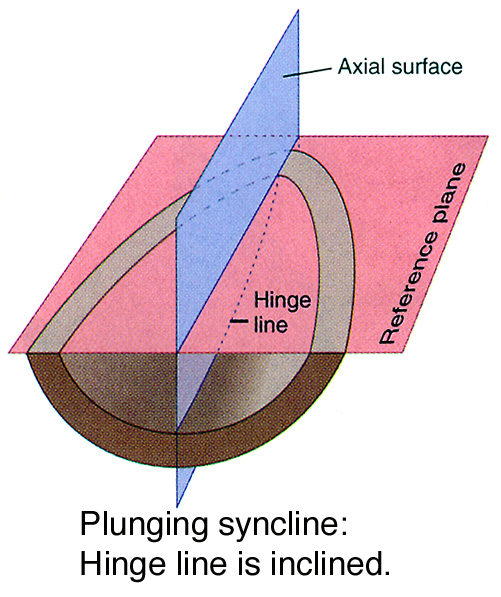
A syncline is the opposite type of fold, having downwardly convex layers with young rocks in the core. Folds typically occur in anticline-syncline pairs. The hinge is the point of maximum curvature in a fold. The limbs occur on either side of the fold hinge. The imaginary surface bisecting the limbs of the fold is called the axial surface. A block diagram is a combination of those two representations and ... structure is called a syncline. Note that the youngest rocks are in the center. Can you ... Plunging Fold Structures Often folds can also be tilted. This results in fold with a nonhorizontal, inclined
Plunging Syncline Block Diagram The three broad classes of folds are (1) anticlines, (2) synclines and (3) Figure 4: Schematic diagrams illustrating horizontal and plunging anticlines. stream cut. A block diagram is a Block Diagrams & Nomenclature Plunging synclines plunge in the direction the "V" opens.
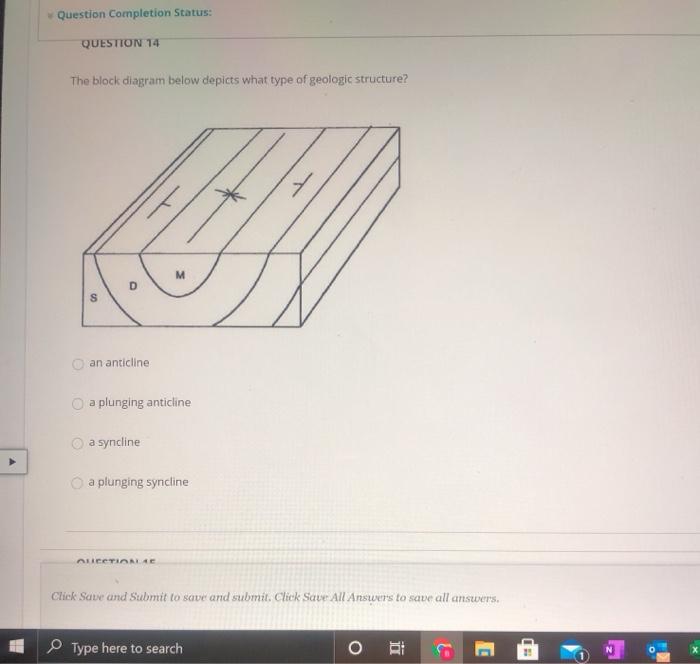
Plunging syncline block diagram
In structural geology, a syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria) is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds. Synclines are typically a downward fold, termed a synformal syncline (i.e. a trough); but synclines that point upwards, or perched, can be found when strata have been overturned and ... However, a cross-section parallel to the axis, such as the right-hand sides of the two block diagrams above, shows the beds dipping downward in the direction the fold is plunging. In map view, a plunging syncline makes a U-shaped or V-shaped pattern that opens up in the direction of plunge. Basins and Domes United States Office of Research and EPA/625/R-00/010 Environmental Protection Development August 2000 Agency Cincinnati, OH 45268 v>EPA Environmental Problem Solving with Geographic Information Systems 1994 and 1999 Conference Proceedings About this CD: This CD, EPA Document Number EPA/625/R-00/010, contains conference proceedings documents from the 1994 and 1999 …
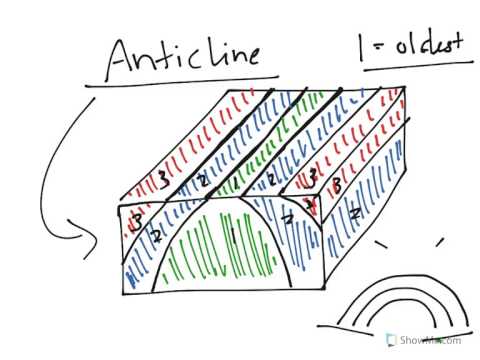
Plunging syncline block diagram. Cross-sectional diagram of an anticline. Anticline exposed in road cut (small syncline visible at far right). Note the man standing in front of the formation, for scale. New Jersey, U.S.A. In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in ... Figure 8.20 | A block diagram of an anticline and syncline. The top of the block represents map view and the side of the block is a cross-section view. Determine the strike and dip symbols that should appear in the ovals. Source: Randa Harris (2015) CC BY-SA 3.0. view source. 01.11.2021 · Twiss' (1988) diagram (Fig. 7d) has to our knowledge never been applied in published research. Furthermore, the classification of asymmetric folds is complicated by requiring six parameters (aspect ratio, folding angle, bluntness of closure, two inclination angles and the hinge tangent angle). In general, the simplest classification of asymmetry is the ratio between the short and long limbs ... 1. Upright fold: Fold layers into an upright, vertical anticline. Slice the top to make it flat topography; slice through the sides with vertical planes to create a block model. Orient your model so that the hinge line trends E-W; vertical axial plane strikes E-W. Sketch the block diagram.
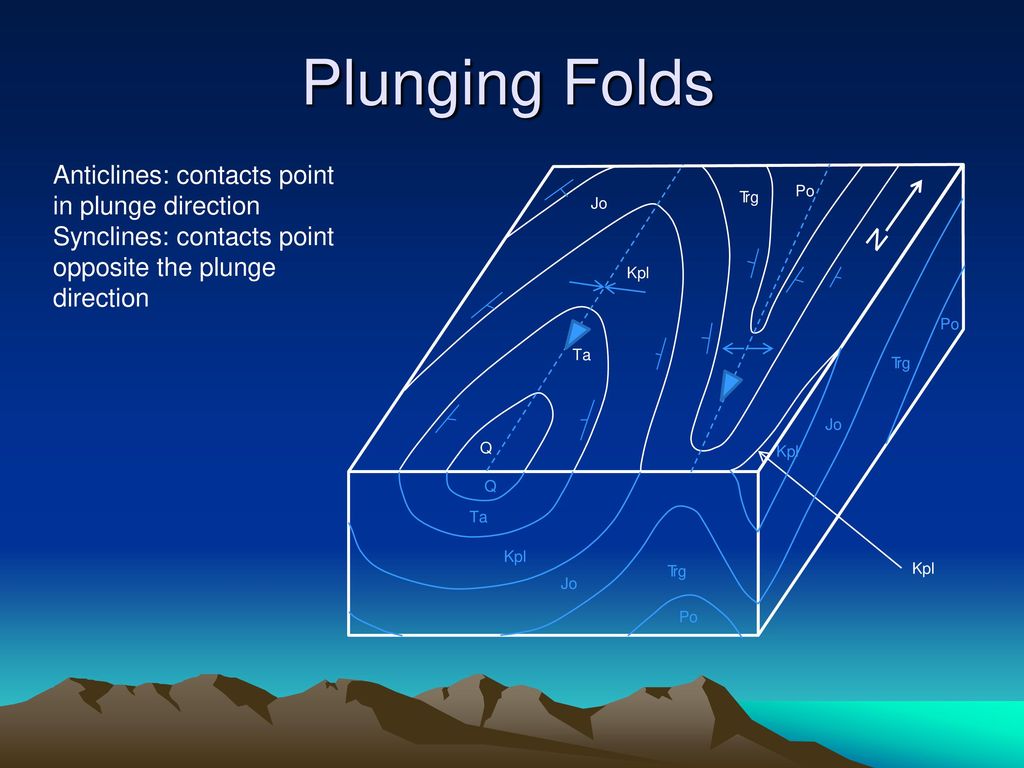
Use concrete-block rather than wood-frame construction. ... On the diagram shown a. block X is the footwall. b. block X is the hanging wall. c. the displacement of layer B shows this is a thrust fault. ... d. a syncline plunging toward the south. c. an anticline plunging toward the north. Block diagram of plunging syncline. #geologic_structure #Geology #structural_geology #syncline We have converted your account to an Organization! You can now invite others to collaborate on your content. Syncline and Anticline. C 1992 West Publishing Company . This diagram depicts an adjacent ANTICLINE and SYNCLINE with their representative FOLD AXIS and AXIAL PLANES. ... Notice the V-shape of the outcrop pattern. This ANTICLINE is plunging toward the top of the picture, therefore, it is a PLUNGING ANTICLINE! ... B Diagram Figure 5.8 c Map Block diagram and geologic map of plunging folds. The map shows the characteristic outcrop pattern of plung.ng folds. Here. ant'clines and one syncline plunge to the west. If this area were in a humid region. the arkose formation would be more resistant to
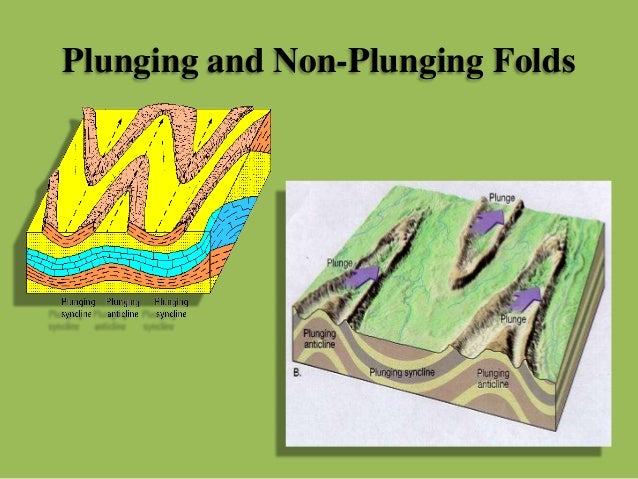
Synclines and anticlines usually occur together such that the limb of a syncline is also the limb of an anticline. In the diagrams above, the fold axes are horizontal, but if the fold axis is not horizontal the fold is called a plunging fold and the angle that the fold axis makes with a horizontal line is called the plunge of the fold. Note that if a plunging fold intersects a horizontal ... (b) A syncline looks like a trough. The beds dip toward the hinge. Plunging hinge (c) A monocline looks like a stair step, and is commonly draped over a fault block. (d) A plunging anticline has a tilted hinge. (e) A dome has the shape of an overturned bowl. (f) A basin has the shape of an upright bowl. In block diagrams like those shown below, the top of the block is the horizontal surface of the earth, the map view. ... A plunging anticline or a plunging syncline is one that has its axis tilted from the horizontal so that the fold is plunging into the earth along its length. Plunge direction is the direction in which the axis of the fold ... Students make sketches of block diagrams of structures of your choosing. These could include horizontal stratigraphy and an upright anticline, or could be of new structures, such as an upright syncline, asymmetrical folds, or anything else you like. We recommend building up gradually from simple structures to more complex ones.
block diagram were eroded uniformly by 30%. What would the map look like? 2. Figure 4: Uniformly dipping planar units cropping out on at horizontal landscape Figure 5: Planar dipping contacts cropping out on a slope The same pattern results from dipping beds on a uniform slope, but the trace of a contact
What are anticline block diagram syncline block diagram. Syncline and Anticline. C West Publishing These diagrams show the affect of plunge on the fold axis. Block diagram of an Anticline and Syncline.Syncline · is a series of down-arched strata with limbs dipping inwards in opposite directions towards the fold axis--an eroded surface ...
Diagram 1 - hanging wall moves up relative to footwall - reverse fault Diagram 2 - hanging wall moves down relative to footwall - normal fault - caused by tensional forces (reverse + thrust faults caused by compressional forces; normal faults caused by extensional forces) A graben is characterized by _____. a hanging wall block that has moved down between two normal faults. What is a terrane ...
Plunging and non-plunging anticlines and synclines can be represented in 3D block diagrams to show how the folded strata behave beneath the surface. Domes - a circular anticline (oldest beds in the core, beds dip away from the core). Basins - a circular syncline (youngest beds in the core, beds dip into the core).
A block diagram is a combination of Block Diagrams & Nomenclature anticline. Contrary to the syncline, the rock beds dip away from the fold axis, and the. The most basic types of folds are anticlines and synclines. In block diagrams like those shown below, the top of the block is the horizontal surface of the earth, .
• Non‐plunging folds have straight contact lines in the map view (horizontal) surface. • Vertical sides of the block diagram perpendicular to the axial traces of folds may contain curved contact lines. Axial traces of folds Anticline symbol Syncline symbol
A plunging anticline or a plunging syncline is one that has its axis tilted from the horizontal so that the fold is plunging into the earth along its length. Plunge direction is the direction in which the axis of the fold tilts down into the earth. In map view, a plunging anticline makes a U-shaped or V-shaped pattern that points, or closes, in the direction of plunge.
A plunging fold is a fold that is tilted downwards in space, parallel to the fold hinge plane. Figure 26. Plunging anticline (left) and plunging syncline (right). The interactive diagrams are linked below. Interactive SketchUp diagram of a plunging anticline: Interactive SketchUp diagram of a plunging syncline:
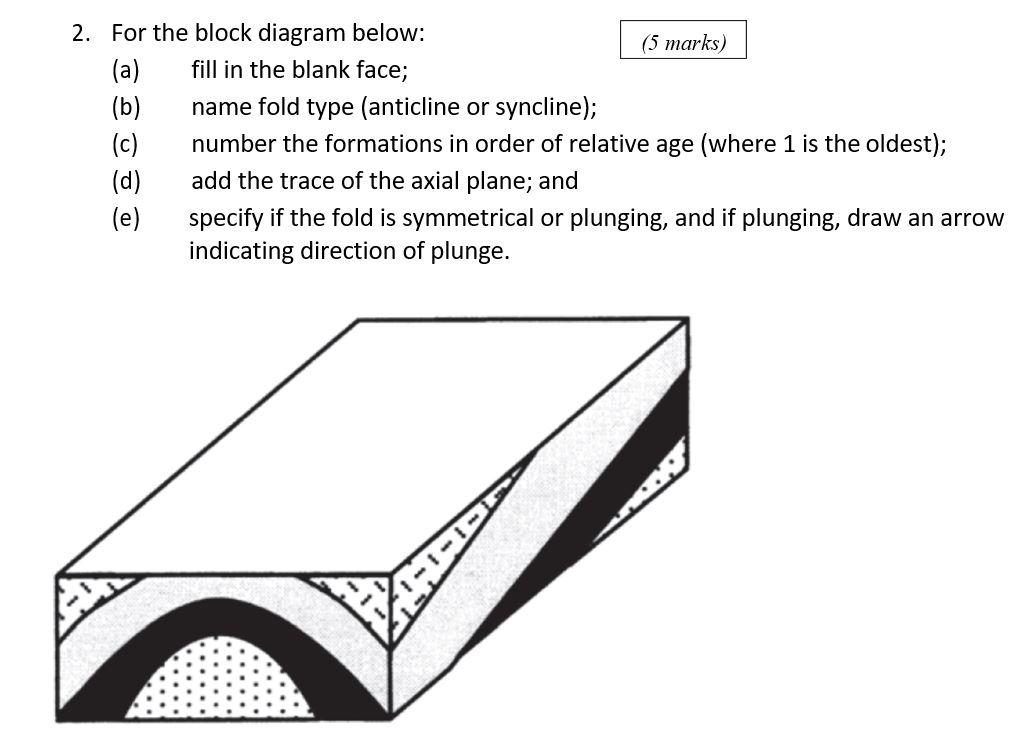
The block in part (a) of the figure on p. 386 shows a vertical fault cutting across a nonplunging syncline. Complete the block diagram by adding arrows to show the sense of slip across the fault and by adding colored bands for the appropriate stratigraphic units in the blank areas.
1.3 Folds on Block Diagrams Figure 6 shows a schematic diagram of an anticline with key components labeled. First, observe that the anticline is symmetrical; both limbs dip the same amount, but in opposite directions. In a way, you can consider fold limbs to be two sets of inclined strata which dip in different. Each limb can be described using ...
an anticline plunging toward the north. Which of the following structures makes a pattern of rock layers on the ground surface that looks like this: parallel stripes, showing bilateral symmetry across a midline (hinge), with rock getting older as you move outward from the hinge. syncline. The East African Rift. has volcanoes along it because asthenosphere is rising under the rift and supplying ...
upwards the structure is an anticline and when the strata are bent downwards the structure is a syncline (Fig. 5). Note that in an anticline the oldest rocks are in the center of the fold while in a syncline the ... The symbols for plunging fold axes are shown below. The direction of plunge is indicated by an arrow. ... On the block diagram ...
maps, cross-sectional diagrams, block diagrams, aerial photographs, and satellite images, as appropriate: • Normal, reverse, and lateral faults • Synclines and anticlines, both non-plunging and plunging • The axis of a fold. State the direction of plunge where relevant. Draw block diagrams to illustrate geological structures.
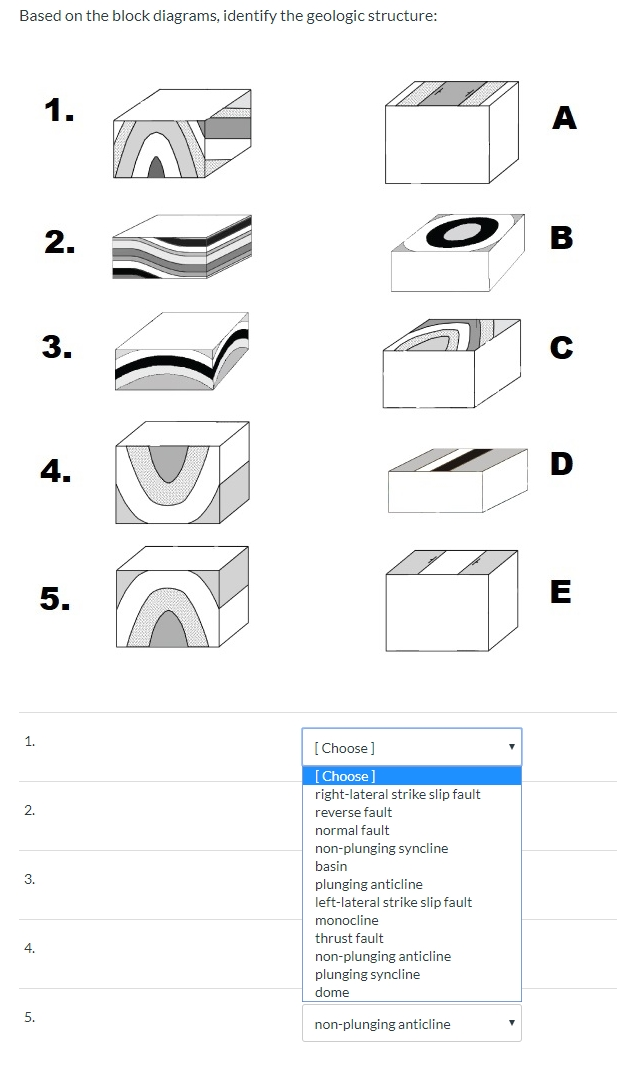
Block diagram B Answer 1Choose...symmetrical plunging anticlineasymmetrical plunging synclinesymmetrical plunging synclineasymmetrical plunging anticlinesymmetrical non-plunging syncline Block Question : Question 1 Not yet answered Marked out of 4 Flag question Question text Matching the block diagrams with its type of fold.
Use the block diagrams to visualize the three-dimensional shapes of the geologic structures. Keep in mind that erosion has stripped away the upper parts of these structures so that map view reveals the interior of these structures. In map view, an anticline appears as parallel beds of the same rock type that dip away from the center of the fold. In an anticline, the oldest beds, the ones that ...
The curved strata comprising a plunging fold form a horseshoe or hairpin pattern on the surface where they plunge into the earth. 7. For anticlines, the horseshoe or hairpin shape closes in the direction that the anticline plunges. 8. For synclines, the horseshoe or hairpin-shape opens in the direction that the syncline plunges. 9.
Plunging Syncline Block Diagram; Cisco Sx80 Wiring Diagram; 1968 John Deere 4020 Console Wiring Diagram; Emg Wiring Diagram 1 Volume 1 Tone 1switch; Trailridge Mirror Wiring Diagram For Dodge Ram 2500 2000 Model; Alpine Ktp-445 Amp Wiring Harness Color Code; Yaesu Ft 60 Wiring Diagram For External; Ruger 10/22 Parts Diagram; 2007 Volkswagen ...
EJ208 block. The EJ208 engine had a die-cast aluminium alloy cylinder block with 92.0 mm bores and a 75.0 mm stroke for a capacity of 1994 cc. The cylinder block had an open-deck design to enhance cooling efficiency and dry-type, cast iron cylinder liners (the outer surfaces of ‘dry type’ liners are in complete contact with the cylinder walls). Crankshaft, connecting rods and pistons. For ...
Transcribed image text: Strike and Dip - together comprise the orientation (attitude) of strata ("beds"). Strike - compass direction of a horizontal line on a bedding plane. Dip (aka "dip angle"): maximum acute angle between the bedding plane and the horizontal Strike Map Symbols 720 Strike and dip Vertical Horizontal Plunging Plunging bedding bedding anticline syncline axial plane - plane ...
This makes the structure in the block diagram to be a plunging syncline. The correct planar view is shown for this block in option B. Ans. 3. In the front section, the beds are dipping away from the center, and in the section, the contact between beds are inclined. This makes the structure to be a plunging anticline.
United States Office of Research and EPA/625/R-00/010 Environmental Protection Development August 2000 Agency Cincinnati, OH 45268 v>EPA Environmental Problem Solving with Geographic Information Systems 1994 and 1999 Conference Proceedings About this CD: This CD, EPA Document Number EPA/625/R-00/010, contains conference proceedings documents from the 1994 and 1999 …
However, a cross-section parallel to the axis, such as the right-hand sides of the two block diagrams above, shows the beds dipping downward in the direction the fold is plunging. In map view, a plunging syncline makes a U-shaped or V-shaped pattern that opens up in the direction of plunge. Basins and Domes
In structural geology, a syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria) is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds. Synclines are typically a downward fold, termed a synformal syncline (i.e. a trough); but synclines that point upwards, or perched, can be found when strata have been overturned and ...





















0 Response to "39 plunging syncline block diagram"
Post a Comment