38 probability tree diagram problems
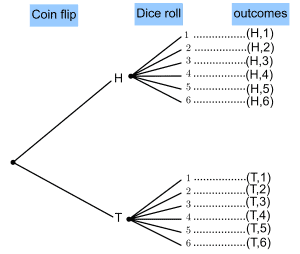
Probability Tree Diagrams For Independent Events. How To Solve Probability Problems Using Probability Tree Diagrams? Example: A coin is biased so that it has a 60% chance of landing on heads. If it is thrown three times, find the probability of getting a) three heads b) 2 heads and a tail c) at least one head. Show Video Lesson Tree Diagrams n if you flip a coin twice, you can model the possible outcomes using a tree diagram or an outcome table resulting in 4 possible outcomes T H T H H T T T TT T H TH H T HT H H HH Simple Event Flip 1 Flip 2 PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version www.pdffactory.com
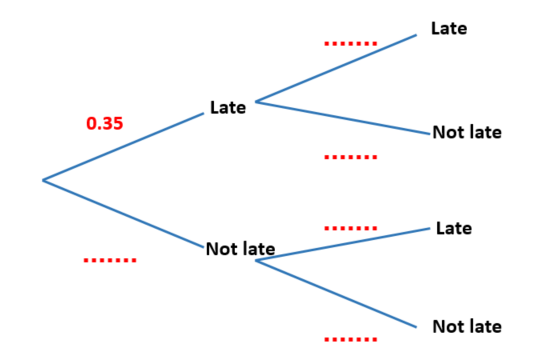
Complete the tree diagram. Today Tomorrow Rain No rain Rain No rain No rain Rain [2] (b) Find the probability that it will rain on at least one of these two days. Answer(b) [3] (c) Find the probability that it will rain on only one of these two days. Answer(c) [3]
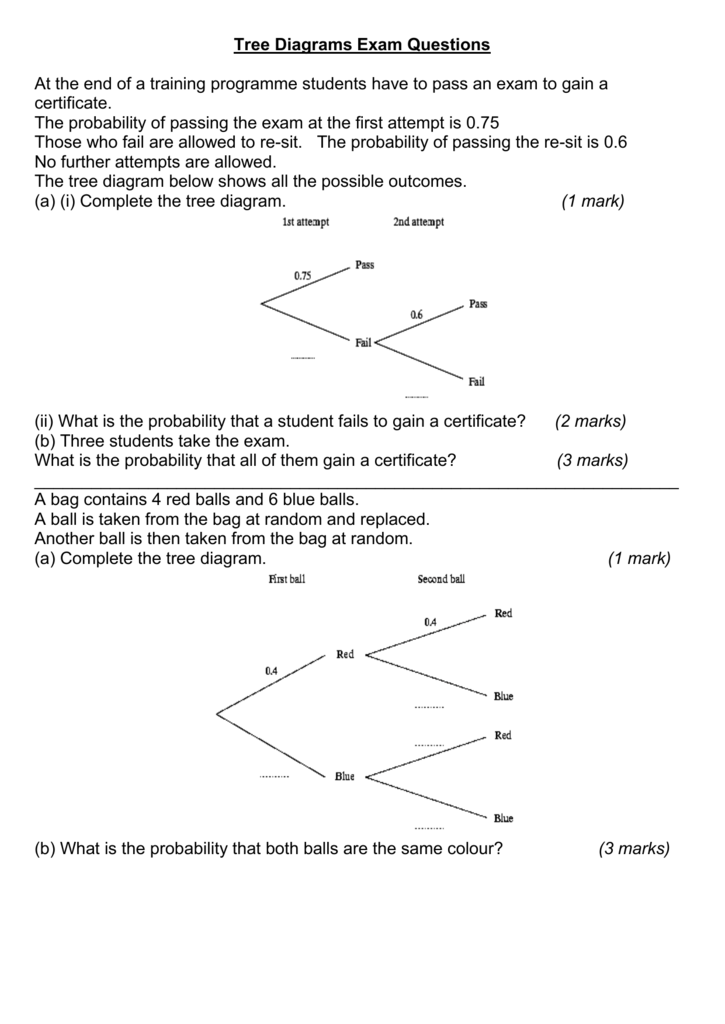
Probability tree diagram problems
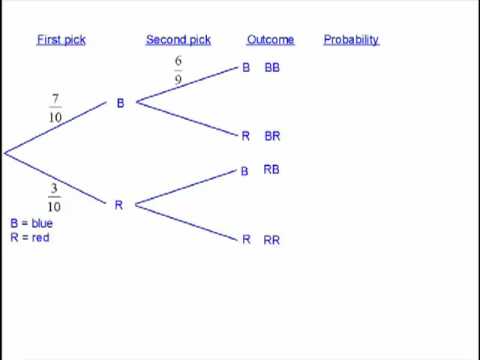
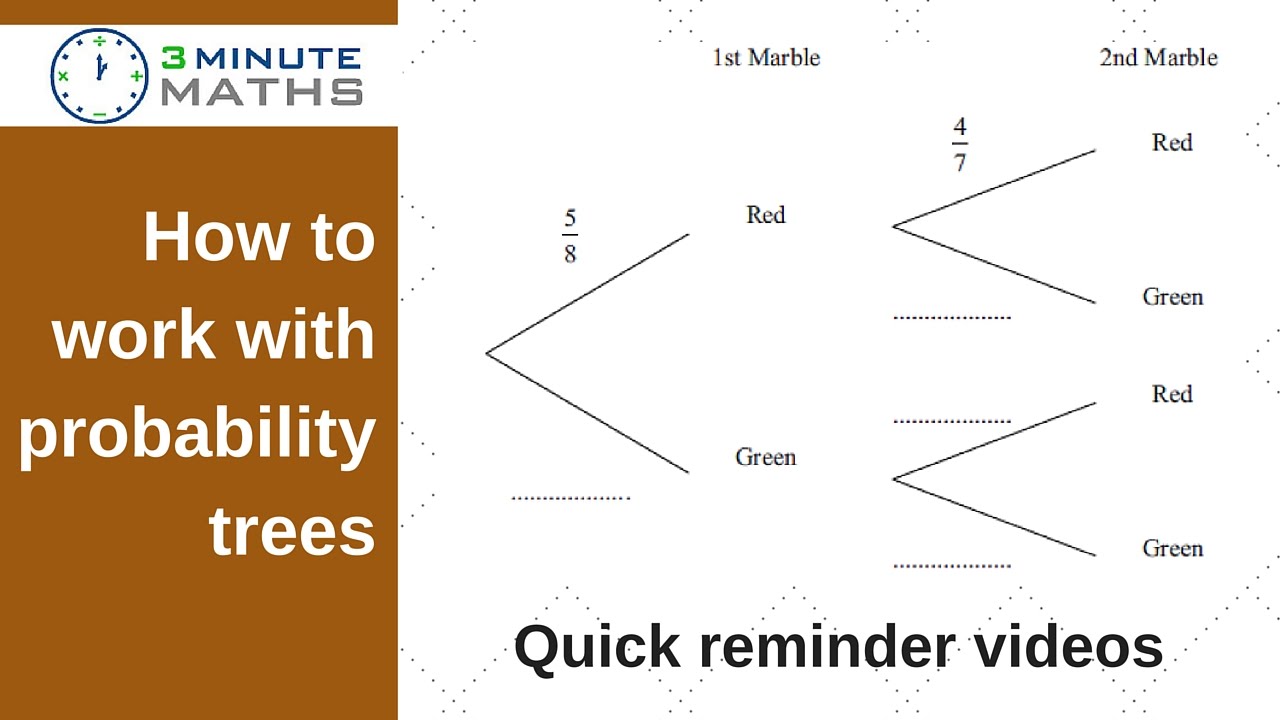
Tree Diagrams A tree diagram is a way of seeing all the possible probability 'routes' for two (or more) events. A game consists of selecting a counter from a bag (containing three red counters and seven blue) twice. Question 1: Find the probability that a player selects two red counters. (This path has been drawn on the tree diagram with arrows.) This simple probability tree diagram has two branches: one for each possible outcome heads or tails.Notice that the outcome is located at the end-point of a branch (this is where a tree diagram ends).. Also, notice that the probability of each outcome occurring is written as a decimal or a fraction on each branch.In this case, the probability for either outcome (flipping a coin and getting ... Conditional probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. This is the currently selected item. Next lesson. Independent versus dependent events and the multiplication rule. Sort by: Top Voted. Conditional probability tree diagram example.
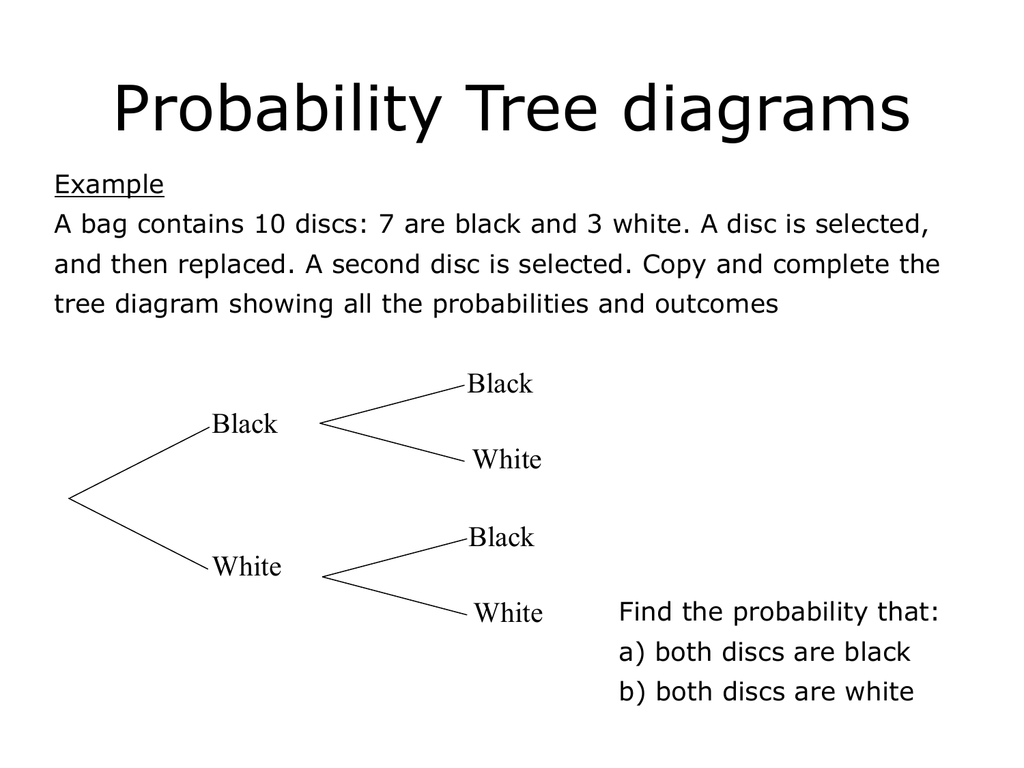
Probability tree diagram problems. Exam Style Questions. Ensure you have: Pencil, ... The probability that he wins on the Teddy Grabber is 0.2. ... (a) Complete the probability tree diagram.12 pages 4 Sep 2021 — As we have already seen, tree diagrams play an important role in solving probability problems. A tree diagram helps us not only visualize, ... Example 1: If a coin is tossed two times, show the probabilities of all events in a tree diagram. Solution: Let, H and T represent the head and tail of a coin. n (H) = 1. n (T) = 1. n (S) = 1 + 1 = 2. It is the case of independent events. From the tree diagram, The probability of both head = P (HH) = ½ × ½ = ¼. b) The sum of numbers landed on is even. c) The two numbers are different. d) Given even first number, the second number is even. e) Given odd first number, the second number is odd. f) The product of the two numbers landed on is less than 6. Solution to this Calculus Tree Diagram Probability practice problem is given in the video below!
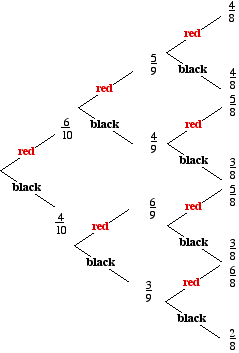
We can extend the tree diagram to two tosses of a coin: How do we calculate the overall probabilities? We multiply probabilities along the branches; We add probabilities down columns; Now we can see such things as: The probability of "Head, Head" is 0.5×0.5 = 0.25 All probabilities add to 1.0 (which is always a good check); The probability of getting at least one Head from two tosses is 0.25 ... 16 Apr 2021 — Sometimes, you'll be faced with a probability question that just doesn't have a simple solution. Drawing a probability tree (or tree diagram) is ... Probability & Tree Diagrams. Probability is the study of how likely things are to happen. This topic will look at how tree diagrams can be used to determine the probability of different types of events happening. Make sure you are happy with the following topics before continuing. Conditional probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. This is the currently selected item. Next lesson. Independent versus dependent events and the multiplication rule. Sort by: Top Voted. Conditional probability tree diagram example.
This simple probability tree diagram has two branches: one for each possible outcome heads or tails.Notice that the outcome is located at the end-point of a branch (this is where a tree diagram ends).. Also, notice that the probability of each outcome occurring is written as a decimal or a fraction on each branch.In this case, the probability for either outcome (flipping a coin and getting ... Tree Diagrams A tree diagram is a way of seeing all the possible probability 'routes' for two (or more) events. A game consists of selecting a counter from a bag (containing three red counters and seven blue) twice. Question 1: Find the probability that a player selects two red counters. (This path has been drawn on the tree diagram with arrows.)


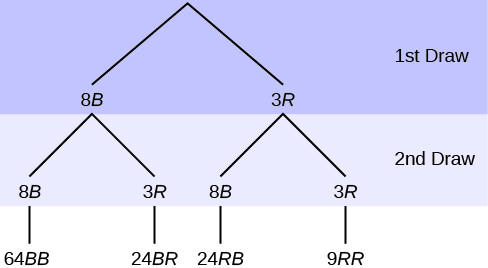
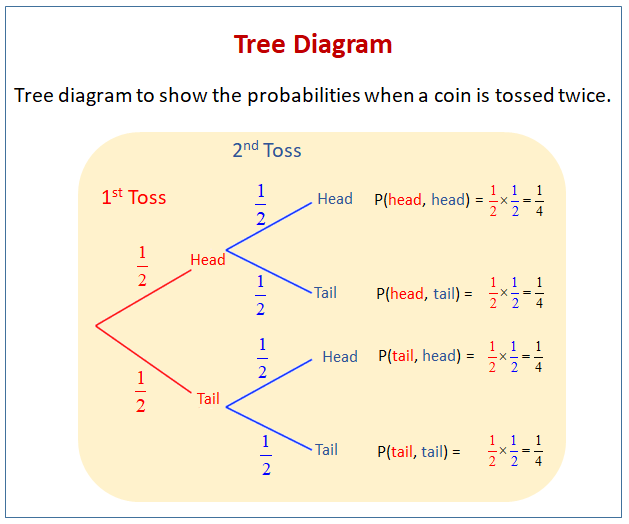
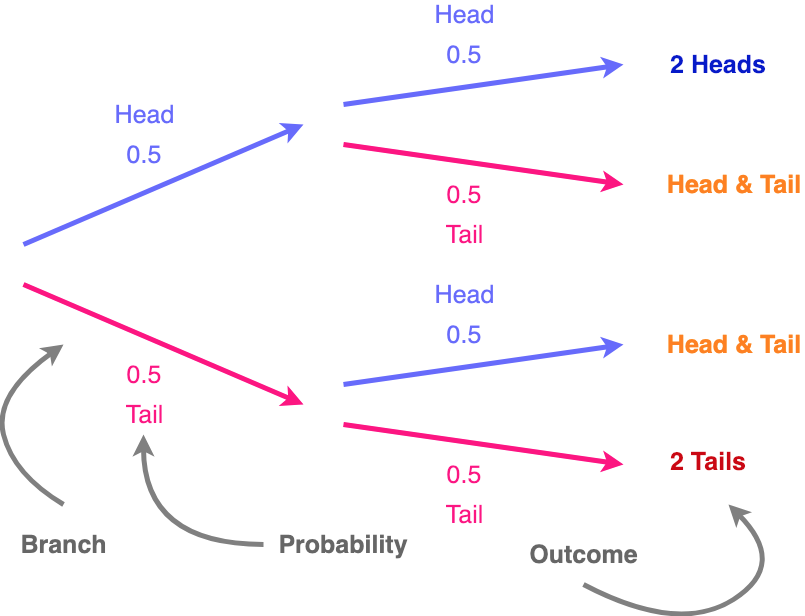




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TreeDiagram2-c209ffffddd14e989cd72e9c38e518f0.png)
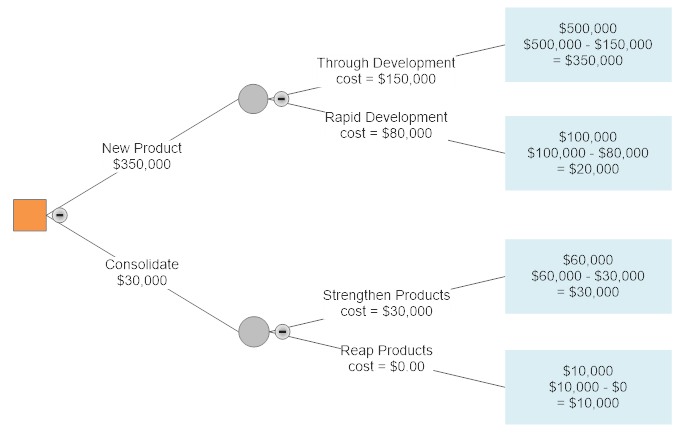
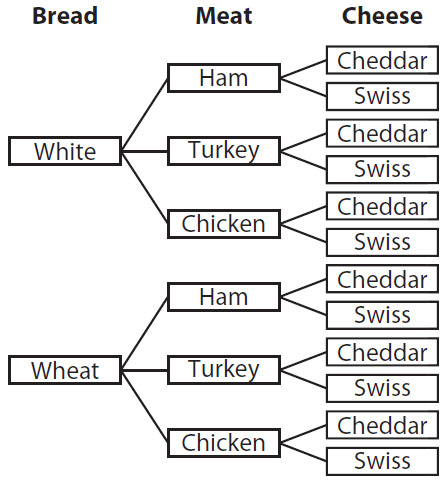

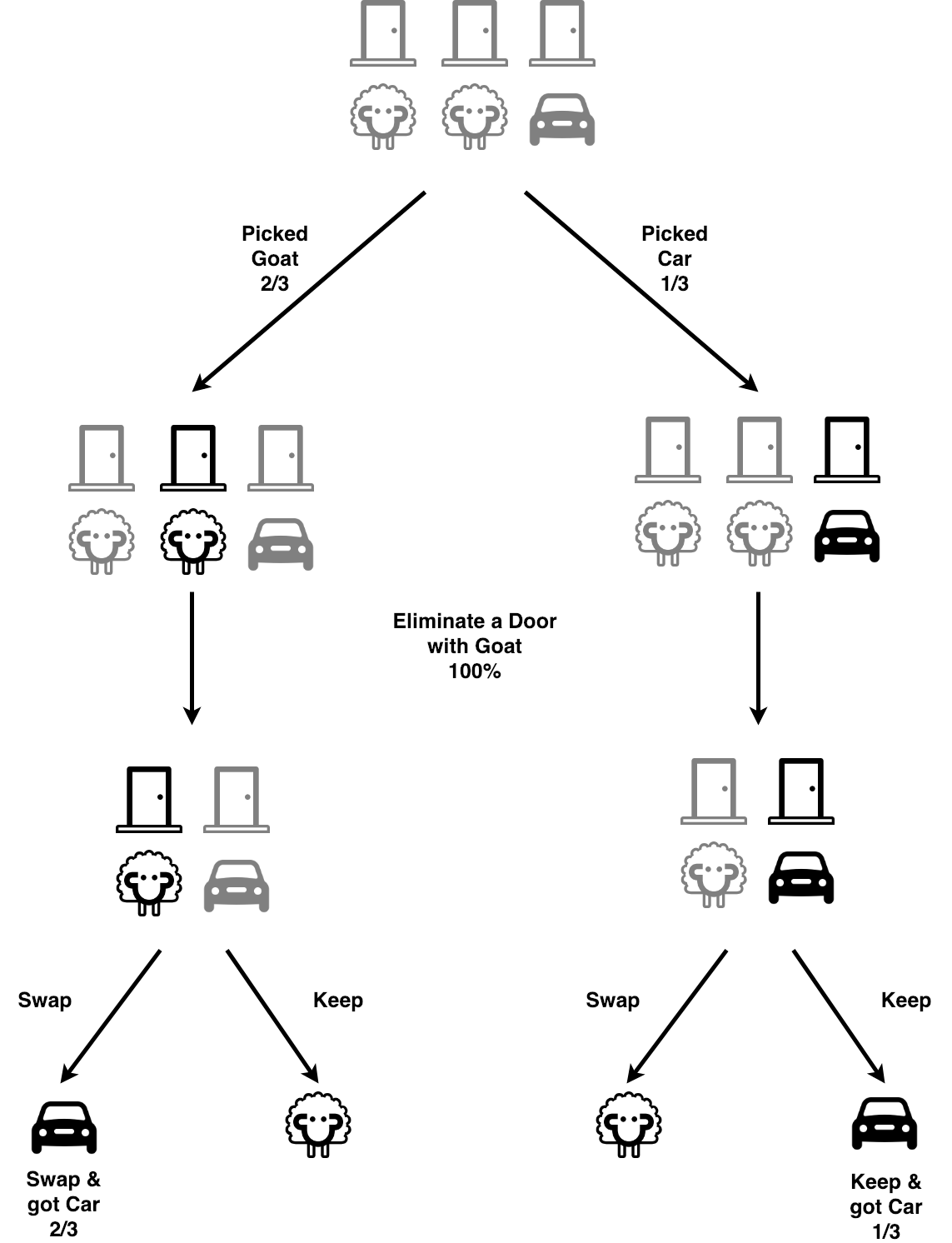
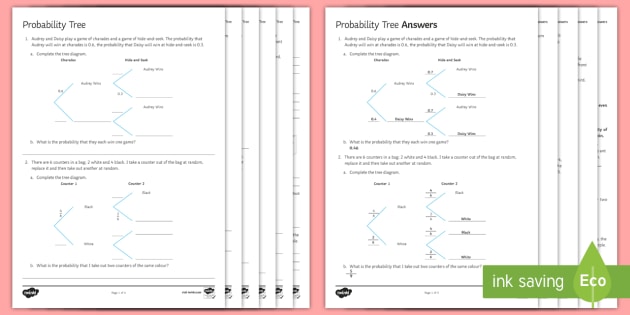









0 Response to "38 probability tree diagram problems"
Post a Comment