39 concave lens ray diagram
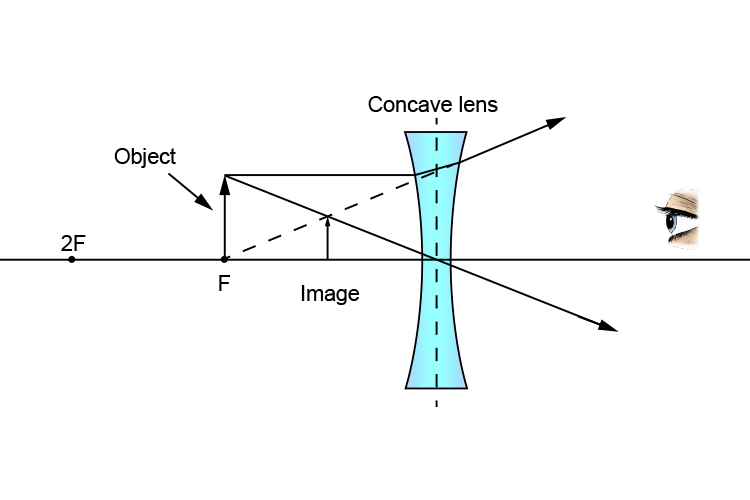
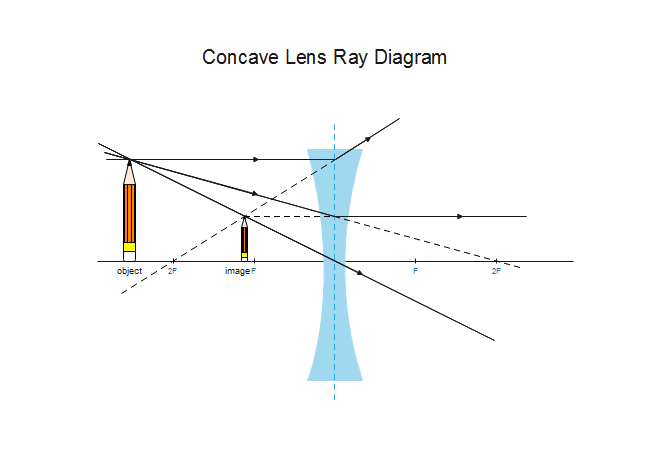
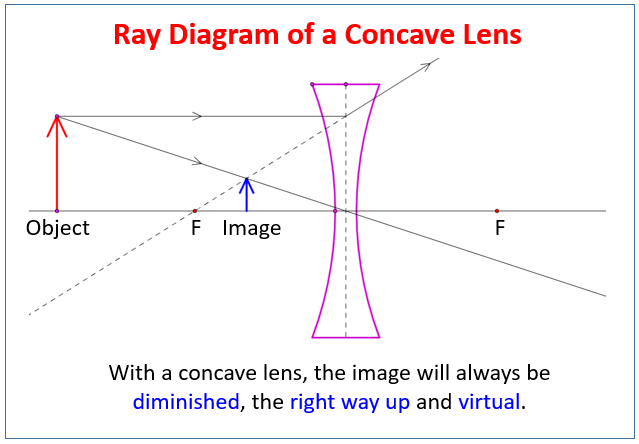
The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a double concave lens will be located at a position behind the double concave lens. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual.Converging Lenses - Ray DiagramsImage formation by convex and concave lens ray diagrams. The second ray goes straight through the center of the lens. The light rays don't converge, but the sight lines do. J.M. Gabrielse f Concave Lens (example) • F optical axis The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and refracts from the focal point. The second ray goes straight through the center of the lens.
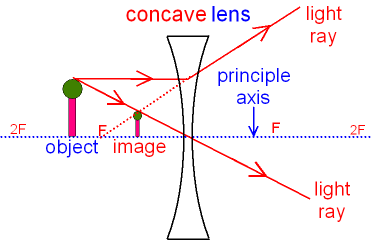
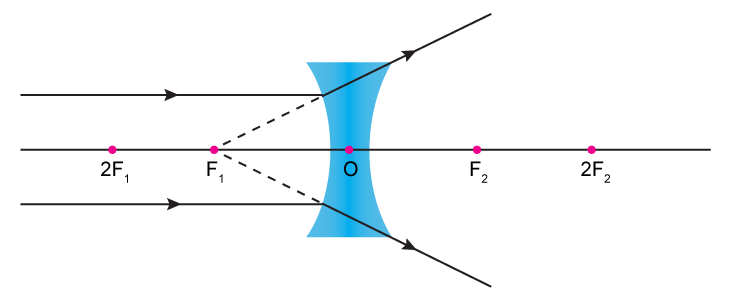
Ray diagram for an object viewed through a concave lens. For an object viewed through a concave. lens, light rays from the top of the object will be refracted. and will diverge. on the other side ...
Concave lens ray diagram
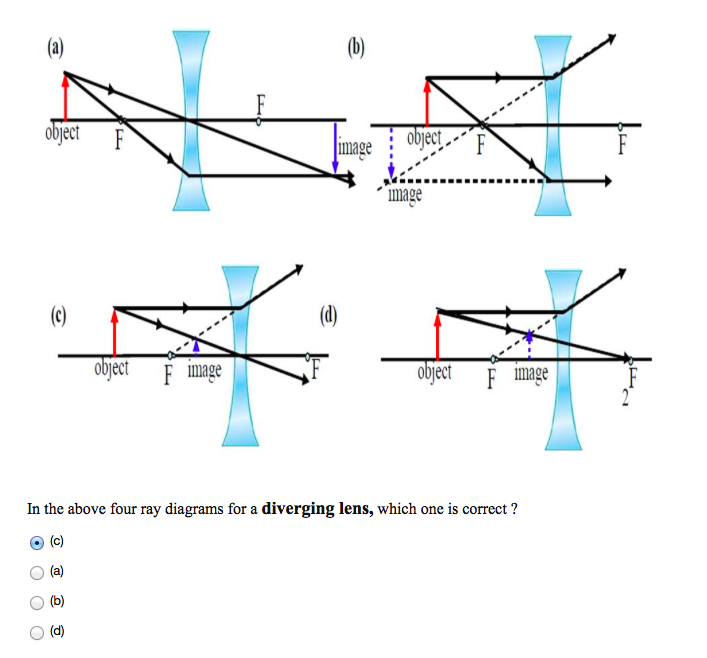
A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses". Concave Lens Ray Diagrams Concave (diverging) lenses can also be used to form images, although the images are always virtual in this case If an object is placed further from the lens than the focal length f then a concave lens ray diagram will be drawn in the following way: Hi ! In this animation of CONCAVE Lens, you get a good confidence to draw Ray Diagrams for various Object Positions. The aim is to have a clear understanding...
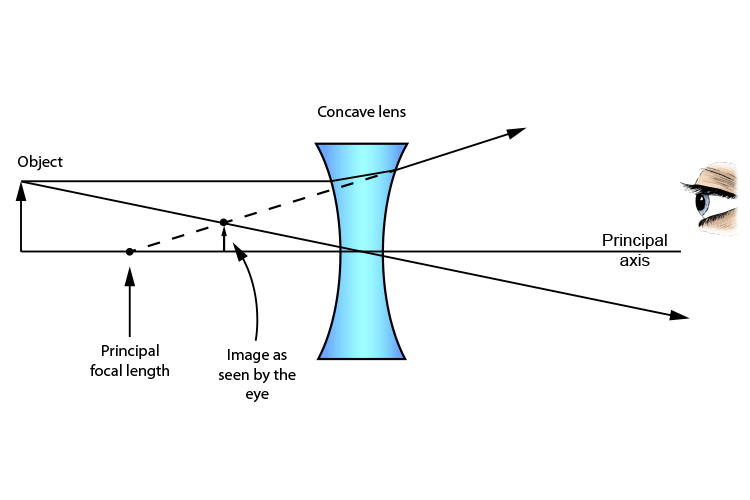
Concave lens ray diagram. Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses. The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results: an erect virtual image smaller than the object. The image is always formed inside the focal length of the lens. With a concave lens, the image will always be diminished, the right way up and virtual. Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed by a concave lens. Describe the properties of an image produced by a concave lens. Draw different ray diagrams with the object at different places in relation to the focus and find out where the image appears. Convex and Concave Lenses are Spherical Lenses. We look at the Image Formation by these spherical lenses using ray diagrams. 1. J.M. Gabrielse Ray Diagrams 2. J.M. Gabrielse Spherical Mirrors (concave & convex) 3. J.M. Gabrielse Concave & Convex (just a part of a sphere) C: the centre of curvature (centre point of the sphere) F: the focus (focus) of the mirror (halfway between C and the mirror) • C • F Principal Axis Curved Surface 4.
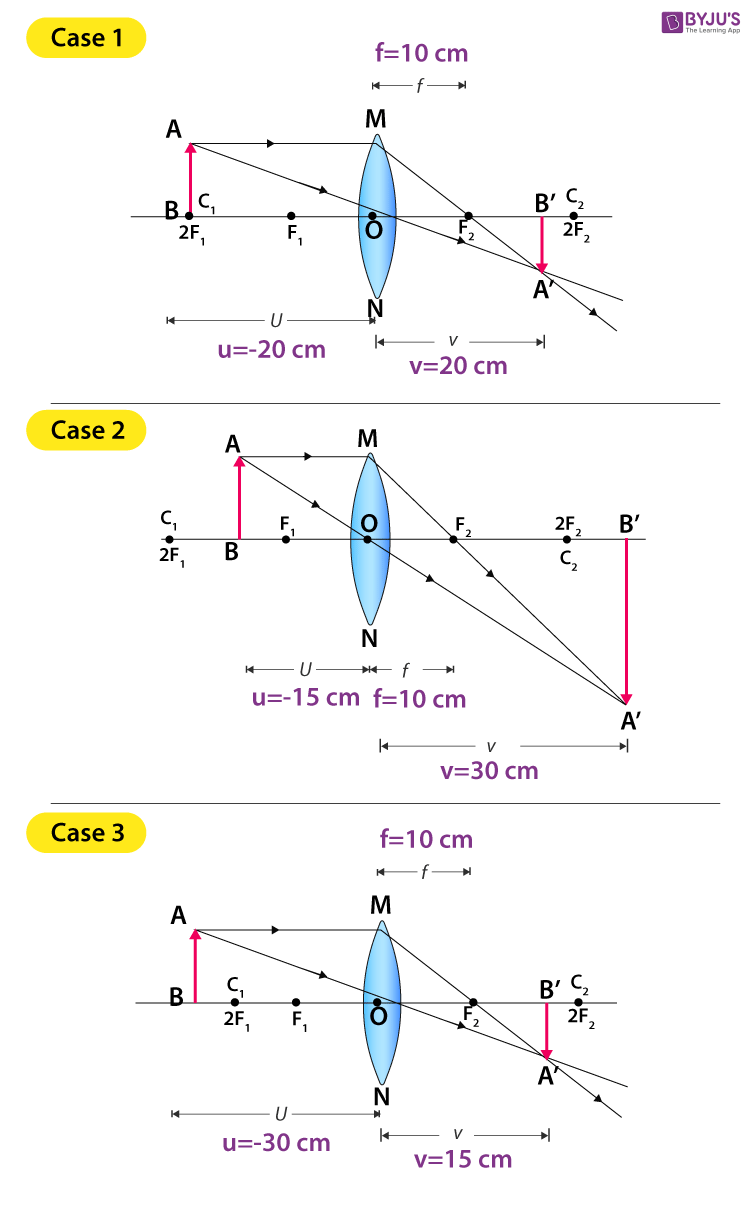
Here in this post, you will get Ray Diagrams for Images formed by convex & concave lenses as a Quick Reference.Image formation by lenses is an interesting topic of the Light chapter. Here along with the ray diagram, you will get the related details like Object position, image position, and nature of the image. Ray […] A concave lens is thinner in the middle than it is at the edges. This causes parallel rays to diverge. A concave lens separates but appears to come from a principal focus on the other side of the lens. In the concave lens ray diagram, a concave lens is drawn as a vertical line with inward-facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens. To create the diagram, a student should pick a point on ... The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a double concave lens will be located at a position behind the double concave lens. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram. The ray passing through the focal point becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens. Ray diagram for concave lens. Image formation in convex lens Case 1:When object beyond 2F: In this case image will form between F and 2F, image will be real, inverted, smaller than the object. ...
The example "Ray tracing diagram for concave lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions. When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object. For a concave mirror to focus light coming from a distance to a single point, in a similar fashion to a concave lens, it must have a parabolic shape, instead of spherical. However, for drawing ray diagrams it is often easier to consider a spherical mirror. The ray diagram shown in Fig3. for diverging lenses was created using the rules given in Table. The first ray, parallel to the axis, appears to come from the focal point on the same side of the lens as the object. This ray is indicated by the oblique dashed line. The second ray passes through the center of the lens and is not refracted.
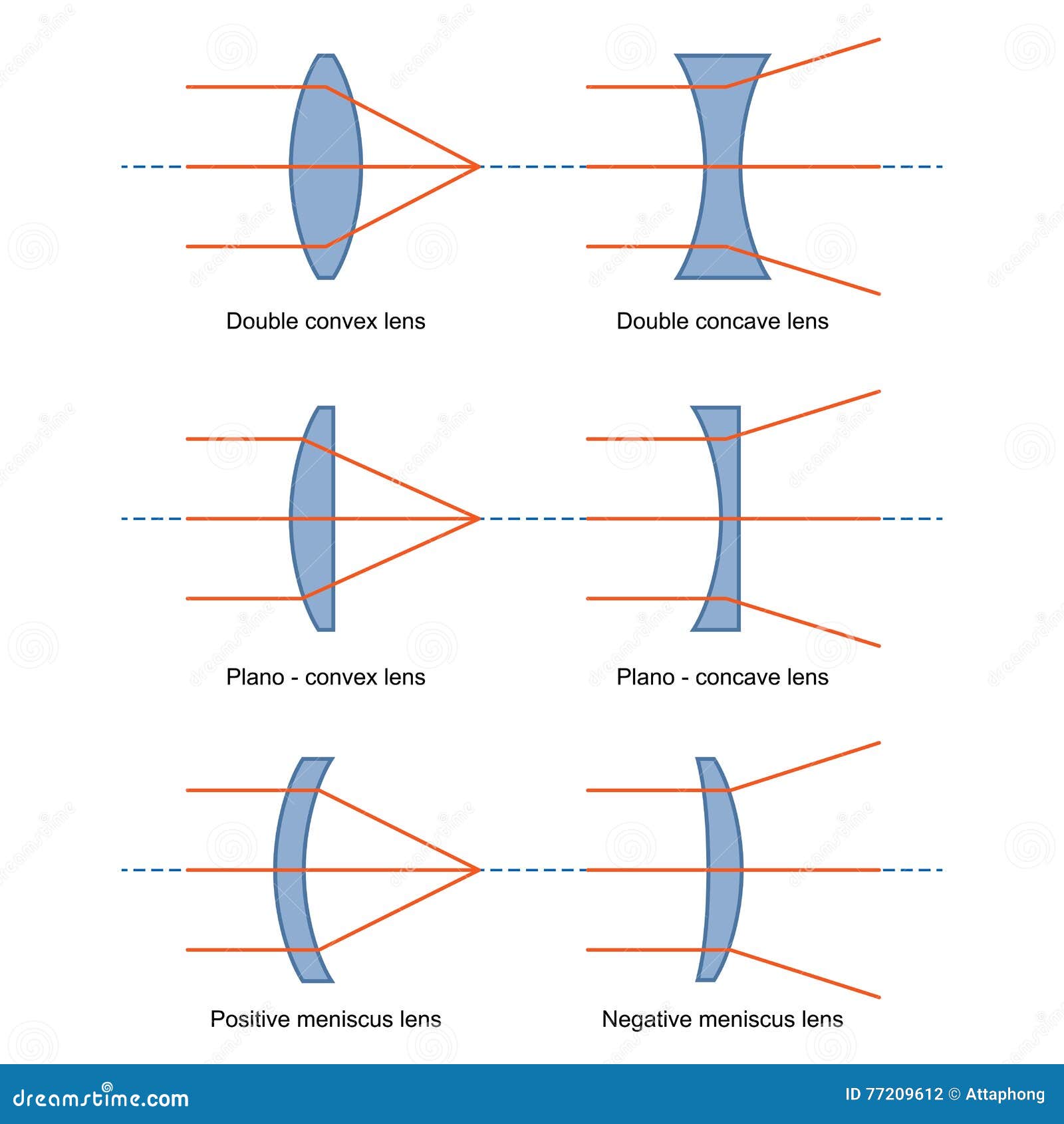
A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ...
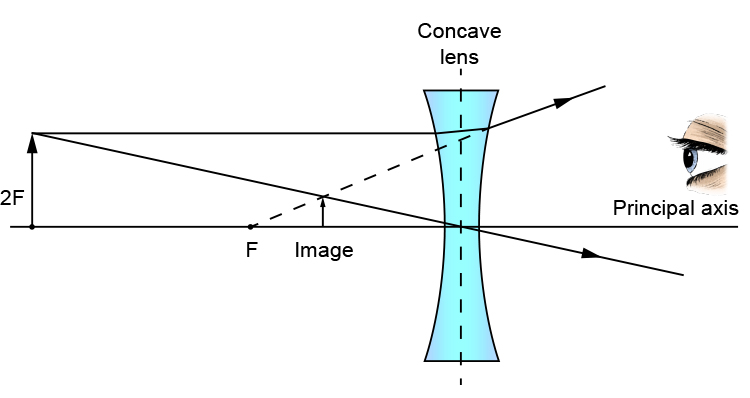
Ray diagrams for diverging (concave) lens. If an object is on one side of the concave lens, the concave lens can form the image of the object. If the position of the object on one side of the concave lens is known, how to draw the image formation of the object? Suppose an object is on the left side of the concave lens as shown in the figure below.
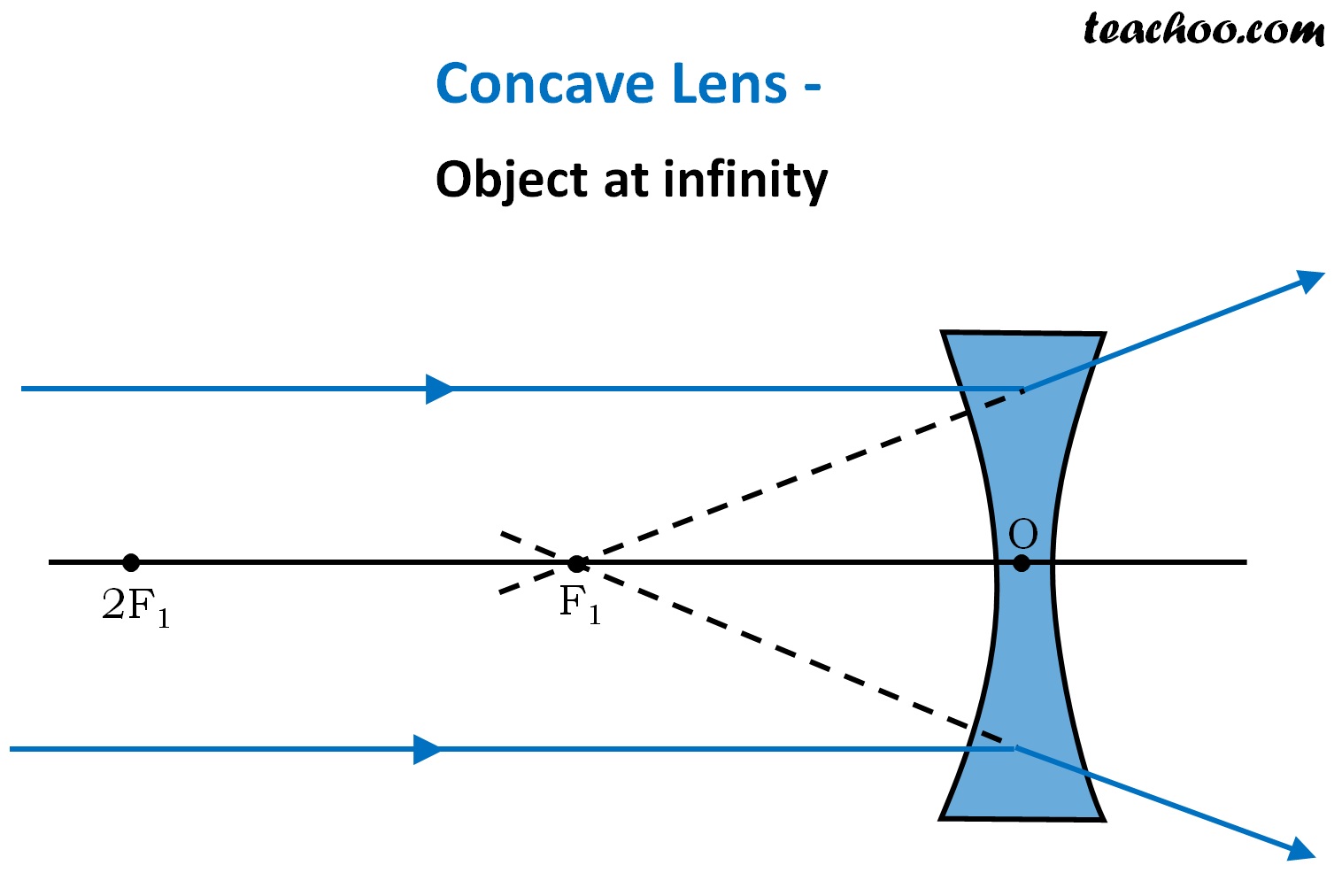
For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
The students can use a convex lens diagram to understand the ray's path after passing through a convex lens. The students may create a convex ray diagram by hand, but the process is lengthy, and at the same time, complicated. If the students fail to place the paths of the light properly, they may end up with a faulty convex lens ray diagram.
Mirror Ray Tracing. Mirror ray tracing is similar to lens ray tracing in that rays parallel to the optic axis and through the focal point are used. A third useful ray is that through the center of curvature since it is normal to the mirror and retraces its path backward.
Voronoi Diagrams with Cones; Juggling 13 Balls; Concave and Convex Lenses. Description Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave ...

Image from page 17 of "The ophthalmoscope : its mode of application explained, and its value shown, in the exploration of internal diseases affecting the eye" (1858)
In a ray diagram, a convex lens is drawn as a vertical line with arrows pointing outwards in both directions. This is to resemble the shape of a convex lens. Whereas a concave lens is drawn as a vertical line with arrows pointing inwards. This is to resemble the shape of a concave lens. You can see this below:
Ray Diagram for an Object Located at the Focal Point. Thus far we have seen via ray diagrams that a real image is produced when an object is located more than one focal length from a concave mirror; and a virtual image is formed when an object is located less than one focal length from a concave mirror (i.e., in front of F). But what happens ...
One goal of a ray diagram is to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image that is formed by the double convex lens. Typically, this requires ...
A concave lens is a piece of round glass that is thinner at the centre than at the edges. It bends the rays of light passing through it away from each other i.e. diverges them. Opticians use concave lenses to correct nearsightedness. They are also used in flashlights to magnify the light, and can be found in door viewers or peepholes. ...
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object.
A ray diagrams helps you understand the chara... This video shows you a simple method for drawing a ray diagram for a concave lens given the location of object.

Image from page 67 of "A compendium of astronomy; containing the elements of the science, familiarly explained and illustrated, with the latest discoveries. Adapted to the use of schools and academies, and of the general reader" (1850)
Concave Lens - Ray diagram Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens Lens Formula Power of a lens NCERT Questions → Class 10. Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1) Concepts NCERT Questions ...

Image from page 234 of "The class-book of anatomy : designed for schools, explanatory of the first principles of human mechanism, as the basis of physical education" (1834)
Hi ! In this animation of CONCAVE Lens, you get a good confidence to draw Ray Diagrams for various Object Positions. The aim is to have a clear understanding...
Concave Lens Ray Diagrams Concave (diverging) lenses can also be used to form images, although the images are always virtual in this case If an object is placed further from the lens than the focal length f then a concave lens ray diagram will be drawn in the following way:
A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses".

Image from page 224 of "A manual of personal hygiene : proper living upon a physiological basis" (1917)

Image from page 879 of "The physiology of the domestic animals; a text-book for veterinary and medical students and practitioners" (1890)

Image from page 31 of "The microscope : an introduction to microscopic methods and to histology" (1911)



















0 Response to "39 concave lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment