38 blood clotting process diagram
The process of forming a clot or thrombus in order to prevent excess loss of blood from the body is called the clotting of blood. A gelly mass like substance is formed by the platelets and fibrin in the blood. Platelets play a vital role in the clotting of blood. Coagulation is a dynamic process and the understanding of the blood coagulation system has evolved over the recent years in anaesthetic practice. Although the traditional classification of the coagulation system into extrinsic and intrinsic pathway is still valid, the newer insights into coagulation provide more authentic description of the same.
the blood clotting process are vasoconstriction, platelet activation, thrombus formation, and dissolution of the clot. Basic laboratory tests used to identify blood clotting problems will also be presented. Blood clotting is initiated in one of two ways. "e #rst, referred to as the intrinsic or internal pathway, occurs when a clot forms inside

Blood clotting process diagram
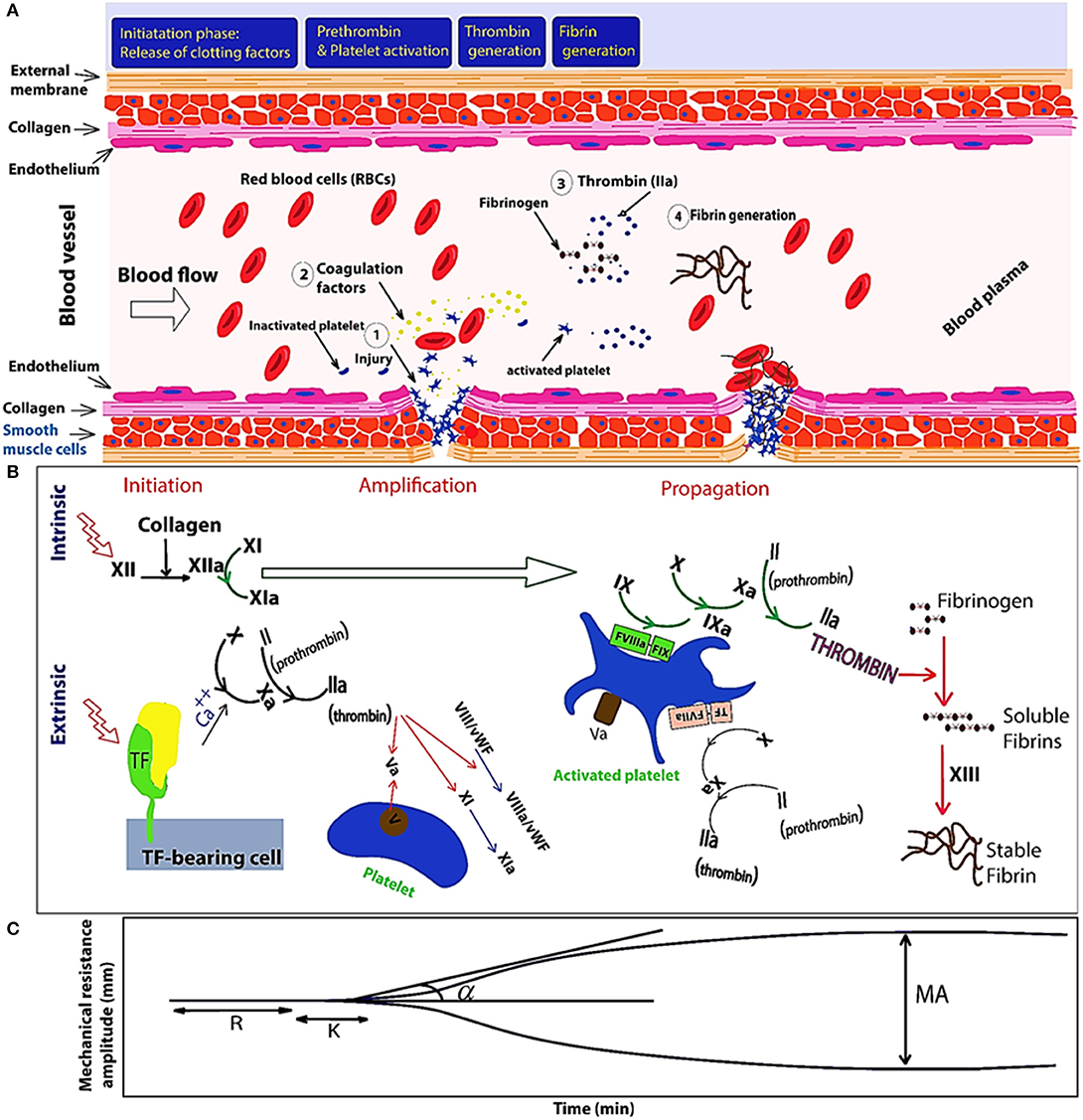
Clotting cascade diagram as simplified as possible If there is damage directly to the blood vessel, the underlying collagen is exposed to the circulating platelets within the blood stream. Platelets bind directly to the collagen and create a "platelet plug". Concept Analysis Diagram - Clotting 5.31.13 Texas Nursing Care ... Normal Clotting Time Coagulation Cascade Clotting A physiologic process in which blood is converted from a liquid to a semisolid gel. (G) Antecedents Intracranial Tissue/Vessel Integrity Functional Bone Marrow Blood clotting occurs in a multi-step process known as the coagulation cascade. The process involves many different proteins. The cascade is a chain reaction in which one step leads to the next. In general, each step produces a new protein which acts as an enzyme, or catalyst, for the next step.
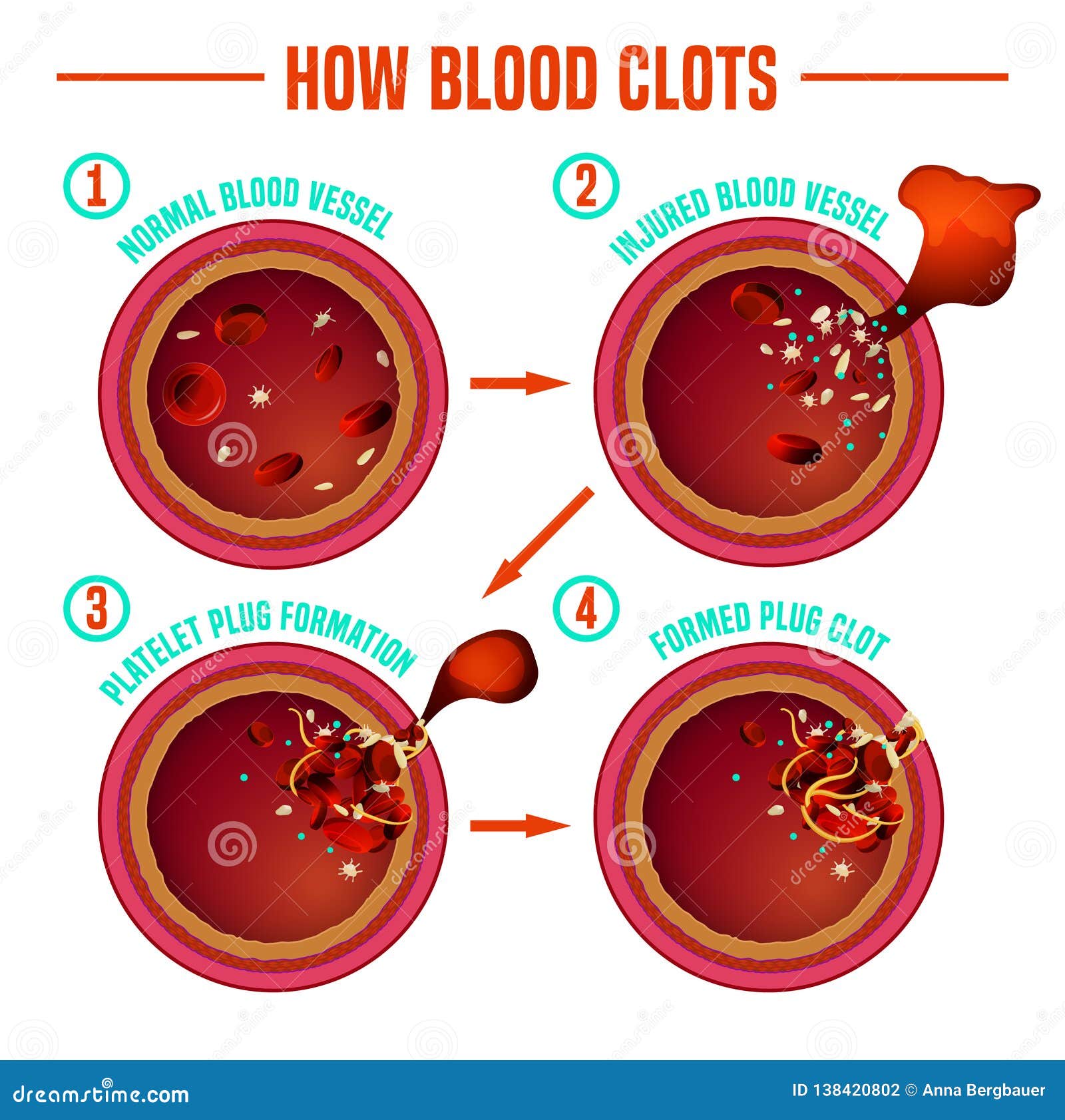
Blood clotting process diagram. normal hemostasis. The other is the contact system, which is the mechanism responsible for the clotting that occurs when blood or plasma comes into contact with "foreign" surfaces such as glass. CONTACT ACTIVATION. Contact activation initiates a major laboratory test of the clotting system called the PTT (see Clotting Tests). Blood Clotting. When a wound causes bleeding, the body responds with a positive feedback loop to clot the blood and stop blood loss. Substances released by the injured blood vessel wall begin the process of blood clotting. Platelets in the blood start to cling to the injured site and release chemicals that attract additional platelets. Blood clotting, or coagulation, is an important process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. Platelets (a type of blood cell) and proteins in your plasma (the liquid part of blood) work together to stop the bleeding by forming a clot over the injury. Typically, your body will naturally dissolve the blood clot after the injury has healed. Hemostasis is a complex process in which multiple components of the blood clotting system are activated in response to vessel injury to control bleeding. Hemostasis is composed of four major events: 1. Primary hemostasis 2. Secondary hemostasis 3. Fibrin clot formation and stabilization 4. Inhibition of coagulation 1.
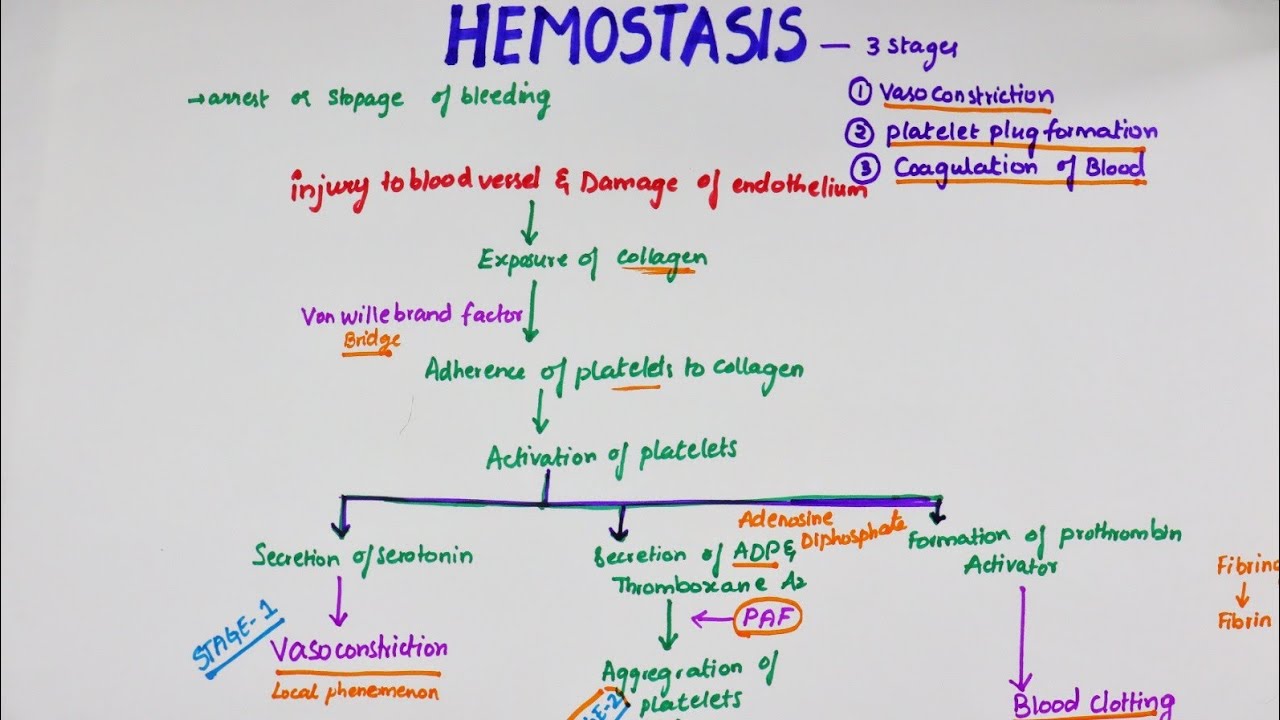
The three stages of blood clotting are the vascular phase, the platelet phase and the coagulation phase. The entire process of blood clotting may be referred to as hemostasis. The process takes place in order to prevent the body from losing too much blood due to injury. When the human body is injured, a natural healing process is initiated in ... 730 blood clotting diagram stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See blood clotting diagram stock video clips. of 8. fibrin clot blood clotting process thrombus (or clot) blocking a blood vessel. blood clotting blood diagram red blood cell diagram hemostasis platelet coagulation coagulation system clotting process. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the stem cells and stages of white blood cell and platelet production. Out of the formed elements in the blood, which one plays the most important role in the clotting process? platelets. The two most important factors affecting almost every aspect of the clotting process are __________. 8 *N35899A0824* 4 Many animals have hearts that pump blood through a network of blood vessels. (a) The table below refers to blood flow in the four major blood vessels of the human heart. If the statement is correct, place a tick (9) in the appropriate box and if the statement is incorrect, place a cross (8) in the appropriate box.(4)
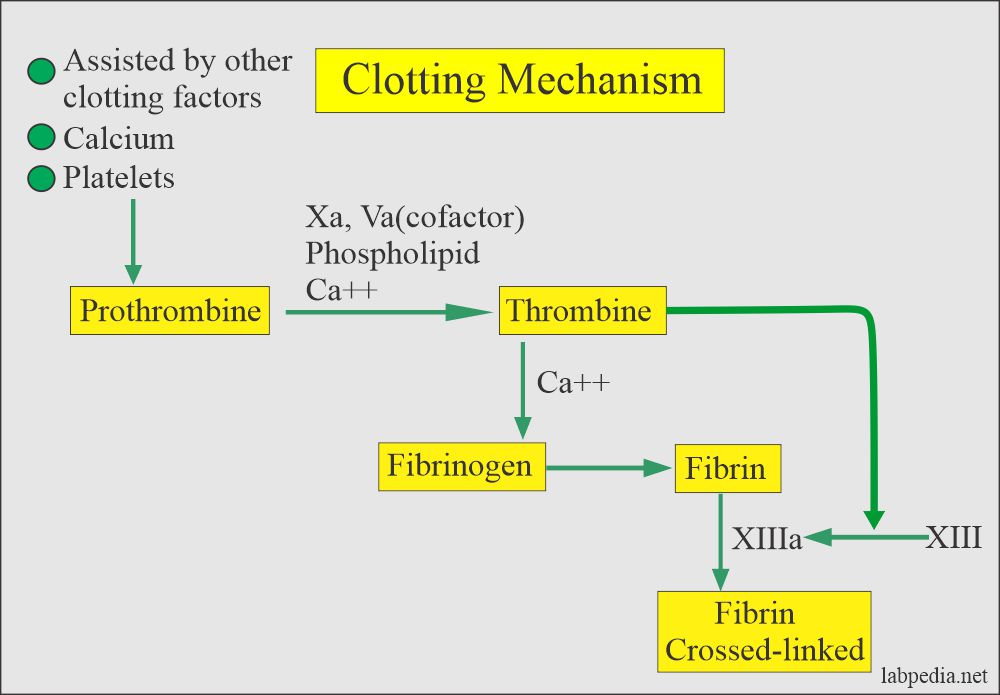
Blood clotting process is a complex process, the basic mechanism of which is formation of insoluble fibrin threads from the soluble plasma protein called fibrinogen. The fibrin threads then form a network within which the red and white blood cells become entangled. Formation of fibrin from fibrinogen is catalyzed by an enzyme named thrombin. Blood clotting. 1. BLOOD CLOTTING When blood is shed out or collected in a container, it looses its fluidity & becomes a jelly like mass after few minutes. This process is called coagulation or clotting of blood. The clot is a mesh of thin fibrils entangling the blood cells. These fibrils consist of fibrin. The fibrin is formed from fibrinogen. 2. Consequently, the body has control mechanisms to limit clotting and dissolve clots that are no longer needed. An abnormality in any part of the system that controls bleeding can lead to excessive bleeding Bruising and Bleeding Bruising or bleeding after an injury is normal (see also How Blood Clots). However, some people have disorders that cause them to bruise or bleed too easily. Coagulation: Host Response to Injury . when there is an injury, the body must mount a response to halt immediate damage, deal with an infection, and heal the wound and restore tissue fxn. the first step in this process is coagulation which not only stops bleeding, but produces mediators such a\
Blood clotting (technically "blood coagulation") is the process by which (liquid) blood is transformed into a solid state. This blood clotting is a complex process involving many clotting factors (incl. calcium ions, enzymes, platelets, damaged tissues) activating each other. Stages of Blood Clotting: 1. Formation of Prothrombinase:
Blood flows through the blood vessels to deliver the needed oxygen and nutrients to the different cells in the body. The blood clotting process or coagulation is an important process that prevents ...
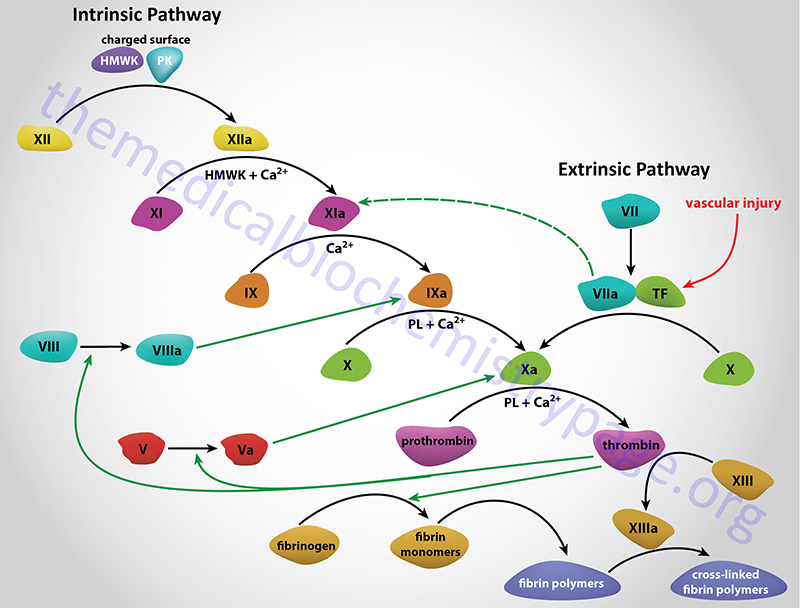
The modified intrinsic coagulation cascade, which displayed in Figure 6, is different from the older one and lacks the significance of factor XII and prekallikren. Apparently, these proteins are not considered to play a crucial role in the coagulation process in vivo. There are two major processes that could initiate the blood clotting mechanism.
Blood clotting is an important process to stop bleeding. It is a complicated process which occurs via series of activation processes collectively called coagulation cascade. Coagulation cascade has two pathways known as intrinsic and extrinsic pathway. The key difference between intrinsic and extrinsic pathways in blood
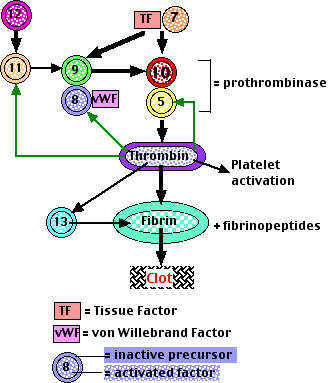
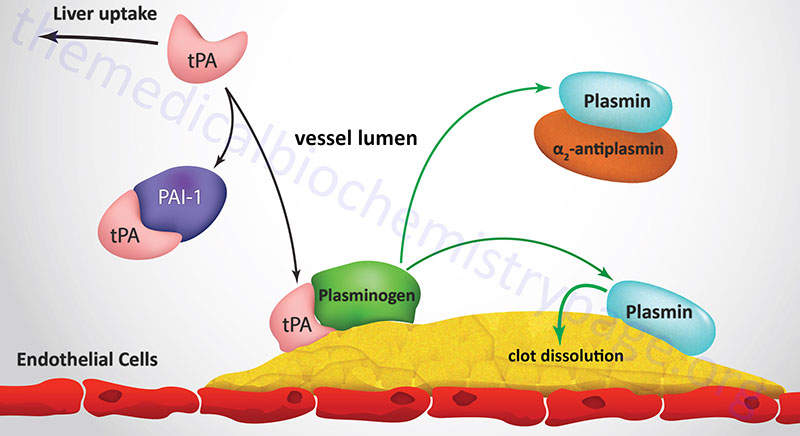
Blood Clotting Cascade Diagram. Schematic representation of the coagulation cascade and the fibrinolytic system. The coagulation cascade (blue arrows) can be activated during hemostasis via. Coagulation (also known as clotting) is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a . The coagulation cascade of secondary hemostasis has two ...
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot.It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair.The mechanism of coagulation involves activation, adhesion and aggregation of platelets, as well as deposition and maturation of fibrin.
The coagulation cascade is a complex chemical process that uses as many as 10 different proteins (called blood clotting factors or coagulation factors) that are found in plasma. Put simply, the clotting process changes blood from a liquid to a solid at the site of an injury.
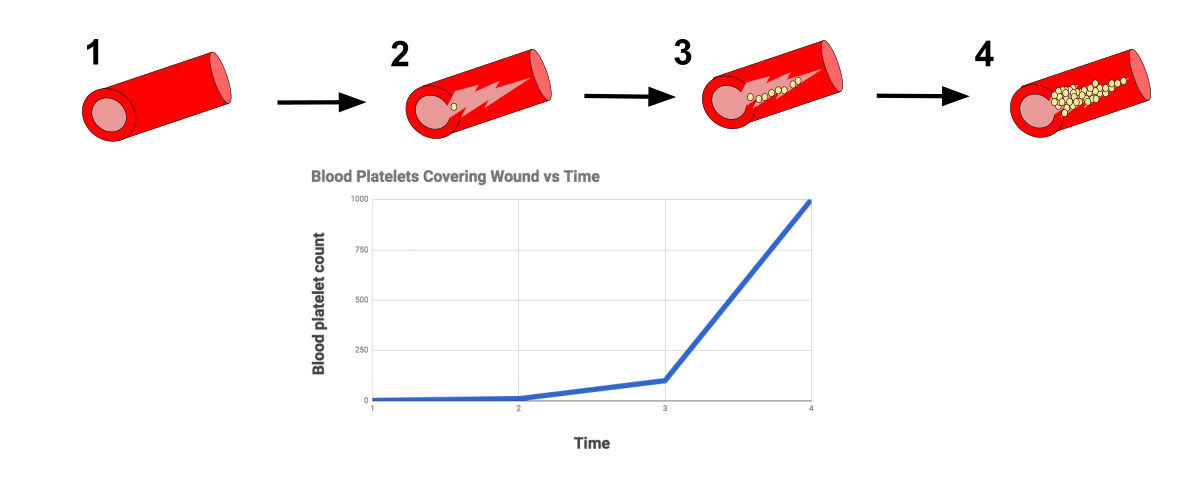
Platelets help the blood clotting process (or coagulation) by gathering at the site of an injury, sticking to the lining of the injured blood vessel, and forming a platform on which blood coagulation can occur. This results in the formation of a fibrin clot, which covers the wound and prevents blood from leaking out. ...
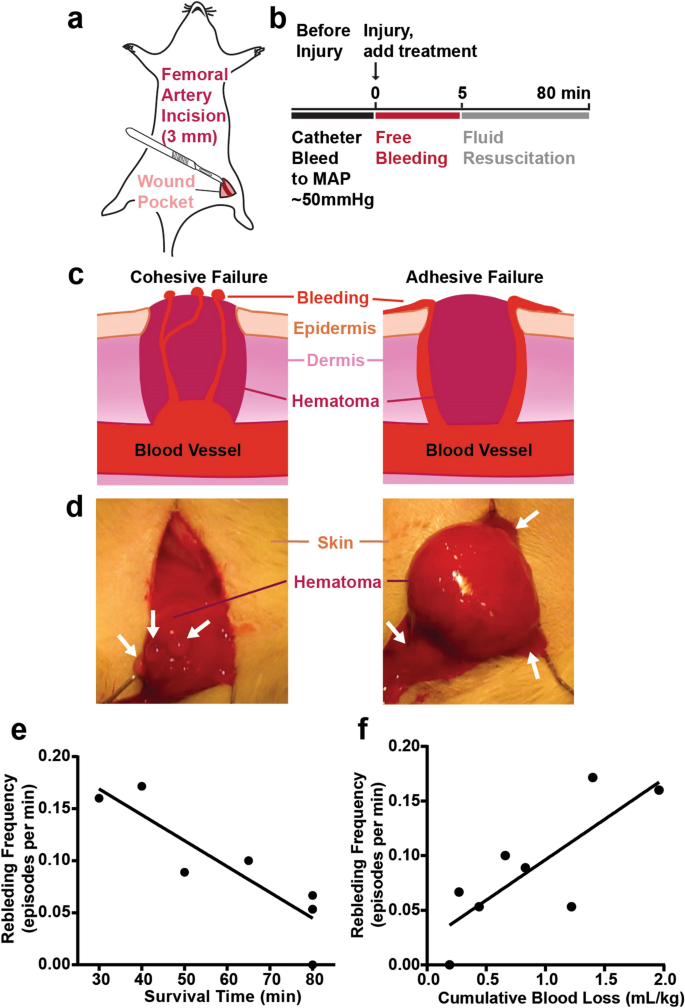
The Adhesion Of Clots In Wounds Contributes To Hemostasis And Can Be Enhanced By Coagulation Factor Xiii Scientific Reports
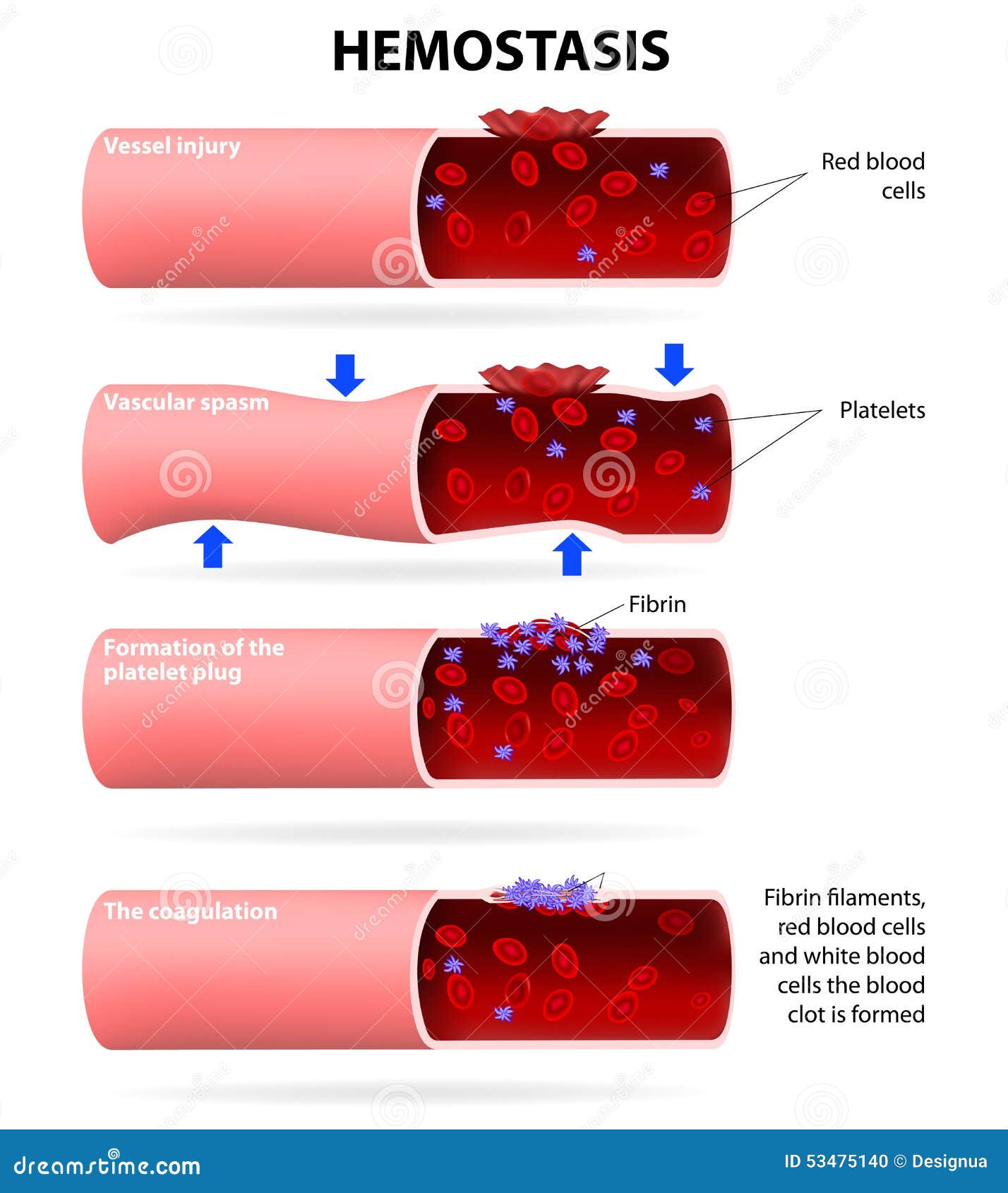
The immediate process of stopping bleeding after injury is known as hemostasis and involves three events which are: blood vessel spasm, the formation of the platelet plug, and the blood clot formation process; known as blood coagulation. Clotting of the blood occurs only when thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin clot.

Platelets Or Thrombocyte Activation Fibrin In Blood Vessel Vector Illustration Diagram Anatomical Blood Circulation System Scheme Educational Information Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image 94570993
Terminology: Blood clotting is also called coagulation. Hemostasis is a word for the process where a blood clot forms. Blood clots form to stop excess blood leaking from your body after you break or cut the surface of your skin. If a blood vessel (a capillary, vein or artery) is damaged (internally or by external injury like a cut) bleeding ...
Mechanisms of Blood Coagulation. Blood coagulation refers to the process of forming a clot to stop bleeding. Coagulation is a complicated subject and is greatly simplified here for the student's understanding. To stop bleeding, the body relies on the interaction of three processes:
Blood clotting occurs in a multi-step process known as the coagulation cascade. The process involves many different proteins. The cascade is a chain reaction in which one step leads to the next. In general, each step produces a new protein which acts as an enzyme, or catalyst, for the next step.
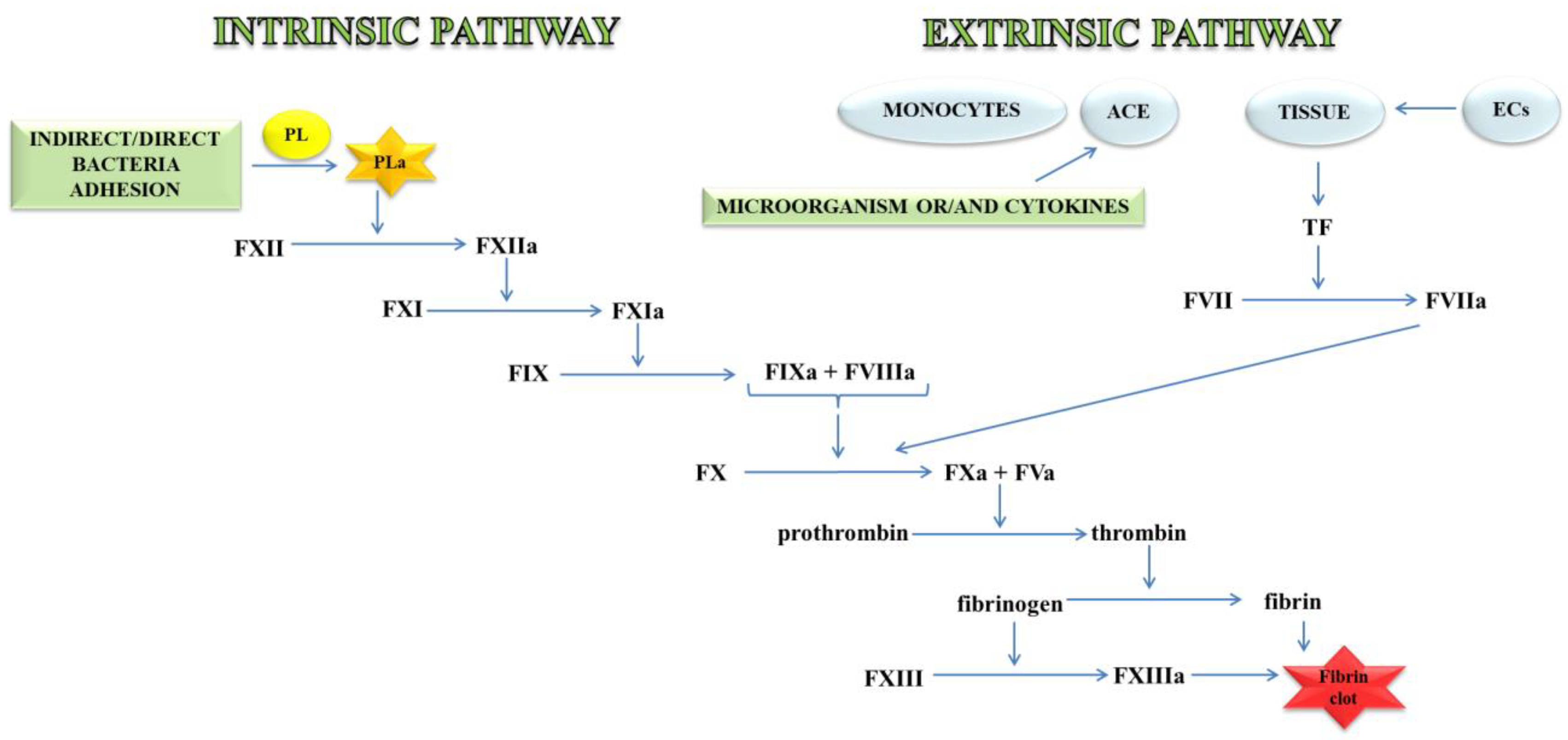
Ijms Free Full Text Factors Affecting The Formation And Treatment Of Thrombosis By Natural And Synthetic Compounds Html
Concept Analysis Diagram - Clotting 5.31.13 Texas Nursing Care ... Normal Clotting Time Coagulation Cascade Clotting A physiologic process in which blood is converted from a liquid to a semisolid gel. (G) Antecedents Intracranial Tissue/Vessel Integrity Functional Bone Marrow
Clotting cascade diagram as simplified as possible If there is damage directly to the blood vessel, the underlying collagen is exposed to the circulating platelets within the blood stream. Platelets bind directly to the collagen and create a "platelet plug".

Platelets Help In Clotting Of Blood At Injured Side Draw A Flow Diagram Of Process Science Life Processes 13971807 Meritnation Com











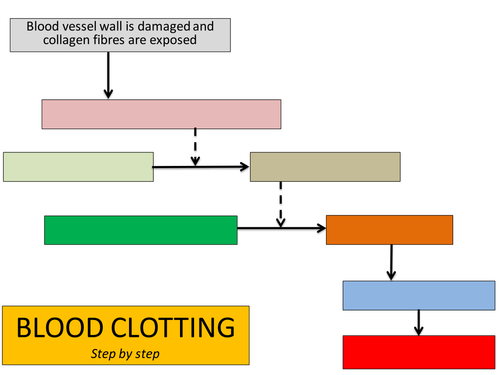











0 Response to "38 blood clotting process diagram"
Post a Comment