38 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.
A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. The physical state of a substance and its phase-transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in Figure 2. Figure 2. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Shown above is a phase diagram for water. Well look now at the phase diagram for sodium chloride solution in some detail. Phase diagrams of pure water and an aqueous solution of a nonvolatile solute. Pure a and pure b are also considered to be α and β phases respectively. It has b atom as the solute component. A terminal phase or ...
Elemental carbon has one gas phase, one liquid phase, and two different solid phases, as shown in the phase diagram: (a) On the phase diagram, label the gas and liquid regions. (b) Graphite is the most stable phase of carbon at normal conditions. On the phase diagram, label the graphite phase.
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Question: Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep ... Diagram of solvent when discussing solutions the solute is the substance which dissolves while the solvent is the substance into which the solute dissolves creating a salt water solution involves dissolving salt in water making salt the solute and water the solvent label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution show transcribed image. A using the two sets of axes provided below sketch ... Skilled solution 100 25 rankings this downside has been solved. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. At that point the substance exists as a mixture of gas liquid and solid all in equilibrium with one another. 11 solid at ap boiling pointliquid of solution temperature. Mole fraction of the pure solvent vp of the pure solvent.
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. The α phase is a solid solution rich in a atom. For example the addition of a solute to a pure solvent making a solution can disrupt important interactions between solvent molecules changing the temperature at which the solvent would typically freeze or boil. A terminal phase or terminal solution is one that exists in the extremes of ... Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. A the molecules are leaving the liquid phase. Expert answer 100 33 ratings. If you have a mixture of 100 g of potassium nitrate and 100 g of water and the temperature is above 57c you have a single phase a solution of potassium nitrate. You can think of this as a simple phase diagram. Show transcribed image text. This is the case for many ... Phase Diagram 1. Chapter-5 PHASE AND PHASE EQUILIBRIUM Prepared By: PALLAV RADIA Asst prof. AITS, RAJKOT. 2. Introduction: One of the most important objective of engineering metallurgy is to determine properties of material. The properties of material is a function of the microstructure which depend on the overall composition and variable such as pressure and temperature. Hence to determine ... Phase Diagrams Revised: 1/27/16 3 The phase diagram in Figure 1 is for a pure compound. When a second compound is introduced to the system forming a homogeneous solution however, the phase diagram drastically changes. For example, the addition of a solute to a pure solvent (making a solution)
the pure solvent is present. Thus the vapor pressure above the solution containing solute will be lower than the vapor pressure of the pure solvent. The dissolved solute molecules physically block the surface of the solvent, preventing some of the solvent molecules from evaporating at a given temperature. Shown below are two phase diagrams for ... The phase diagram for a pure substance is shown above. Use this diagram and your knowledge about changes of ... Label the axes and label the regions in which the solid, ... Pure Solvent Solution 0 Time 0 5 10 15 20 0 Time 0 5 10 15 20 (b) Information from these graphs may be used to determine the molar mass of the unknown solid. Binary Solutions Solubility Phase Matter. Assignment 3 Winter 2017 With Solutions Studocu. Fragrance Systems Studied In This Work Compris Ing Binary. Label The Phase Diagram Of Pure Solvent And A Solution. Vapour Liquid Equilibrium Vle An Algorithm Inspired. 21 Oct 2016 — Chemistry 4 qs missed. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Skilled solution 100 25 rankings this downside has been solved.
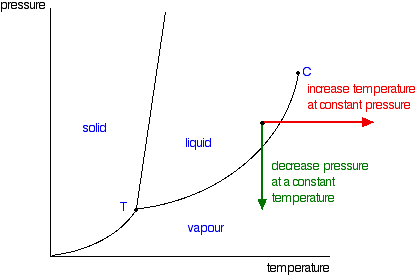
Transcribed image text: The phase diagrams for a pure solvent and the solvent in a solution are shown. Identify the normal freezing (fp_solv) and boiling (bp_solv) points for the pure solvent and the normal freezing (fp_soln) and boiling (bp_soln) points of the solution at 1 atm. Assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that freezes from solution is pure solvent. Phase diagrams. A phase diagram lets you work out exactly what phases are present at any given temperature and pressure. In the cases we'll be looking at on this page, the phases will simply be the solid, liquid or vapour (gas) states of a pure substance. This is the phase diagram for a typical pure substance. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Phase diagrams are useful tools for the design of processes. 12716 3 the phase diagram in figure 1 is for a pure compound. The liquid vapor pressure curve is shifted downward to lower pressures but the solid vapor pressure sublimation curve is unaffected. These phases are called terminal solid solutions. When a second compound is ... A phase diagram is a graph which shows under what conditions of temperature and pressure distinct phases of matter occur. The simplest phase diagrams are of pure substances. These diagrams plot pressure on the y-axis and temperature on the x-axis. Although phases are conceptually simple, they are difficult to define precisely.
The completely solidified alloy in the phase diagram shown is a solid solution because: Alloying element (Cu, solute) is completely dissolved in host metal (Ni, solvent) Each grain has same composition Atomic radius of Cu is 0.128nm & that of Ni is 0.125nm, Both elements are FCC; HRRs are obeyed. 12/3/2013 11:12 PM
- Solutions - solid solutions, single phase - Mixtures - more than one phase • Solubility Limit : Max concentration for which only a single phase solution occurs. Question: What is the solubility limit at 20°C? Answer: 65 wt% sugar . If Co < 65 wt% sugar: syrup If Co > 65 wt% sugar: syrup + sugar. 65 Sucrose/Water Phase Diagram Pure ...
In phase diagrams these phases are separated from the composition extremes 0 and 100. Assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that freezes from solution is pure solvent. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution freezing point of solution gas solution pure solvent 1 atm boiling pointfreezing point of of solvent solvent.
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Which is defined as the maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given quantity of solvent at a specific temperature? solubility
At 22.0°C the two solutions in equilibrium have x = 0.24 and x = 0.48, respectively, and at 21.5°C the mole fractions are 0.22 and 0.51. Sketch the phase diagram. Describe the phase changes that occur when perfluorohexane is added to a fixed amount of hexane at (a) 23°C, (b) 22°C.
Expt. 5: Binary Phase Diagram CHEM 366 V-3 Combination1,2,3 of equations (2), (3), (6), (7) and (10) leads to the equation T≅TA+ RTA 2 ΔHA lnXA (11) or T≅TA+ RTA 2 ΔHA ln(1−XB) (12) or T≅TA- RTA 2 ΔHA lnXB (13a) T≅TB- RTB 2 ΔHB lnXA (13b) where T and TA are freezing points (K) of the mixture II and pure A, R is 8.314 J/K mole, ΔHA is the molar enthalpy of fusion of A and XB ...
Consider the following general phase diagram: Now, consider the pure substance, whose phase diagram was represented by the black curves. The normal freezing point of the pure substance at constant pressure is indicated by B, and its reduced normal freezing point (due to addition of nonvolatile solute to the pure liquid substance) is A, since Tdarr leftwards.
The phase diagram for sodium chloride solution. What the phase diagram looks like. ... because adding a non-volatile solute to a solvent increases its boiling point. ... in this case, that's the pure ice crystals. On the other end, it hits the sloping line - this tells you the composition of the remaining salt solution. ...
III.1. Draw phase diagrams for the following type systems. Label the regions and in-tersections of the diagrams, stating what materials (possibly compounds or azeotropes) are present and whether they are solid, liquid or gas. (a) One component, pressure-temperature diagram, liquid density greater than that of solid. (b) Two component,
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that freezes from solution is pure solvent. 12716 3 the phase diagram in figure 1 is for a pure compound. The liquid vapor pressure curve is shifted downward to lower pressures but the solid vapor pressure sublimation curve is unaffected.
Problem: Label the diagram of pure solvent and a solution. FREE Expert Solution Recall that a phase diagram shows the transition of matter between solid, liquid, and gas phases as temperature and pressure changes.
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.. The phase diagrams for a pure solvent and the solvent in a solution are shown. Nothing happens until you get down to the eutectic temperature. For example the addition of a solute to a pure solvent making a solution can disrupt important interactions between solvent molecules changing the temperature at which the solvent would typically ...
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. The vaporization curve for the solution lies below the curve for pure water at all temperatures which results in an increase in the boiling point and a decrease in the freezing point of the solution. This is the case for many solutions comprising liquid solvents and nonvolatile solutes. A solute reduces the vapor pressure of a solvent at ...
These diagrams indicate the physical states that exist under specific conditions of pressure and temperature, and also provide the pressure dependence of the phase-transition temperatures (melting points, sublimation points, boiling points). A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1.
Skilled solution 100 25 rankings this downside has been solved. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. At that point the substance exists as a mixture of gas liquid and solid all in equilibrium with one another. 11 solid at ap boiling pointliquid of solution temperature. Mole fraction of the pure solvent vp of the pure solvent.
Diagram of solvent when discussing solutions the solute is the substance which dissolves while the solvent is the substance into which the solute dissolves creating a salt water solution involves dissolving salt in water making salt the solute and water the solvent label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution show transcribed image. A using the two sets of axes provided below sketch ...
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Question: Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep ...

0 Response to "38 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution."
Post a Comment