39 be2 molecular orbital diagram
34 Be2+ Molecular Orbital Diagram. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals method in particular. C would this ion exist. The first ten molecular orbitals may be arranged in order of energy as follow: σ(1s ) ∗(1s) Molecular orbital energy level for Be2. The molecular orbital electronic configuration,Magnetic property: Since bond order is zero, Be2 molecule does not exist. It is diamagnetic due to the absence of.1.
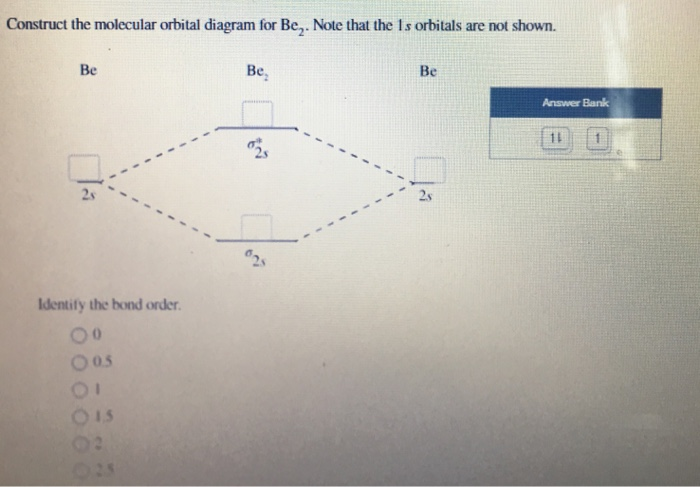
Solved Construct the molecular orbital diagram for Be2. Note | Chegg.com. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for Be2. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Be Ho Be Answer Bank IL | Identify the bond order. O 0 O os O 1s. Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for Be2. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown.

Be2 molecular orbital diagram
(i) Be2 molecule: The electronic configuration of Be(Z = 4) is: 4 Be 1s 2 2s 1 Be 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms. Number of valence electrons in Be atom = 2 Thus in the formation of Be 2 molecule, two outer electrons of each Be atom i.e. 4 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies. Be2 bond Order How do you discover the binding order in be2? What is the mandatory stimulate of He2? The _valence shell configuration is 1s2 2s2. Two atomic orbitals joined to type a molecular orbital through a bonding, non-bonding and also antibonding orbital. I Be _ 1s2 2s2 has actually 2 bonding and also 2 antibonding orbitals. B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is formed as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both ...
Be2 molecular orbital diagram. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... on Molecular Orbital Diagram For Be2. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory helps us to explain and understand certain Part B - Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams & Bond Order . + and Be2. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are ... For the molecule Be2:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this molecule exist?d) Write the electron configuration of th... Hint: According to the molecular orbital theory, the bond order is defined as the number of covalent bonds in a molecule. Bond order is equal to half of the difference between the number of electrons in bonding (\[{{N}_{b}}\]) and antibonding molecular orbitals (\[{{N}_{a}}\]).
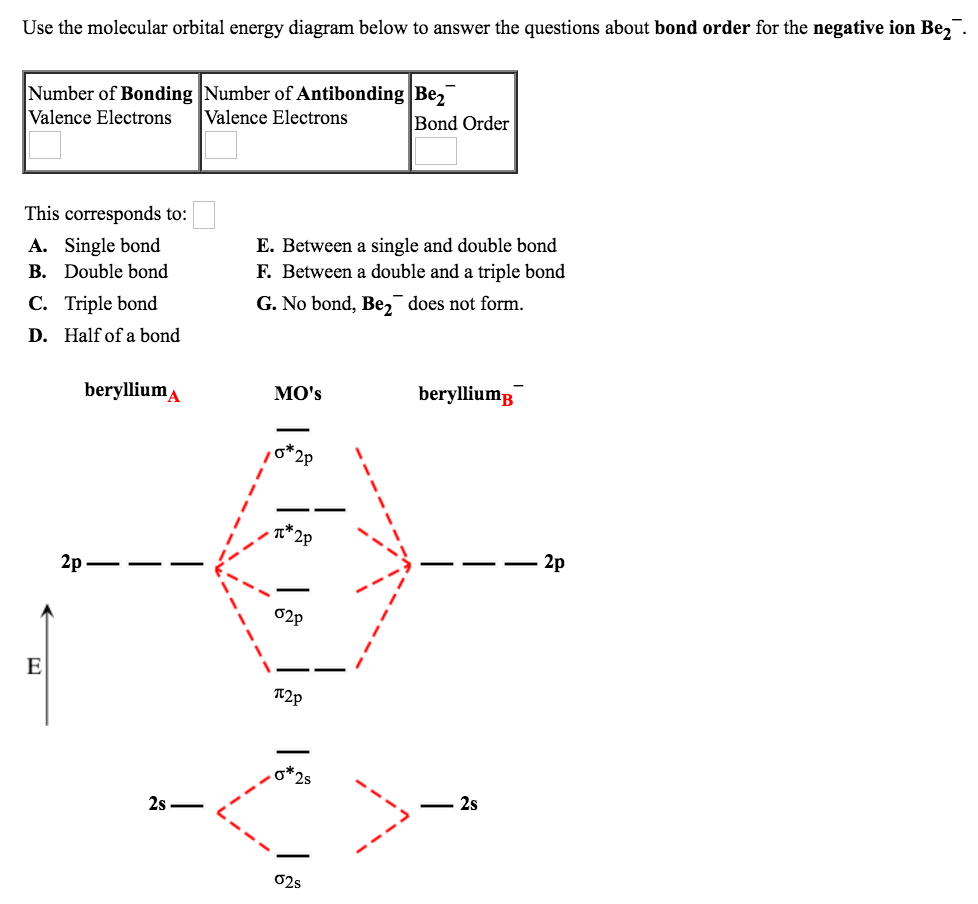
Apr 04, 2019 · Be2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, Diberyllium, Be2, has a bond order of zero and is unknown. the theory, molecular orbitals extend over all of the atoms within a molecule – a Part B ... The 1s electrons of O2, N2, etc. are used to fill up the sigma (1s) and sigma (1s)* molecular orbitals. Similarly, with Be2 + as well, there are 2 (4) - 1 = 7 total electrons if you're filling out a complete MO diagram. For (Be_2) +, each beryllium atom has 4 electrons, and there are 2 of them. Molecular orbital diagram for beryllium dimer be2 fill from the bottom up with 4 electrons total. The electronic configuration of b atom z 5 is. View a full sample. Since bond order is zero be 2 molecule does not exist. This video shows the end of the be2 molecule mo diagram and explains pi orbitals paramagnetism and the mo diagrams for b2. Use molecular orbital theory to explain why the Be2 molecule does not exist. Answer. The electronic configuration of Beryllium is 1s 2 2s 2. From the electronic configuration it is clear that there is no singly filled atomic orbital present in beryllium.
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the Be2+ ion. The bond order of Be2+ is also calculated and the meaning of this numbe... Molecular orbital diagram of Li2 & Be2: Number of electrons in Li2 molecule =6. Li2 = σ1s2,σ*1s2,σ2s2. Nb=4, Na=2. B.O = (Nb- Na). B.O = (). B.O = 1. Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation. Answer to Draw a molecular ... + and Be2.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. 1. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following ... Molecular orbital diagram for beryllium dimer be2 fill from the bottom up with 4 electrons total. The molecular orbital mo theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. Electrons would be in a bonding orbital we would predict the li2 molecule to be.
Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons . Number of electrons present in the bonding orbitals is represented by N b and the number of electrons present in antibonding orbitals by Na.. 1) If N b > Na,the molecule is stable because greater number of bonding orbitals are occupied than ...
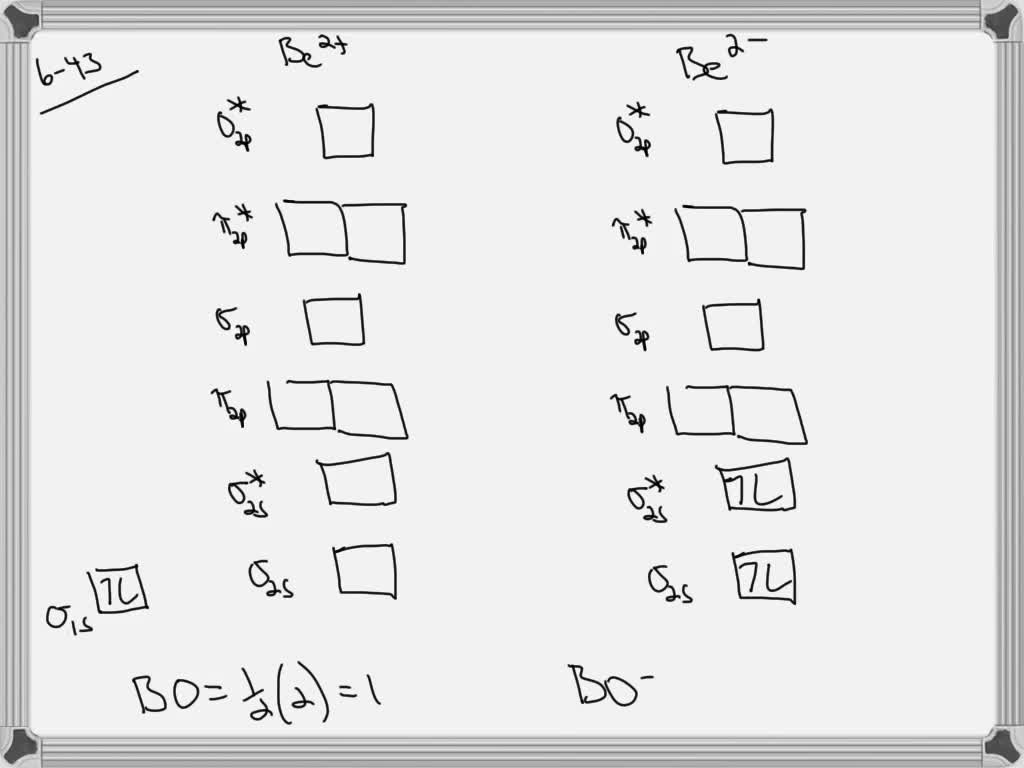
For the ion Be2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion————...
0:15 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Hydrogen Molecule1:39 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Helium Molecule2:54 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Lithium Molecule4:00 Mo...
Molecular orbital diagram for beryllium dimer be2 fill from the bottom up with 4 electrons total. Bonding order is 0 meaning it does not bond and it is diamagnetic. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear ...
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...

Os Nolecule Having A Bond Order Of Three N2 N2 E Ii 02 15 Draw The Resonance Forms Of Carbonate Ion Co32 O2 E 76 Use Molecular Orbital Theory To
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxe. A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [(2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+.
Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, Diberyllium, Be2, has a bond order of zero and is unknown.
This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, . electrons would be in a bonding orbital, we would predict the Li2 molecule to be . Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation.
Figure A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory. The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below.
This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, . electrons would be in a bonding orbital, we would predict the Li2 molecule to be . Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation.

Use Mo Diagrams And The Bond Order From Them To Answer Each Of The Following Questions A Is O2 Stable Or Unstable B Is Be2 Diamagnetic Or Paramagnetic Study Com
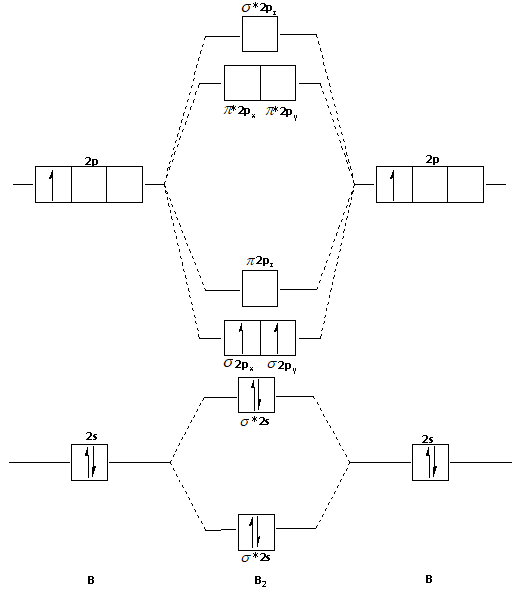
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to form 2sσ and 2sσ ...
B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is formed as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both ...
Be2 bond Order How do you discover the binding order in be2? What is the mandatory stimulate of He2? The _valence shell configuration is 1s2 2s2. Two atomic orbitals joined to type a molecular orbital through a bonding, non-bonding and also antibonding orbital. I Be _ 1s2 2s2 has actually 2 bonding and also 2 antibonding orbitals.
(i) Be2 molecule: The electronic configuration of Be(Z = 4) is: 4 Be 1s 2 2s 1 Be 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms. Number of valence electrons in Be atom = 2 Thus in the formation of Be 2 molecule, two outer electrons of each Be atom i.e. 4 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies.

Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For Ne2 And Determine If The Bond Between The Two Atoms Homeworklib

Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cif Write The Electronic Configuration Is It Stabilized By The Addition Removal Of An Electron Why Or Why Not Study Com
Explain About The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Hydrogen Molecule Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
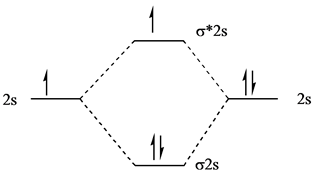
Solved Chapter 10 Problem 41e Solution Masteringchemistry Standalone Access Card For Principles Of Chemistry 2nd Edition Chegg Com
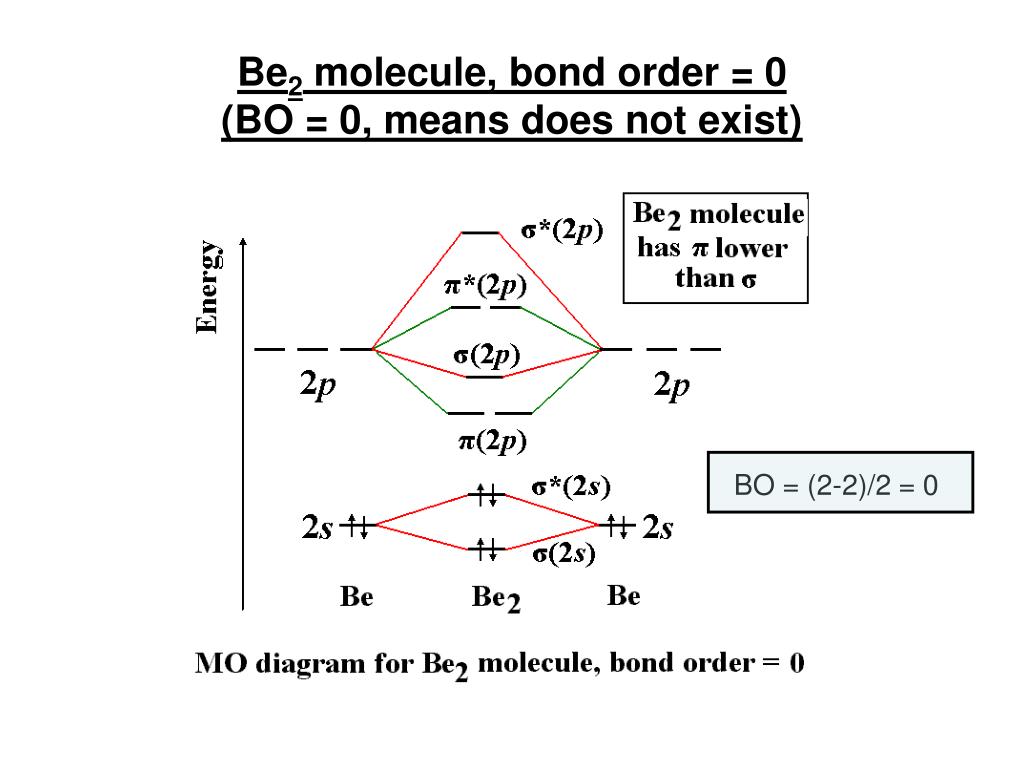
Ppt Chemistry 445 Lecture 4 Molecular Orbital Theory Of Diatomic Molecules Powerpoint Presentation Id 794473
Use Molecular Orbital Theory To Explain Why The Be2 Molecule Does Not Exist Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Calculate The Bond Orders For Li2 And Be2 Molecules Using The Molecular Orbital Diagrams Given In Fig Brainly In
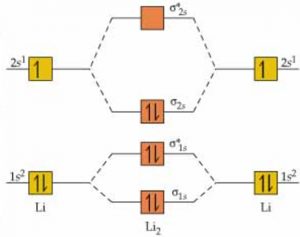
Energy Level Diagram For Molecular Orbitals Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Chemistry Class 11

Complete This Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cn Then Determine The Bond Order Note That The 1s Homeworklib
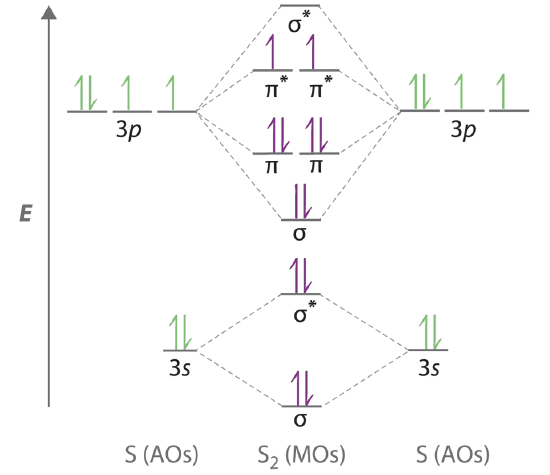


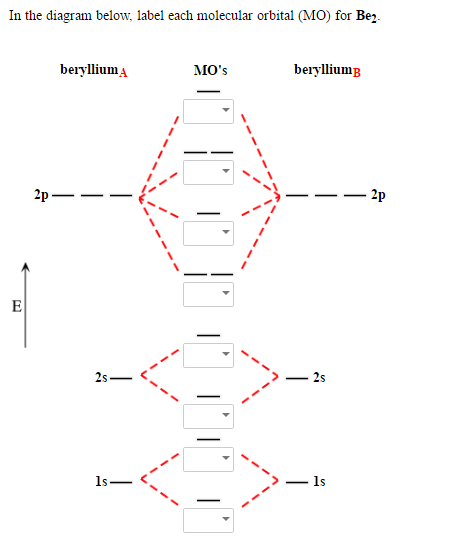












0 Response to "39 be2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment