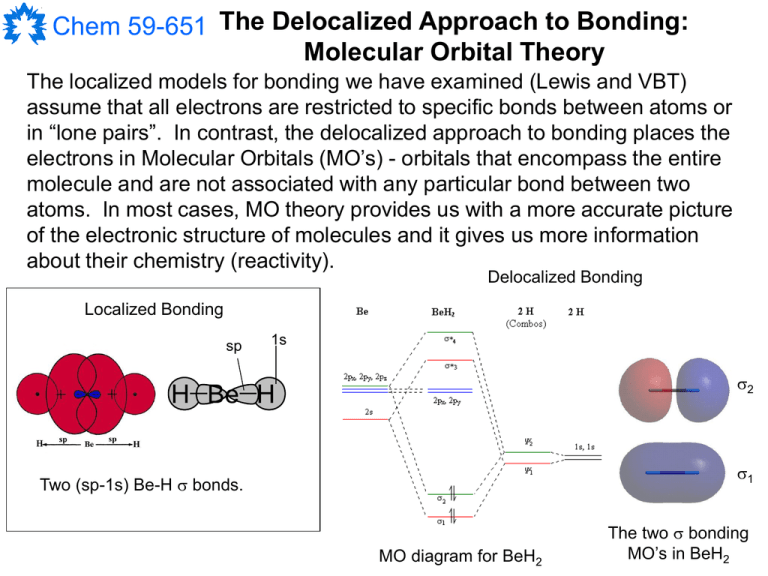
38 mo diagram for he2
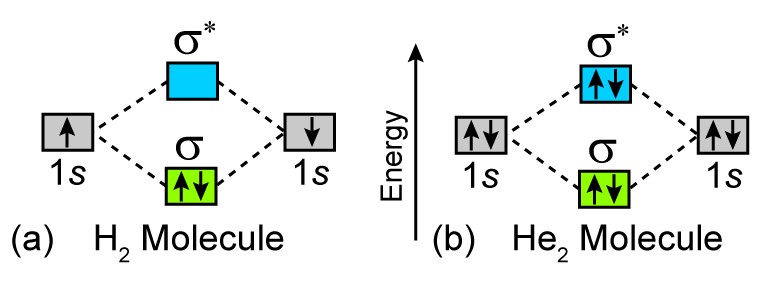
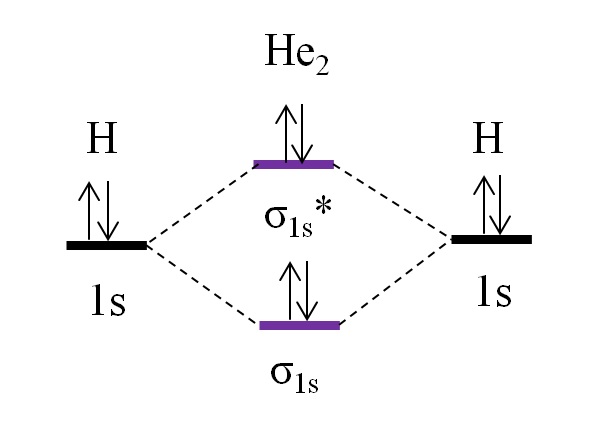
In He2 (dihelium), the two 1s atomic orbitals overlap to create two molecular orbitals: sigma(1s) and sigma(1s)*. You fill these molecular orbitals with the... He2+ MO diagram. Eg: Li + H; Li has 1s + 2s, while H has 1s. This mix to form a sigma orbital from H1s+Li2s, a sigma* orbital and H1s-Li2s. The bond order of a simple molecule can be determined by looking at the number of electrons in bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals.
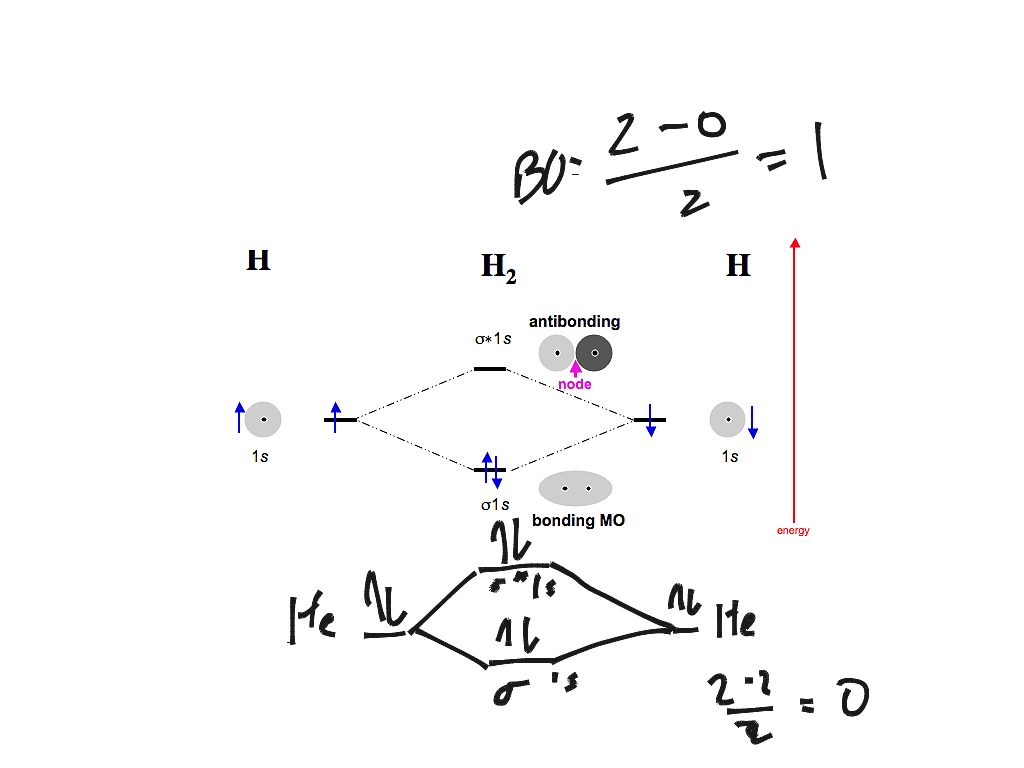
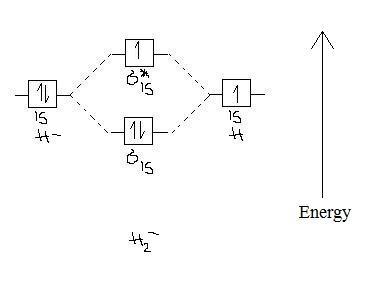
Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, "H"_2^(-) has three electrons while "H"_2^(+) has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one sigma_(1s) and one sigma_(1s)^"*" MO by conservation of orbitals.
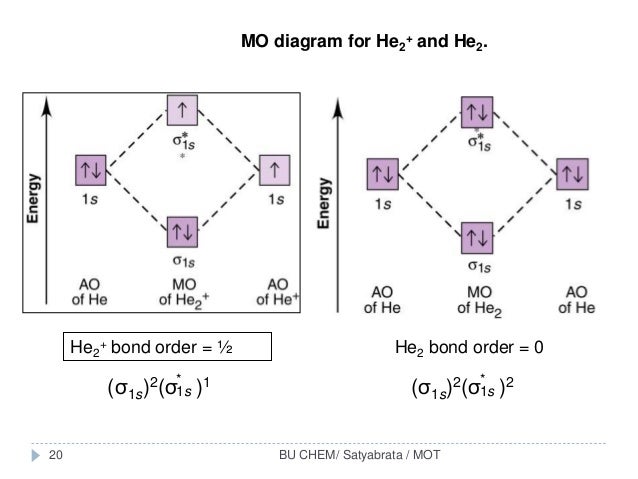
Mo diagram for he2
molecular orbital theory build h2 for the ion h2 a draw the molecular orbital diagram b calculate the bond order c would this ion exist. figshare. electron ejection from mo by he he and he 2 electron ejection from mo by he the slowest ions observed were found to eject 0 25 0 72 and 0 13 electron per ion for he he and he 2. wiki figure 10 MLCT. Our videos prepare you to succeed in your college classes. Let us help you simplify your studying. If you are having trouble with Chemistry, Organic, Physics, Calculus, or Statistics, we got your back! Our videos will help you understand concepts, solve your homework, and do great on your exams. Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer.
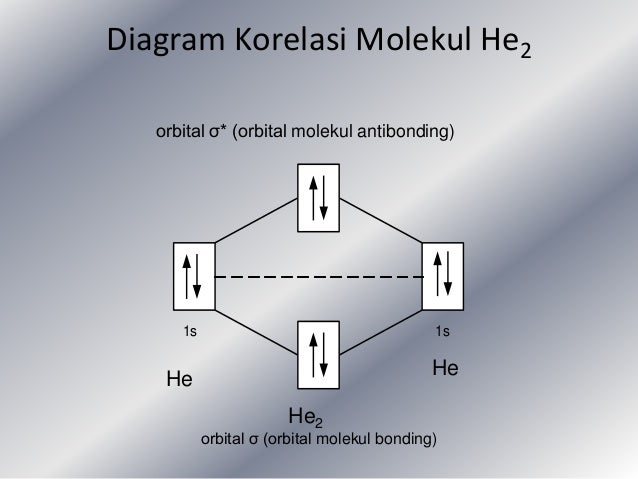
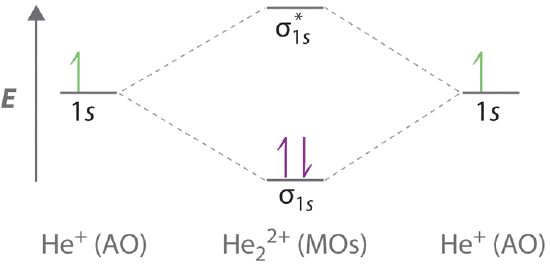
Mo diagram for he2. Answer (1 of 5): In He2 molecule, Atomic orbitals available for making Molecular Orbitals are 1s from each Helium. And total number of electrons available are 4. Molecular Orbitals thus formed are:€1s2€*1s2 It means 2 electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals and 2 are in antibonding molecul... Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the He2^2- molecular ion. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Click Images to Large View Trip Epiphanies Visualising String Theory Whilst Off Your. Feminist. 02 Molecular Orbital Diagram. MO Diagram for F2. Nodes Molecular Orbitals. BH3 MO Diagram. Adult Learning. Human Behavior. Valence Bond Theory Examples. Use molecular orbital theory to determine whether He2 2+ or He2+ is more stable. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for each and explain.
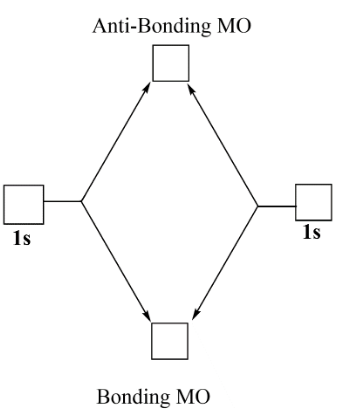
MO DIAGRAM FOR DIATOMIC HYDROGEN MOLECULE & ION Now, let us draw the MO diagram for the "H"_2 neutral molecule. Each hydrogen contributes one electron, which therefore fills the lower-in-energy sigma_(1s) bonding orbital. Add one electron, and you will get "H"_2^(-), thus giving an electron in the antibonding sigma_(1s)^"*" MO. A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2 . A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical ... Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Figure 7.7.12. This shows the MO diagrams for each homonuclear diatomic molecule in the second period. The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and ...
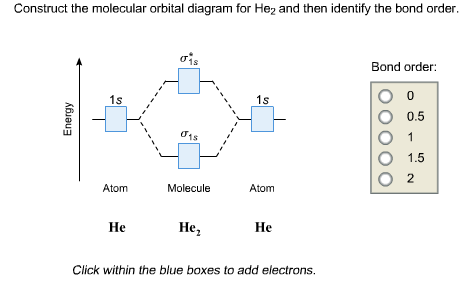
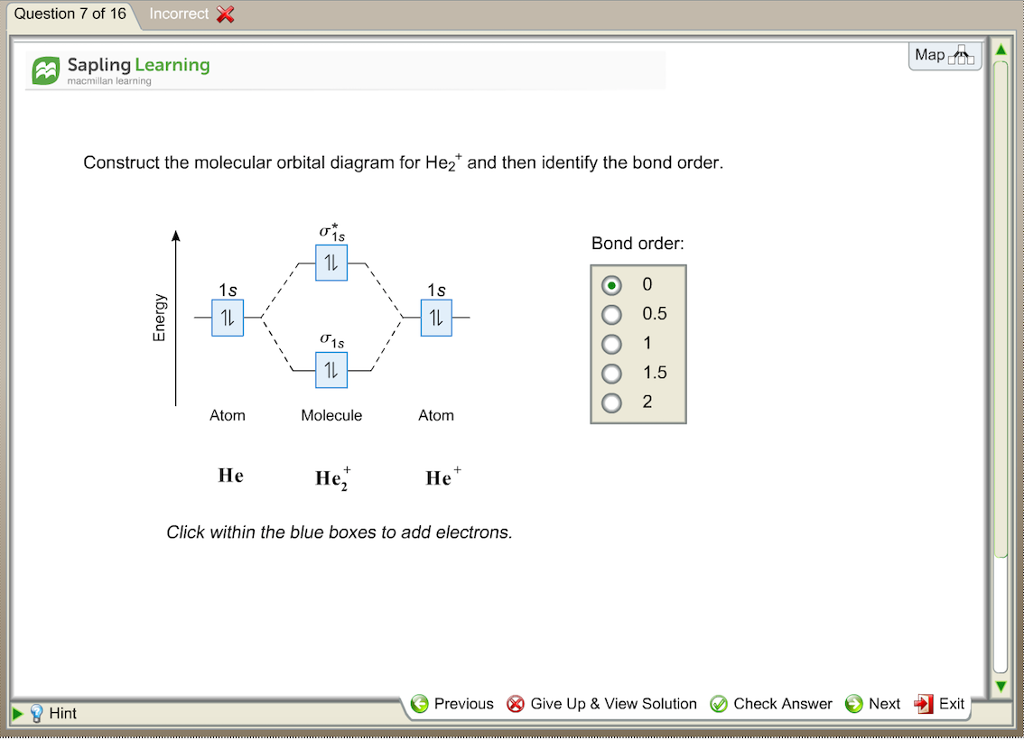
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for he 2 and then identify the bond order. Click calculate to proceed. The lewis structure for h2 is h h predicting a single bond between each hydrogen atom with two electrons in the bond. Please note the diagram is for he2 but the he h is very similar eg. He h forms a very weak bond. MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine Problem: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Click within the blue boxes to add electrons.Bond order: a) 0b) 0.5c) 1 d) 1.5e) 2 Hint: As we know that molecular orbital theory assumes that in molecules the atomic orbitals lose their identity and the electrons in molecules are present in new orbitals called molecular orbitals. Molecular orbitals energy diagrams show the relative energies of molecular orbitals. Complete step by step answer: The molecular orbital theory assumes that the atomic orbitals in molecules lose ...
Mo Diagram He2. Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxe. According to Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory, two atoms mix their orbitals to form one that is spread out over both atoms. The mixing of two.
Chemistry questions and answers. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order.
Answer to Create an MO diagram for H2+ H2 and H Post the Lumo, lumo -, homo, homo + near its energy level. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: Following the MO treatment of H2+, assume the (normalized) ground electronic state wavefunction is . Qualitative MO theory orbital diagram for homonuclear diatomics composed of 1st or.
Valence Bond Model vs. Molecular Orbital Theory . Because arguments based on atomic orbitals focus on the bonds formed between valence electrons on an atom, they are often said to involve a valence-bond theory.. The valence-bond model can't adequately explain the fact that some molecules contains two equivalent bonds with a bond order between that of a single bond and a double bond.
Solution. Verified by Toppr. Electronic configuration of He is 1s 2. Molecular Orbital Diagram for He 2. . is. (Refer to Image) Bond order= 2(No. of electrons in bonding molecular orbital)- (No. of electrons in anti-bonding Molecular orbital) .
The valence electrons of he are in the 1s orbital and the 1s orbitals combine to give an mo diagram like that for h 2 or he 2 figure 933. The electron in the sigma 1s mo. He exits as a single atom molecule not as he2 with a complete 2s2 structure.
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure 13. On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding ...
Molecular orbital diagram has been drawn for the given molecule. This has totally 4 electrons in it. In molecular orbital diagram, it is clearly shown that the bonding orbital and the antibonding orbitals has two electrons each. Therefore, the number of bonding electrons are 2 and the number of anti-bonding electrons are 2.
How to write simple Molecular Orbital Diagrams and determine the Bond order
1) H2- 2) H2+ 3) H2 4) He2+. A species is said to be diamagnetic when it has all the paired electrons. Similarly if the species contain unpaired electron it is said to be paramagnetic. To know the magnetic character of molecules we can use MO diagram. When we draw MO diagram for dihydrogen anion ( H2-) we find one unpaired electron in ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram For He2 2+ Two electrons total, both occupy the sigma orbital, two more electrons in bonding than antibonding He2 is not possible. Please note the diagram is for He2+ but the He-H is very similar answered Mar 21 '13 at A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and ...
Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer.
Our videos prepare you to succeed in your college classes. Let us help you simplify your studying. If you are having trouble with Chemistry, Organic, Physics, Calculus, or Statistics, we got your back! Our videos will help you understand concepts, solve your homework, and do great on your exams.
molecular orbital theory build h2 for the ion h2 a draw the molecular orbital diagram b calculate the bond order c would this ion exist. figshare. electron ejection from mo by he he and he 2 electron ejection from mo by he the slowest ions observed were found to eject 0 25 0 72 and 0 13 electron per ion for he he and he 2. wiki figure 10 MLCT.
















0 Response to "38 mo diagram for he2"
Post a Comment