38 schmidt cassegrain telescope diagram
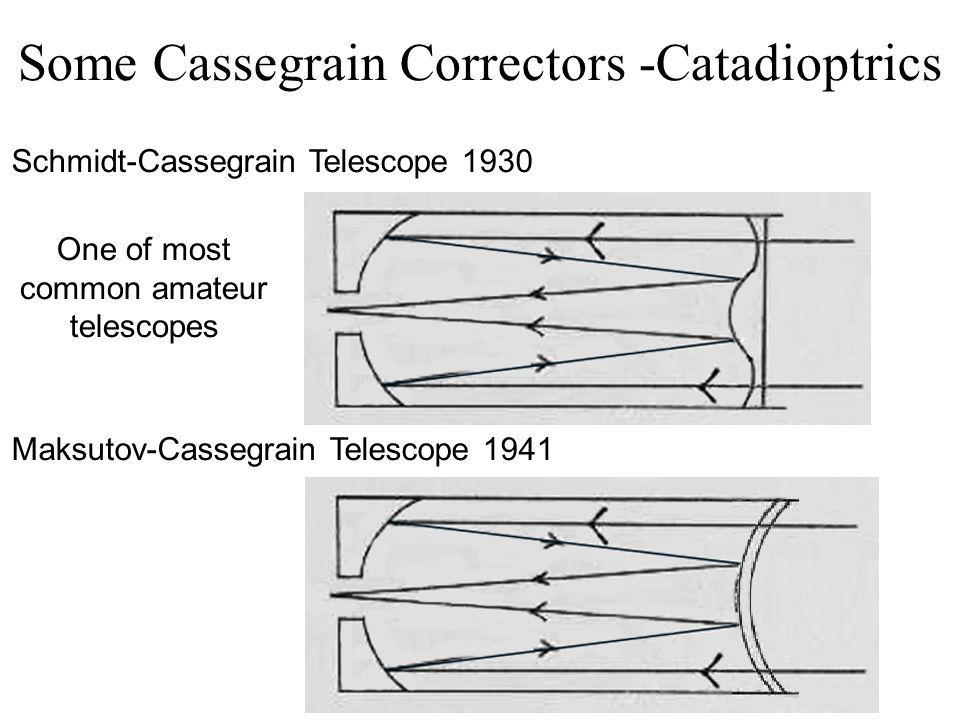
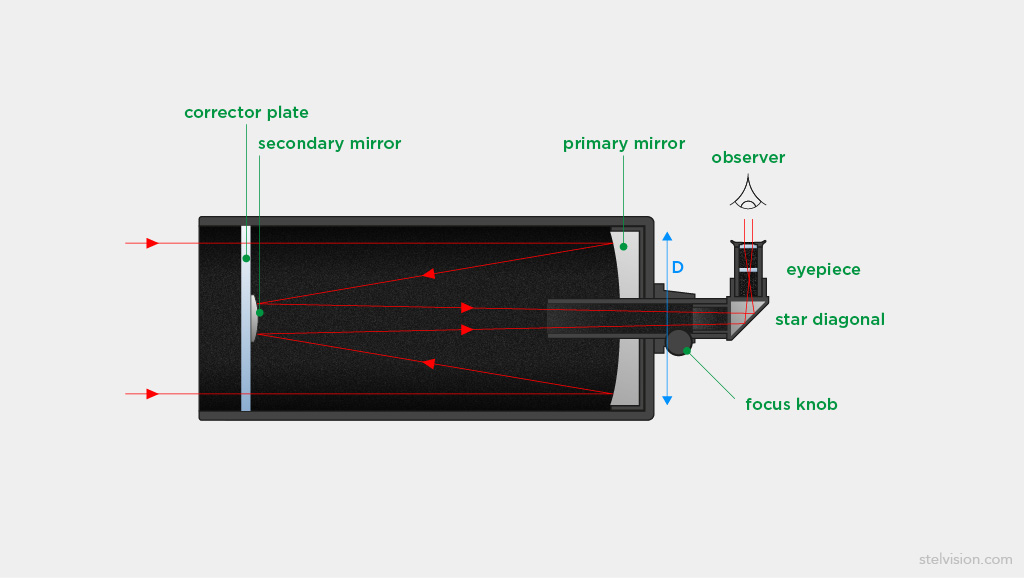
8" AND 10" LX50 Schmidt-Cassegrain Telescope: Meade 8" and 10" LX50: Meade 8" and 10" Schmidt - Cassegrain Telescopes, with standard equatorial wedge and optional variable-height standard field tripod. Advanced optical and electronic technology at the most affordable prices ever. The Meade Schmidt-Cassegrain Optical System (Diagram not to scale) In the Schmidt-Cassegrain design of the Meade 8", 10", and 12" models, light enters from the right, passes through a thin lens with 2-sided aspheric correction ("correcting plate"), proceeds to a spherical primary mirror, and then to a convex aspheric secondary mirror.
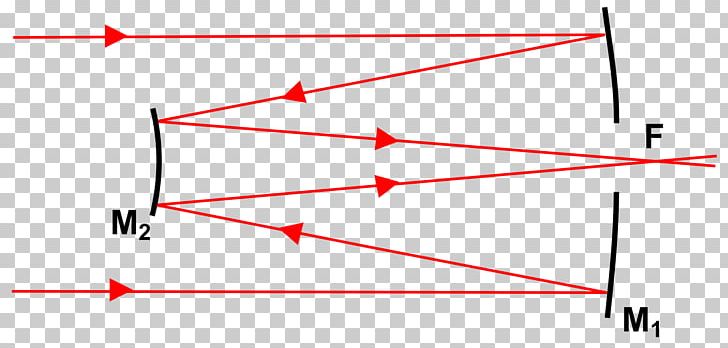
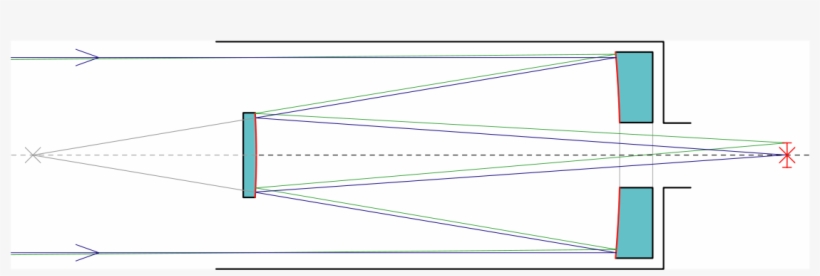
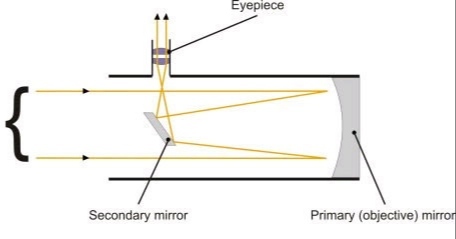
A Schmidt-Cassegrain has a Schmidt correcting lens that collects an object's light. From that aspherical, or non-round, lens, the light goes to a round mirror, which reflects it back toward the telescope's front to another mirror and then to the eyepiece, which is at the telescope's back.
Schmidt cassegrain telescope diagram
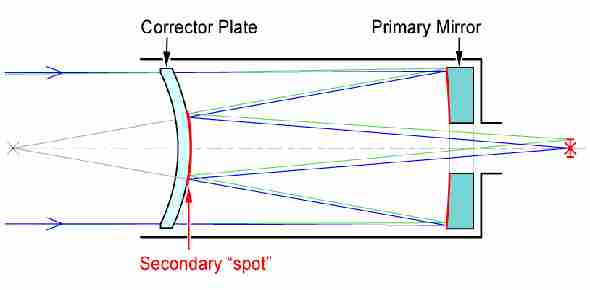
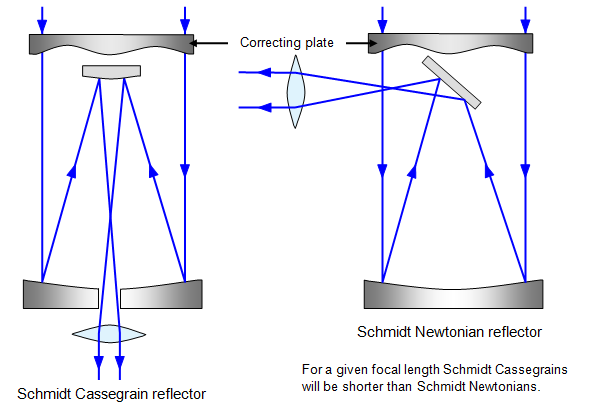
The Schmidt Cassegrain Telescope (SCT) The Schmidt Cassegrain, or SCT, is a bit stubbier (shorter) for a given aperture, as illustrated above. It uses a somewhat complex curve on a nearly flat corrector plate to compensate for the spherical primary. The aspheric curvature of the corrector plate is exaggerated in this diagram. Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes. The Schmidt-Cassegrain is not a telescope you will find in major research observatories, but it is arguably the most widespread design used in the amateur telescope market. As its name implies, it is a hybrid of the Schmidt and Cassegrain designs. The light passes through a corrector lens and reflects off a concave spherical primary, just like in a Schmidt telescope. View the secondary mirror holder from the corrector plate end of the Schmidt-Cassegrain Telescope. The collimation screw nearest the ground is labeled "A". Screws "B" and "C" are as shown in the center of the diagram above. The eyepiece should be oriented upward opposite to the position of screw "A" as shown by "EP" in the ...
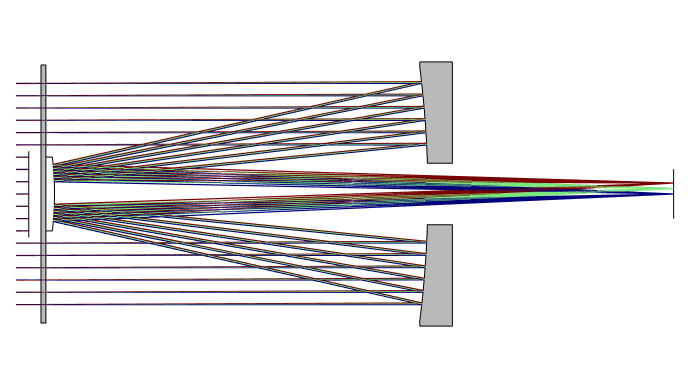
Schmidt cassegrain telescope diagram. A Cassegrain Telescope Uses Two Mirrors As Shown In Figure Below Such Is Built With The 20 Mm Apart If Radius Of Curvature Large Mirror. Schematic Drawing Of The Adapted Meade Schmidt Cassegrain Telescope Scientific Diagram. Draw A Schematic Diagram Of Reflecting Telescope Construction Write Its Two Advantages Over Refracting Sarthaks Econnect ... FIGURE 174: Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope is a Cassegrain-like two-mirror system combined with a full-aperture Schmidt corrector.Various combinations of corrector separation and mirror conics are possible, with somewhat different image field properties. Prevailing commercial arrangement is a compact design with fast spherical primary and usually also spherical secondary mirror, resulting in ~ƒ ... Figure 1-1. This cross-section diagram shows the light path of the Schmidt-Cassegrain optical system. Note that the light rays travel the length of the telescope tube three times, making this a compact design. Note that the curve of the corrector plate is greatly exaggerated. Collimating a Schmidt Cassegrain Telescope with a Laser. A star test is the most accurate way to check that your telescope is correctly collimated, however, with care, a laser collimator can do an excellent job for you. ... The laser collimator is now calibrated for this one telescope. See the diagram over the page. In future, insert the ...
The Meade Schmidt-Cassegrain Optical System 8.25" 7" Primary Baffle Tube Secondary Baffle Field Stops Primary Mirror (f/2.5) Focal Plane The Meade 7" (178mm) Maksutov-Cassegrain Optical System Meniscus Lens The Meade 7" Maksutov-Cassegrain design optimizes imaging performance by utilizing a combination of a two-sided Reflector Telescopes Joseph A. Shaw - Montana State University Dall-Kirkham • Primary mirror = ellipse • Secondary = sphere • Spherical = 0 (on axis, obj at inf) • Spherical secondary generates additional aberrations … • Field limited by coma, to about times smaller than for classical cassegrain. "poor man's cassegrain" Cassegrain Telescopes. Whether you're visually observing or imaging, find your perfect Cassegrain Telescope for any use at OPT! Cassegrain telescopes are great optical performers, and offer a variety of designs for any use. There's the Schmidt Cassegrain, the Maksutov Cassegrain, and the Ritchey-Chretién design, among many others. File:Schmidt-Cassegrain-Telescope.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 800 × 400 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 160 pixels | 640 × 320 pixels | 1,024 × 512 pixels | 1,280 × 640 pixels | 2,560 × 1,280 pixels.
This completes the major dimensions of the Cassegrain telescope. All that is left is to determine the shape of the primary and secondary mirrors. This is done with the two formulas below. The first is the shape of the primary which is: s = a / B = 27.375 / 20.875 = 1.31 102mm Wide View Manual. 11-inch Dovetail Bar Diagram. 14-inch Dovetail Bar Diagram. 2013 Sport Optics Guide. 21036-WM Instruction Manual Addendum. 28 pc. Microscope Kit Manual. 4 Color LCD Weather Station Manual (English, French, German, Italian, Spanish) 44310 LCD Handheld Microscope Manual (English, French, German, Italian, Spanish) While there are many variations of the Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope design (both mirrors spherical, both mirrors aspherical, or one of each), they can be divided into two principal types: compact and non-compact.In the compact form, the corrector plate is located at or near the focus of the primary mirror. In Schmidt- Cassegrain (SCT) scopes, the rear of the glass corrector plate is flat - the required, complex curvature of the corrector plate is ground into the front of the plate only. Thus for SCTs the hyperbolic secondary mirror must be a separate mirror - it is held in a mechanical assembly that is mounted in a hole drilled in the center of ...
In short, a Maksutov-cassegrain telescope is generally better for planet viewing due to the narrow and generally large focal ratios, however this also does compromise the astrophotography performance of Mak telescopes, which is an area Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes don't suffer nearly as much from whilst still having plenty of ability when viewing planets.
Collimating a Schmidt-Cassegrain. Collimation is critical to obtaining the best performance from your telescope. Aligning the optics of a Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope (SCT) is much easier than collimating a Newtonian telescope and can easily be learned by any user. However, there are some tricks to doing it right, and some things to avoid.

Cassegrain Reflector Reflecting Telescope Catadioptric System Schmidt Cassegrain Telescope Mirror Angle Furniture Text Png Pngwing
Precise collimation is essential to good performance for any Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope. For SCTs, it's done by small adjustments to the tilt and position of the secondary mirror in its cell. Celestron SCTs use 3 small Phillips or hex head screws for adjustment. Some optical tubes hide the screws under a cover that you can easily pry off ...
There are three basic types of telescopes - reflectors, refractors, and Schmidt Cassegrain telescopes. Refractor telescopes gather light with the objective lens, the one where light enters the ...
The Meade Schmidt-Cassegrain Optical System 8.25" 7" Primary Baffle Tube Secondary Baffle Field Stops Primary Mirror (f/2.5) Focal Plane The Meade 7" (178mm) Maksutov-Cassegrain Optical System Meniscus Lens The Meade 7" Maksutov-Cassegrain design optimizes imaging performance by utilizing a combination of a two-sided
Catadioptric Cassegrain telescopes comprised of two mirrors along with a spherical primary mirror for reducing cost. Refractive corrector element(s) are often combined in the design to rectify the resulting aberrations. Schmidt-Cassegrain Telescope. The Schmidt-Cassegrain reflector design was built based on the wide-field Schmidt camera.
Answer (1 of 6): Here's a diagram of a Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope (SCT). The label at the bottom refers to a general class of telescopes which use a combination of mirrors and lenses. As you can see, incoming light is reflected from the primary mirror, bounced of a secondary mirror, and back th...
The kind of telescope illustrated in the diagram (of course, not to scale!) is a Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope on a fork mount. The telescope is rotated to point in different directions relative to a surface which is tilted to be at the same angle as the ground at the North Pole. A pole is actually shown in the diagram, to make the Earth's axis ...
It is a Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope, with a 4″ aperture, 1200mm focal length. A cassegrain reflector uses a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror to form the image, thus giving the telescope its name. A schematic diagram of the telescope is given here.
Answer (1 of 2): Most reflecting telescopes have central obstructions, but they don't produce blind spots in the visual field. The obstruction is so close to the image plane (your eyepiece, if you like) that it's completely out of focus. As an analogy, think of a speck of dust on a pair of glasse...
Cassegrain Reflector Ritchey Chretien Telescope Reflecting Telescope Maksutov Telescope Wikipedia Png Clipart Angle Area Cassegrain Reflector
The telescope features a 6″ Schmidt Cassegrain Optical Tube Assembly and an Aluminum Optical Tube. It has StarBright XLT coatings, which are the premium choice in this industry. This innovative coating is made up of three different layers that greatly increase contrast and light transmission.
View the secondary mirror holder from the corrector plate end of the Schmidt-Cassegrain Telescope. The collimation screw nearest the ground is labeled "A". Screws "B" and "C" are as shown in the center of the diagram above. The eyepiece should be oriented upward opposite to the position of screw "A" as shown by "EP" in the ...
Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes. The Schmidt-Cassegrain is not a telescope you will find in major research observatories, but it is arguably the most widespread design used in the amateur telescope market. As its name implies, it is a hybrid of the Schmidt and Cassegrain designs. The light passes through a corrector lens and reflects off a concave spherical primary, just like in a Schmidt telescope.
The Schmidt Cassegrain Telescope (SCT) The Schmidt Cassegrain, or SCT, is a bit stubbier (shorter) for a given aperture, as illustrated above. It uses a somewhat complex curve on a nearly flat corrector plate to compensate for the spherical primary. The aspheric curvature of the corrector plate is exaggerated in this diagram.
Is There A Blind Spot In The Middle Of The Image From A Schmidt Cassegrain Reflecting Telescope Quora
















0 Response to "38 schmidt cassegrain telescope diagram"
Post a Comment