38 nf+ molecular orbital diagram
Answer (1 of 6): The answer should be 3 as per MOT where bond order is half of No of bonding MO- No of bonding ABMO so σ1s2,σ*1s2,σ2s2,σ*2s2,σ2pz2,2px1+1π=π2py1+1 from which we get 10-4/2 and we get 3 as answer Structure and Bonding Solutions: #4. 4.* (1997 1 7) Consider the diatomic molecule NF. Draw its molecular orbital energy diagram. A. Using the LCAO-MO scheme, indicate the ground-state MO description for NF, i.e. complete the following: 1(s) 2. . .The LCAO-MO description is: 1s 2 2s 2 3s 2 4s 2 5s 2 1p 4 2p 2. B.
When the atomic orbitals of the two atoms combine, the electrons occupy the molecular orbital of lowest energy, the σ1s bonding orbital. A dihydrogen molecule, H2, readily forms because the energy of a H2 molecule is lower than that of two H atoms.
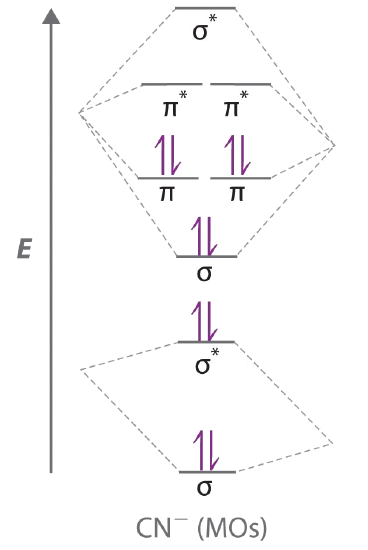
Nf+ molecular orbital diagram
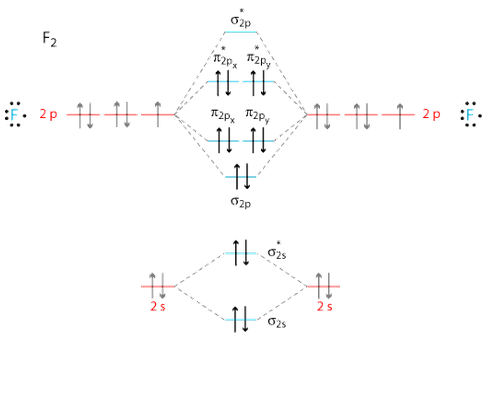
Three‐dimensional potential energy and dipole moment surfaces have been calculated for the 24 electron triatomics O 3, CF 2, NO − 2, and NF + 2 using complete active space self‐consistent field wave functions (CASSCF) and a basis set of 87 (99 for NO − 2) contracted Gaussian‐type orbitals (cGTOs).The analytical potential energy functions (PEFs) have been used in perturbation and ... 4. Draw the valence molecular orbital diagram for NF. State the bond order, the molecular orbital configuration and determine whether each of the following molecules/ions is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Answer. Explanation :According to the molecular orbital theory, the general molecular orbital configuration will be,As there are 7 electrons present in nitrogen and 9 electrons in fluorine.(a) The number of electrons present in molecule = 7 + 9 = 16The molecular orbital configuration of molecule will be,The formula of bonding order = The bonding order of = (b) The number of electrons present ...
Nf+ molecular orbital diagram. Answer to: Use molecular orbital theory to complete the ground state electron configuration for each of the molecules: a. NF b. NF+ c. NF- By... How are molecular orbitals different from atomic orbitals. because the electrons filling them are under the influence of two or more nuclei rather than just one nucleus. Electron density increases between. 2 nuclei in bonding molecular orbitals. Electron density decreases between. Molecular Orbital Diagram for NF. Post by Christine Van 2E » Thu Nov 05, 2015 6:35 am . Hi! I have a quick question about the molecular orbital diagram for NF. Lavelle said that whenever we have a heteronuclear molecule, if one or both atom(s) has Z<8, then we would use the diagram where the pi px and pi py are lower than the Sigma pz. However ... Method 1Method 1 of 3:Finding Bond Order Quickly. Know the formula. In molecular orbital theory, bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. Bond order = [ (Number of electrons in bonding molecules) - (Number of electrons in antibonding molecules)]/2 .
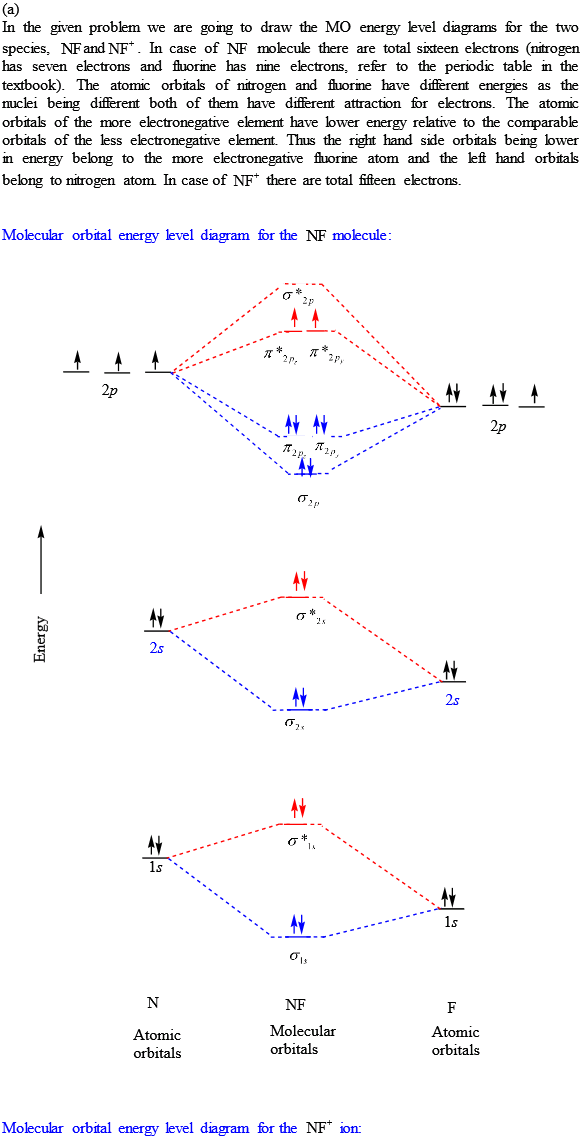
Solutions for Chapter 9 Problem 34E: For each of the two species NF and NF+, (a) draw MO energy level diagrams; (b) write out electron configurations; (c) determine bond orders and predict relative stabilities; and (d) predict diamagnetism or paramagnetism. … Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook? This paper presents a comprehensive theoretical treatment of the low-lying electronic states of the molecular ions NF+ and PCl+ correlating with the lowest dissociation asymptote N+, P+ (3P) + F ... Abstract A method for the use of natural orbital iterations in limited CI calculations is discussed. This method is then applied to the ground X2II state of the nitric oxide molecule at its experim... Learn how to apply molecular orbital theory to determine the shapes of bonded orbitals, recognize molecular orbital diagrams, calculate bond order, and determine relative bond strength.
ANSWERS TO MOLECULAR ORBITALS PROBLEM SET 1. (a) N2 +(13 e-): σ2 1sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ12p N2 2+(12 e-): σ2 1sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22p N2 (14 e-): σ2 1sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ22p N2-(15 e-): σ21sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ22pπ*12p N2 2-(16 e-): σ21sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ22pπ*12pπ*12p (b) Bond orders are: N2 + = 2.5 ; N 2 2+ = 2.0 ; N In Table 5 we give the dominant electron configuration for each state in terms of natural orbitals (15), i.e., the orbitals which diagonalize the first order reduced density matrix. These orbitals are in this case molecular orbitals, which can be given in terms of the raw atomic Slater type basis, as is done in Table 6 for the X 3-'- state of NF. Bond order, as introduced by Linus Pauling, is defined as the difference between the number of bonds and anti-bonds.. The bond number itself is the number of electron pairs (bonds) between a pair of atoms. For example, in diatomic nitrogen N≡N the bond number is 3, in ethyne H−C≡C−H the bond number between the two carbon atoms is also 3, and the C−H bond order is 1. ©2021 Prof Adam J Bridgeman | close window : ©2021 Prof Adam J Bridgeman | close windowProf Adam J Bridgeman | close window
Is there a way to determine if a molecule is diamagnetic or paramagnetic without drawing it's molecular orbital diagram? For example, in the workbook there is a question that asks you to identify the non-paramagnetic molecule out of OF+, NO+, CO+, NF+, and CF.
molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p * orbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the
C. Symmetry Orbitals and Molecular Orbitals The XAO MO's of the homopolar N2 and O2 molecules belong in sets to the irreducible representations of the point group D, h. To obtain proper symmetry for these MO's, symmetry orbit&s (ref. 15) are introduced. The MO's of a given
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Draw an M0 energy level diagram for the NF+ ion. Use sketches to show clearly how the atomic s and p orbitals interact to form molecular orbitals. What is the HOMO? the LUMO? How is the polarity of the molecular ion indicated in this diagram? Toward which atom would the HOMO be polarized and why? Which MO's correspond to the lone pairs on the ...
For NF+ and PC1+ the only other low lying doublet bound state is 2II whereas for PF+ it is 2Z+. In each case there is a bound 4H state and a bound 4~- state but the equilibrium bond lengths are very different and one would expect the Franck- Condon factors for the 4~- ~ 4i-[ transition to be unfavourable. ... Molecular orbitals for each spin ...
Use molecular orbital theory to complete the ground state electron configuration for each of the molecules. Molecule Ground state electron configuration. NF (σ1s) (σ1s ) (σ2s) (σ2s ) (π2p) (σ2p) (π2p*)
NF bond order: NF+ bond order: NF− bond order: Classify each molecule according to its magnetic properties. Diamagnetic Paramagnetic Answer Bank NF NF+ NF−. Use molecular orbital theory to complete the ground state electron configuration for each of the molecules. Determine the bond order of each of the molecules.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
Transcribed image text: Draw and label a molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monofluoride,NF. Use atleast half a page Give the bond order Give the magnetism, and explain your choice briefly (a few words are enough) If you ionized NF to give NF+, would the bond be shorter or longer? Explain your reasoning briefly (again a few words are plenty)

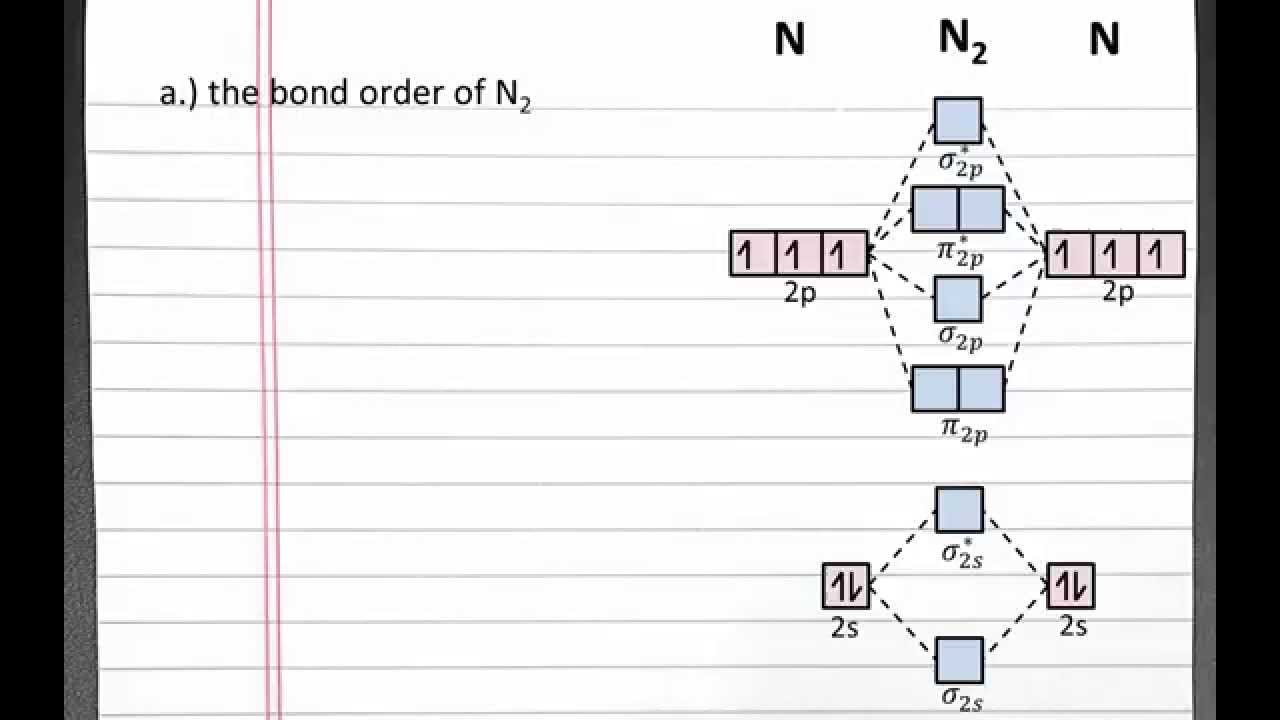
Given N22 Using Molecular Orbital And Valence Bond Theory A Write The Molecular Orbital Configuration B Determine The Bond Order C Determine The Stability D Is It Paramagnetic Or Diamagnetic Study Com
Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms; in diatomic nitrogen (N≡N) for example, the bond order is 3, while in acetylene (H−C≡C−H), the bond order between the two carbon atoms is 3 and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order indicates the stability of a bond. In a more advanced context, bond order does not need ...
Answer. Explanation :According to the molecular orbital theory, the general molecular orbital configuration will be,As there are 7 electrons present in nitrogen and 9 electrons in fluorine.(a) The number of electrons present in molecule = 7 + 9 = 16The molecular orbital configuration of molecule will be,The formula of bonding order = The bonding order of = (b) The number of electrons present ...
4. Draw the valence molecular orbital diagram for NF. State the bond order, the molecular orbital configuration and determine whether each of the following molecules/ions is paramagnetic or diamagnetic.
Three‐dimensional potential energy and dipole moment surfaces have been calculated for the 24 electron triatomics O 3, CF 2, NO − 2, and NF + 2 using complete active space self‐consistent field wave functions (CASSCF) and a basis set of 87 (99 for NO − 2) contracted Gaussian‐type orbitals (cGTOs).The analytical potential energy functions (PEFs) have been used in perturbation and ...

Use Mo Diagrams And The Bond Order From Them To Answer Each Of The Following Questions A Is O2 Stable Or Unstable B Is Be2 Diamagnetic Or Paramagnetic Study Com
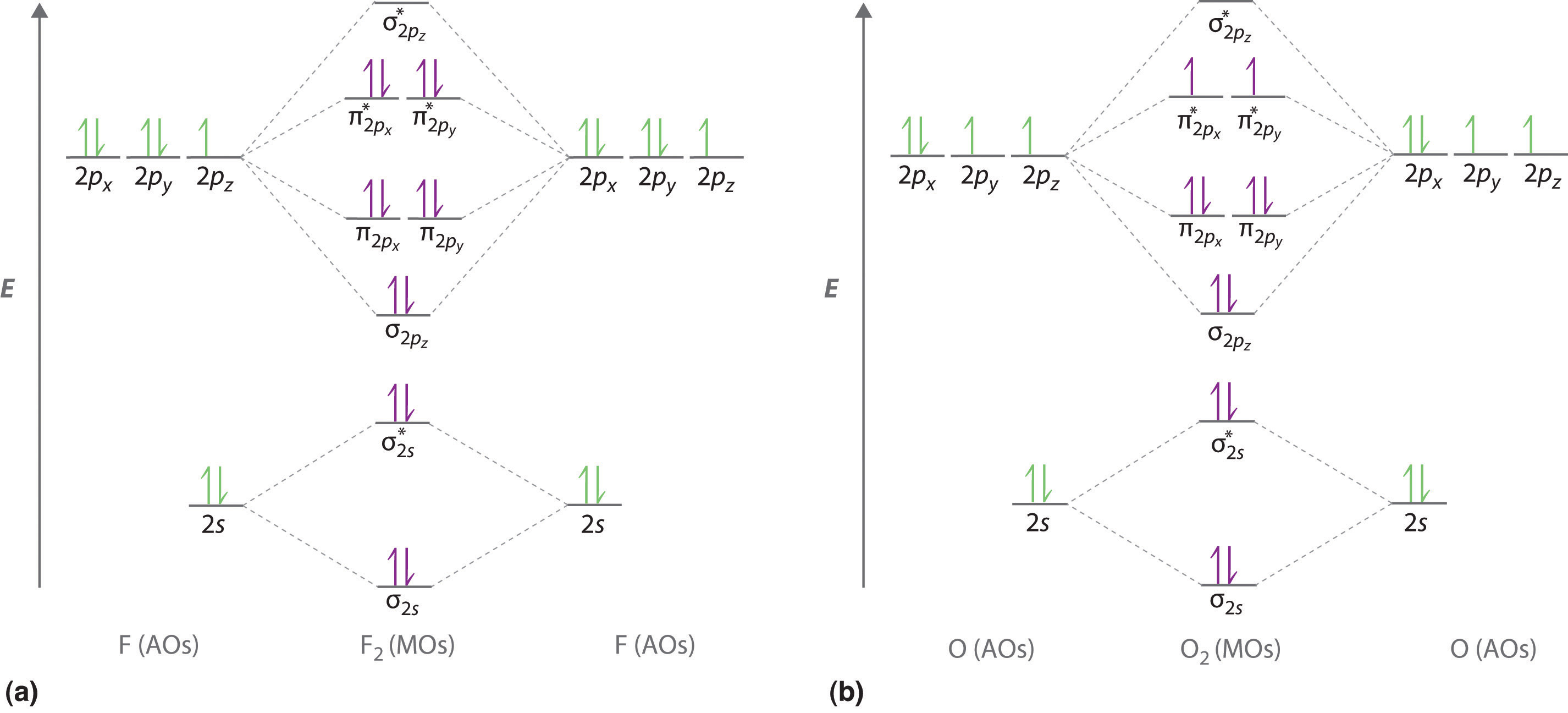
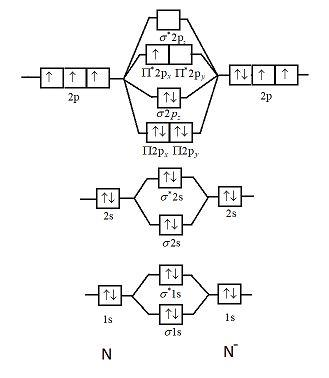
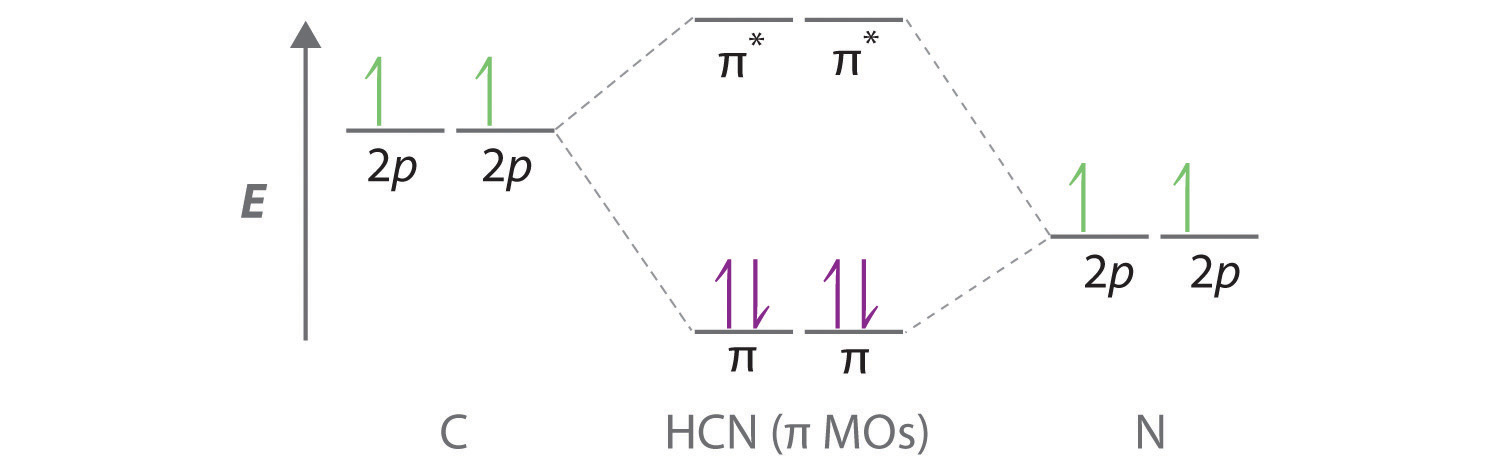



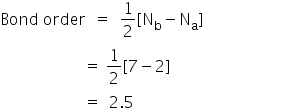




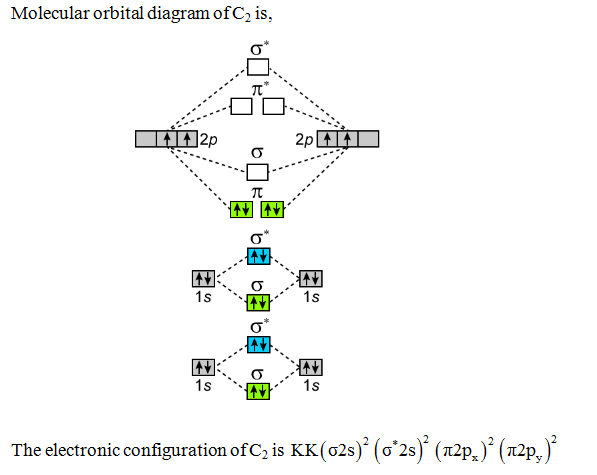

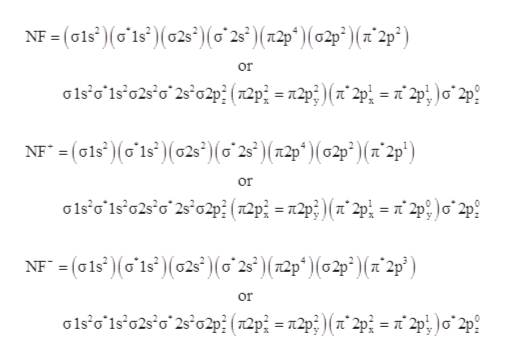


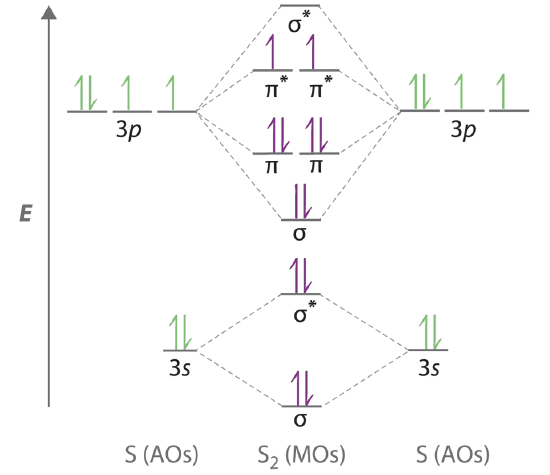

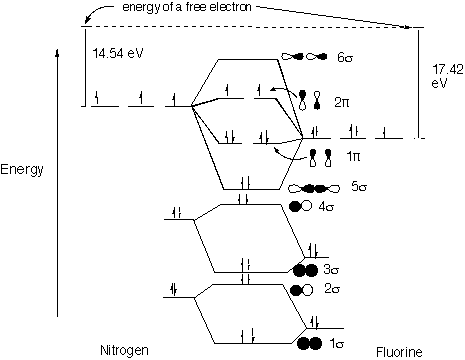

0 Response to "38 nf+ molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment