38 ray diagram of concave mirror
In this video you will learn how to draw ray diagrams for concave mirror in an easy way. Shows how to draw ray diagrams and locate the image for concave mirrors. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscience.c...
Hi, this video with animation explains how the reflection happens in a CONCAVE MIRROR , and how to develop the Ray Diagrams , step by step, in order to get t...

Ray diagram of concave mirror
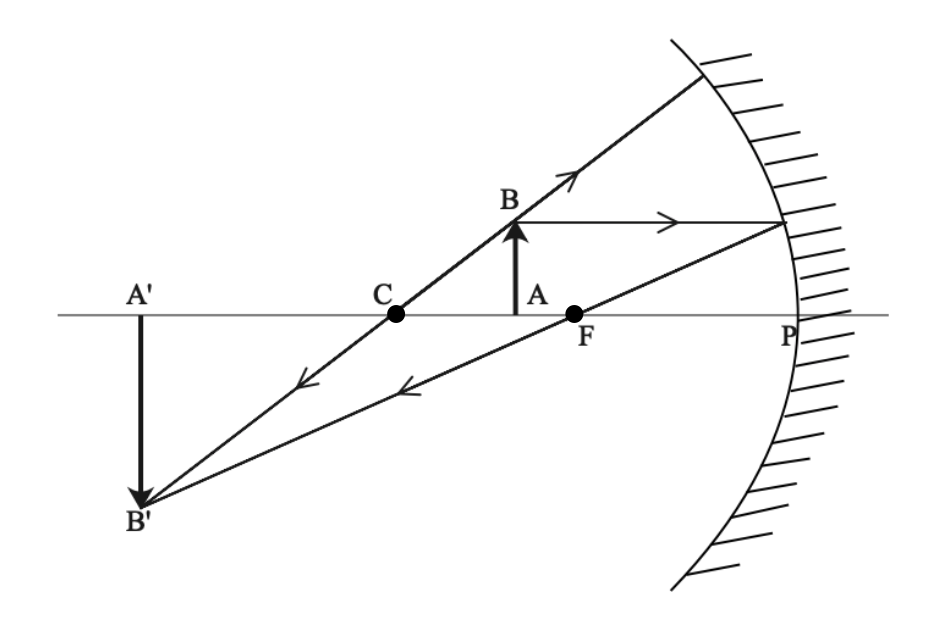
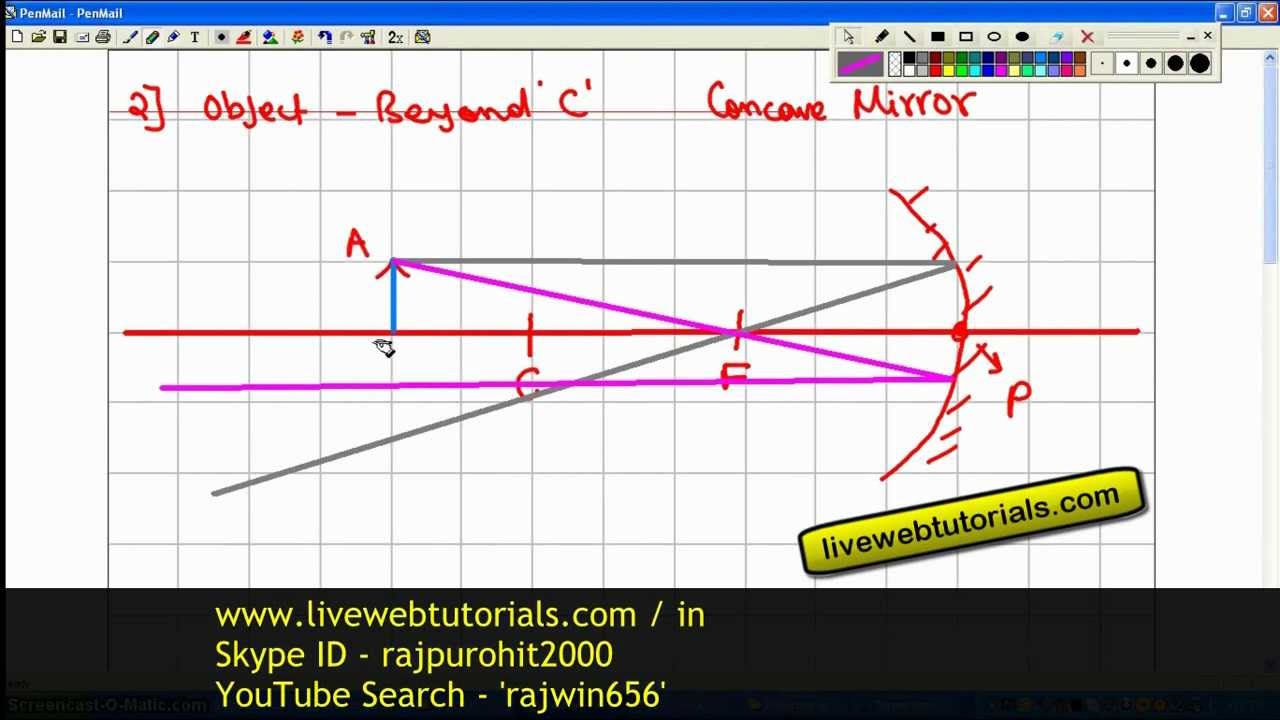
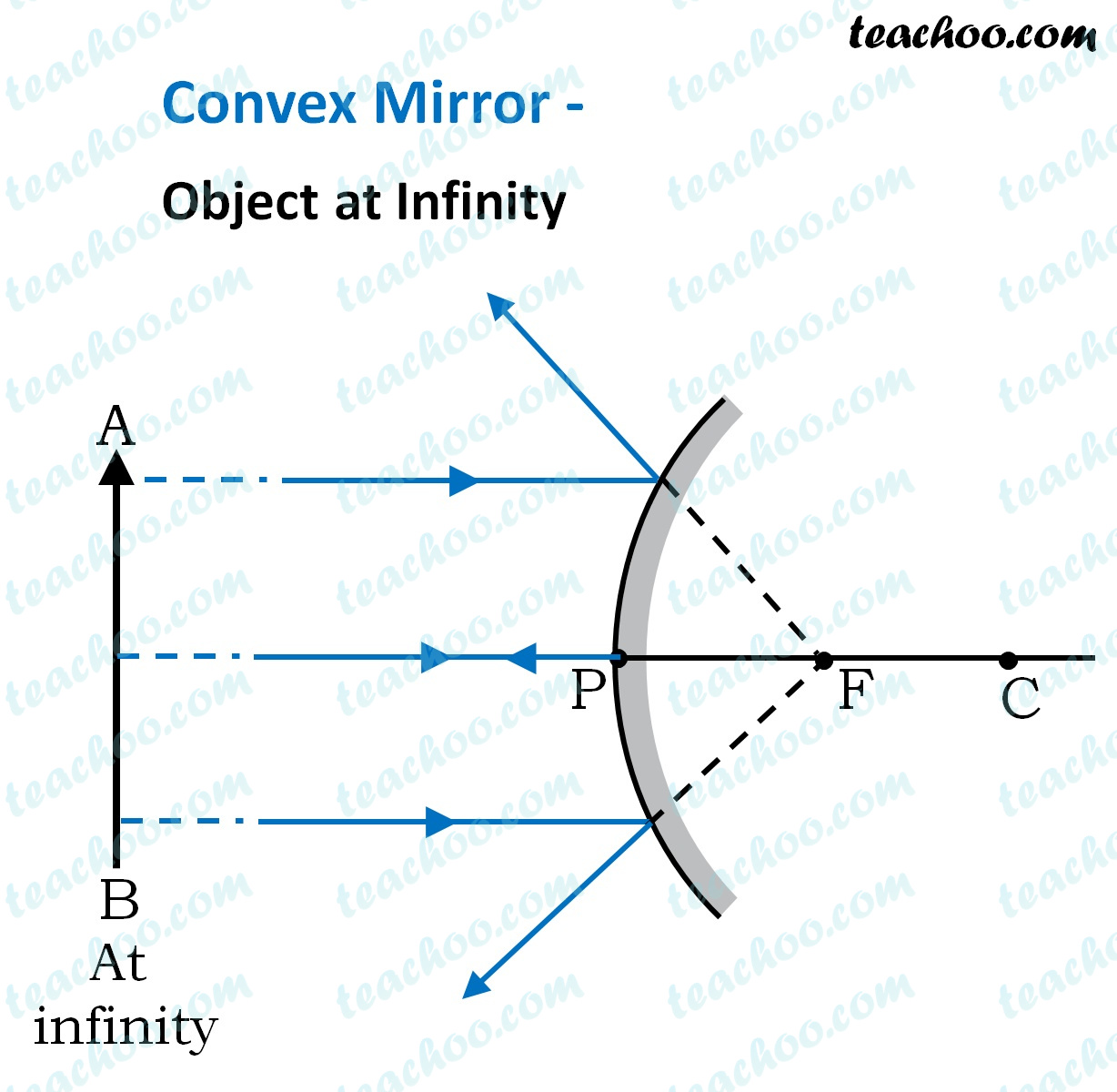
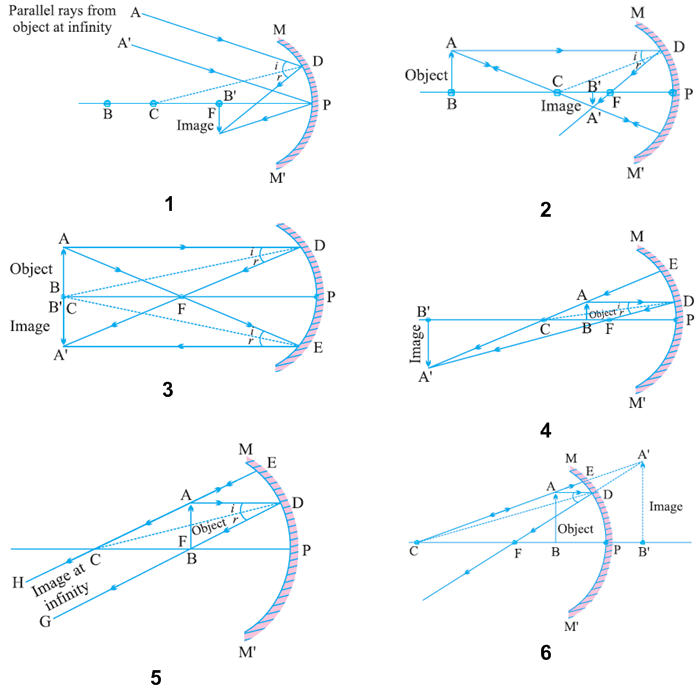
For a Concave mirror, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes t Ray Diagrams of Concave and Convex Mirrors travelling parallels to the principle axis passes through the focal point after reflect by the mirror. A ray passes through the Centre of curvatures of the mirror is reflected back along its on path. Draw the following diagrams in which a ray of light is incident on a concave/convex mirror. show the path of this rays, after reflection in each case. 4:21This video explains very easy method to draw ray diagram of concave mirror when the object is placed at ...11 Oct 2020 · Uploaded by Funscience
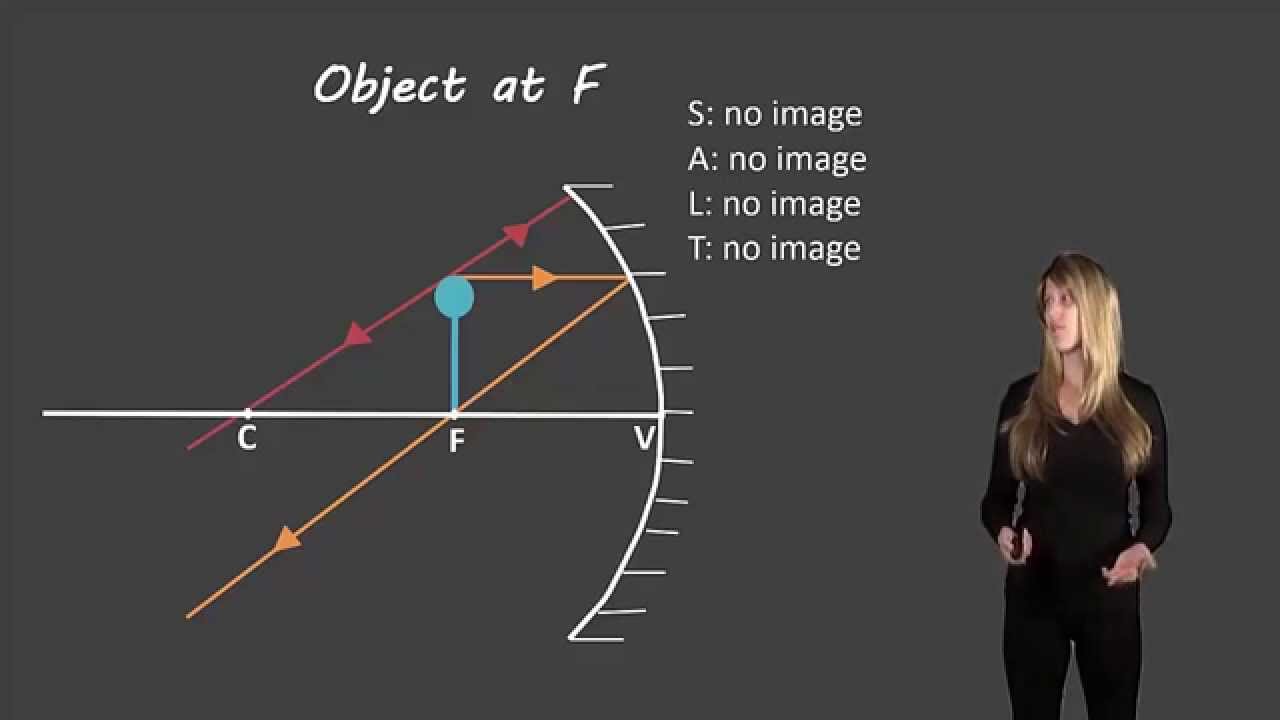
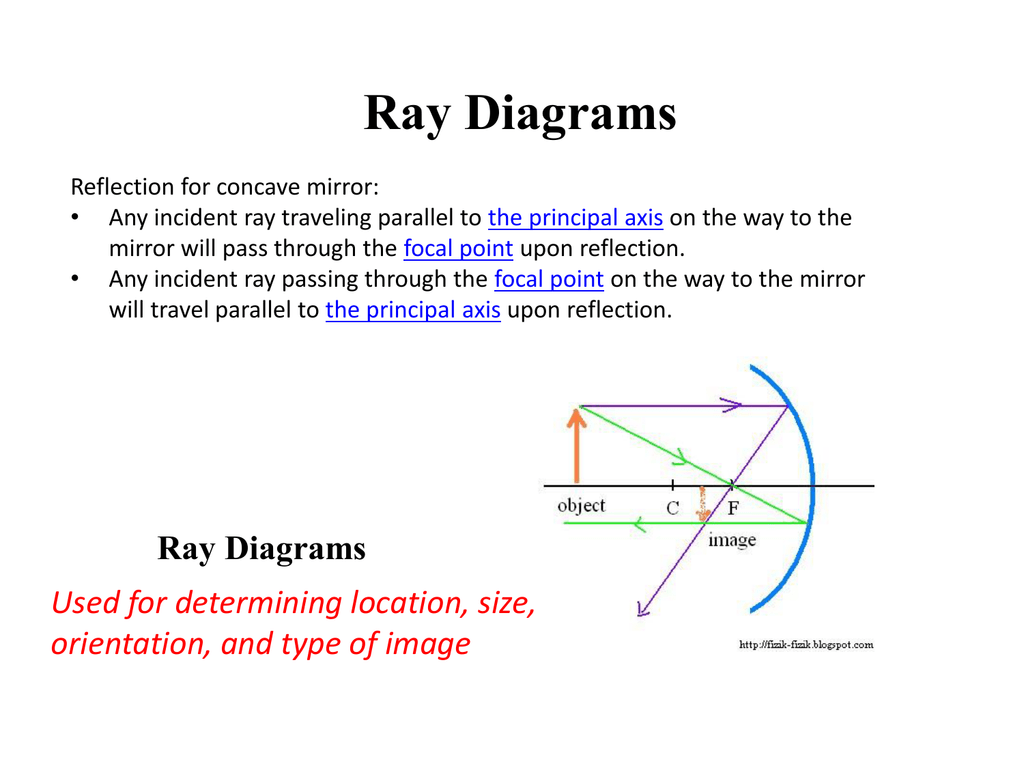
Ray diagram of concave mirror. Previously in Lesson 3, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the general location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by concave mirrors. Perhaps you noticed that there is a definite relationship between the image characteristics and the location where an object is placed in front of a concave mirror. The purpose of this portion of the lesson is to summarize these ... In a concave mirror, the principal axis is a line that is perpendicular to the center of the mirror. The easiest way to visualize what a image will look like in this type of mirror is a ray diagram. Before that can be done, the focal point must first be defined. This point is half way between the mirror and the center of curvature on the principal axis. The distance to the focal point from the ... Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors and its use. For a Concave Mirror, an object can be placed at any position so that image is created at different - different positions. We can find image position, its nature, and its size using Ray Diagrams. To get an image of an object we need at least two rays coming from the object to meet somewhere. Draw the reflected ray corresponding to the ray incident on a concave mirror as shown in the ray diagram? Medium. View solution > Write the characteristics of the image formed by an object placed at the center of curvature of a concave mirror? Hard. View solution > Compare and contrast between the image formation by a concave and convex mirror, write the similarities in the common space and ...
Simple ray diagram showing typical chief and marginal rays. A meridional ray or tangential ray is a ray that is confined to the plane containing the system's optical axis and the object point from which the ray originated. A skew ray is a ray that does not propagate in a plane that contains both the object point and the optical axis. Such rays do not cross the optical axis anywhere, and are ... 31.10.2021 · An object with a height of 48 cm is placed 1.8 m in front of a concave mirror with a focal length of 0.57 m \\ Part A: Determine the approximate location of the image using a ray diagram. \\ … This is a Physics practice problem showing how to draw a ray diagram for a concave mirror.Look here for a website which describes what f and c arehttp://www.... Images formed by concave mirror using ray diagram ... Question 1 The image formed by concave mirror is seen to be virtual,erect and larger than the object.What is ...
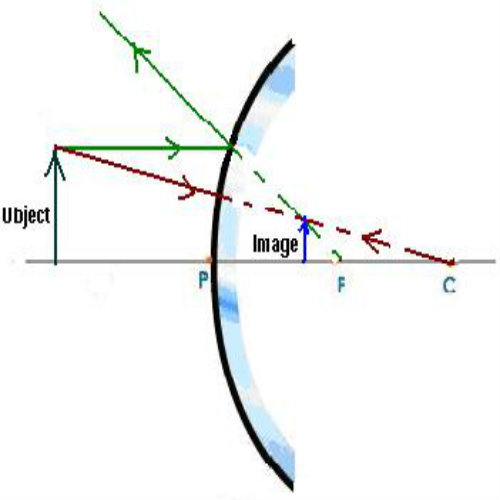
2:42Ray diagram of concave mirror when object placed at infinity#raydiagramofconcavemirror ...8 Sep 2020 · Uploaded by Tutor Talk Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus. The size of the image is smaller than compared to that of the object. When ... Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams A spherical mirror is a reflective segment of a sphere with a radius of curvature R. It can be convex (outside surface of a sphere) or concave (inside surface). First we will consider a concave spherical mirror. The mirror has a radius R, and the distance from the mirror to the object is p. The ray coming from the horizontal mirror to the vertical mirror is determined using the law of reflection. A normal line is drawn (in black) and the angle of reflection is measured; this angle is then used to determine the angle of incidence at the vertical mirror's surface. A ray is then traced backwards at this angle to the horizontal mirror. The light originated from the top of the object ...
Ray Diagram for a Concave Mirror, p . f. The angle of reflection is denoted by angle ____. CONCAVE MIRRORS Extra Practice Worksheet a) Draw a raydiagram for each to locate the imageHand drawn worksheet for practice constructing ray diagrams for a plane mirror. They are most often shown as two circles that intersect in the middle of the page. Ray Diagrams Physics Classroom. On the diagram ...
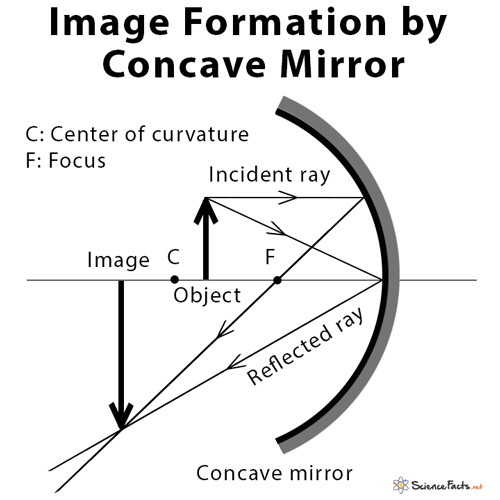
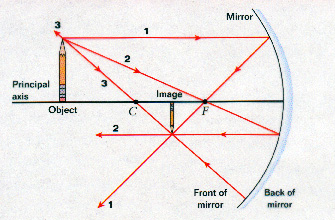
A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Incident rays - at least two - are drawn along with their corresponding reflected rays. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Every observer would observe the same image location and every light ray would follow the law of reflection.
Now based on the type of reflecting surface we can classify mirrors as concave, convex, or plane mirror. Here we will be talking about the plane mirror only. So to form an image we require at least two rays from the object which meet or appear to meet at a point. In the case of a plane mirror, here we have used three images for better clarity in the ray diagram shown below. For the ray ...
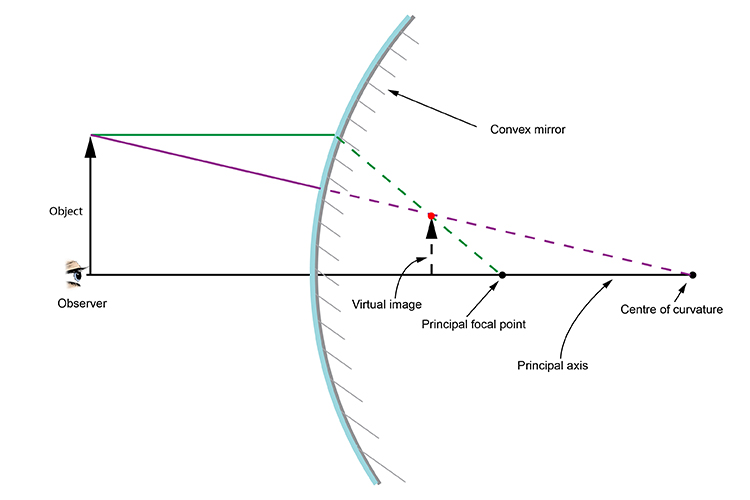
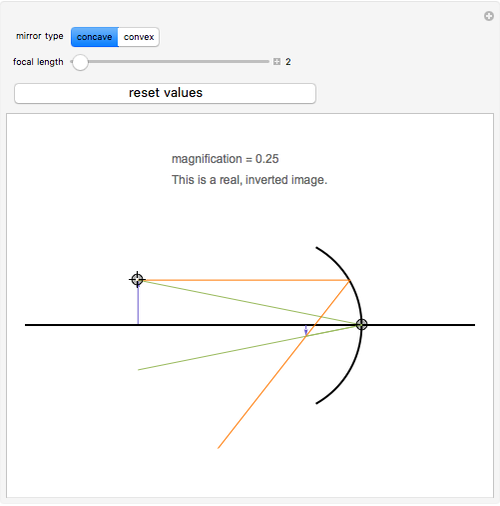
Concave and Convex Mirrors. Description Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror. ...
4:21This video explains very easy method to draw ray diagram of concave mirror when the object is placed at ...11 Oct 2020 · Uploaded by Funscience
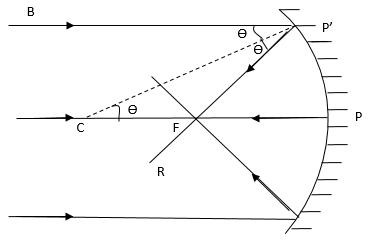
Ray Diagrams of Concave and Convex Mirrors travelling parallels to the principle axis passes through the focal point after reflect by the mirror. A ray passes through the Centre of curvatures of the mirror is reflected back along its on path. Draw the following diagrams in which a ray of light is incident on a concave/convex mirror. show the path of this rays, after reflection in each case.
For a Concave mirror, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes t

Draw A Neat Two Ray Diagram To Illustrate How A Concave Mirror Is Used As A Shaving Mirror Physics Shaalaa Com

Practice And Draw The Ray Diagrams For Concave Mirror For Class 10 Chapter Light Subject Science Brainly In
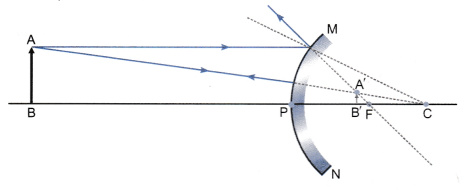
List Two Properties Of The Images Formed By Convex Mirrors Draw Ray Diagram In Support Of Your Answer Cbse Class 10 Science Learn Cbse Forum

Diagram By Akita Your Diagram Source From Akita Concave Mirrors Spherical Mirror How To Memorize Things















0 Response to "38 ray diagram of concave mirror"
Post a Comment